Public cloud offers scalable resources and cost-efficiency by utilizing third-party data centers, making it ideal for businesses with variable workloads and limited IT infrastructure. Hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud environments, providing enhanced security, compliance, and flexibility by enabling data and application mobility across platforms. Organizations leverage hybrid cloud to balance control with scalability, optimizing performance and cost management according to specific operational needs.
Table of Comparison
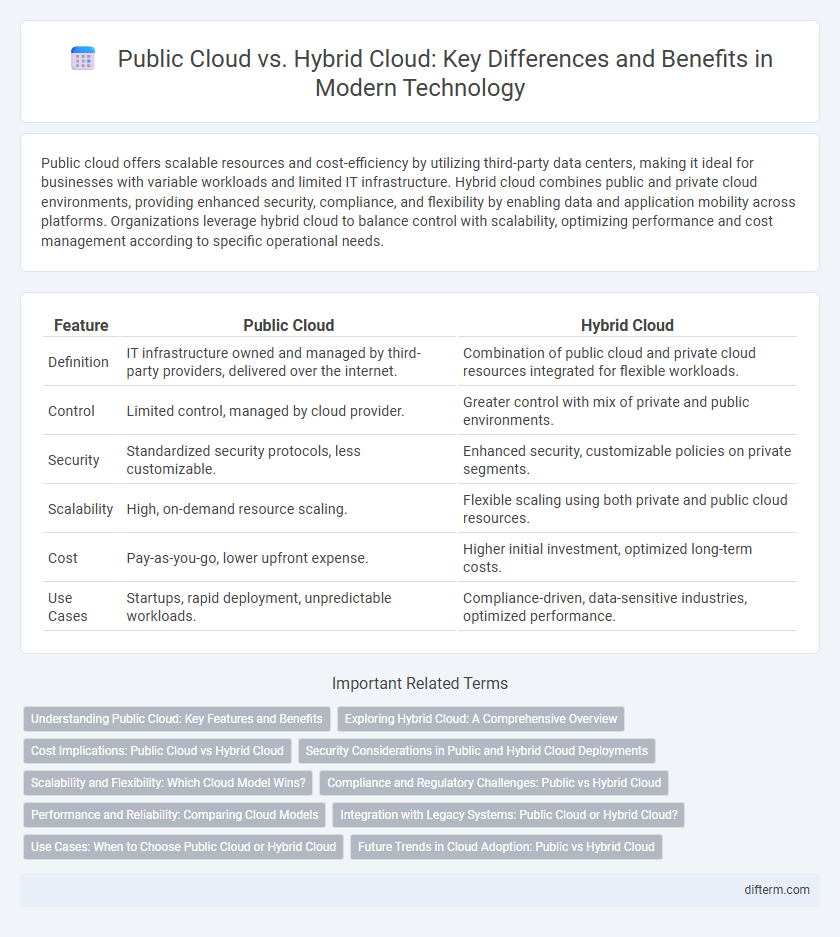
| Feature | Public Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | IT infrastructure owned and managed by third-party providers, delivered over the internet. | Combination of public cloud and private cloud resources integrated for flexible workloads. |
| Control | Limited control, managed by cloud provider. | Greater control with mix of private and public environments. |
| Security | Standardized security protocols, less customizable. | Enhanced security, customizable policies on private segments. |
| Scalability | High, on-demand resource scaling. | Flexible scaling using both private and public cloud resources. |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go, lower upfront expense. | Higher initial investment, optimized long-term costs. |
| Use Cases | Startups, rapid deployment, unpredictable workloads. | Compliance-driven, data-sensitive industries, optimized performance. |
Understanding Public Cloud: Key Features and Benefits
Public cloud platforms, such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, offer scalable and cost-effective infrastructure by leveraging shared resources across multiple users. Key features include on-demand self-service, broad network access, and rapid elasticity, allowing organizations to quickly scale computing power and storage without upfront investments. Benefits encompass reduced IT maintenance, enhanced disaster recovery options, and seamless integration with various SaaS applications, enabling businesses to innovate faster and optimize operational costs.
Exploring Hybrid Cloud: A Comprehensive Overview
Hybrid cloud integrates on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services, offering enhanced flexibility and scalability tailored to dynamic business needs. By enabling seamless workload portability and optimized resource allocation, hybrid cloud solutions improve operational efficiency and data security compliance. Enterprises leverage hybrid cloud to balance cost-effectiveness while maintaining control over sensitive information and critical applications.
Cost Implications: Public Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud
Public cloud solutions often present lower upfront costs due to their pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to scale resources without significant capital expenditure. Hybrid cloud environments typically involve higher initial investments in private infrastructure alongside ongoing public cloud service fees, leading to more complex cost management. Organizations must weigh these cost structures against their operational needs, data security requirements, and long-term scalability goals to optimize total cloud spending.
Security Considerations in Public and Hybrid Cloud Deployments
Public cloud environments demand robust encryption and identity management to mitigate risks of data breaches and unauthorized access, leveraging shared responsibility models for security. Hybrid cloud deployments enhance security by combining on-premises infrastructure control with public cloud scalability, enabling sensitive workloads to remain in private environments while offloading less critical data to public clouds. Comprehensive security measures in hybrid clouds often include advanced threat detection, compliance monitoring, and seamless integration of security policies across both cloud types.
Scalability and Flexibility: Which Cloud Model Wins?
Public cloud offers unmatched scalability by providing virtually unlimited resources on demand, making it ideal for businesses with fluctuating workloads. Hybrid cloud combines the flexibility of private infrastructure with the scalability of public cloud, enabling tailored resource allocation and optimized performance for diverse applications. For organizations prioritizing rapid scalability and cost-efficiency, public cloud excels, while hybrid cloud wins in scenarios requiring customized control and seamless integration across environments.
Compliance and Regulatory Challenges: Public vs Hybrid Cloud
Public cloud environments often face stricter compliance challenges due to multi-tenant architectures and global data residency requirements, making it difficult to maintain data sovereignty and meet specific regulatory mandates. Hybrid cloud solutions offer greater flexibility by enabling sensitive data to remain on private infrastructure while leveraging public cloud resources, thereby improving adherence to compliance frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Enterprises deploying hybrid clouds can implement granular access controls and localized data management, reducing regulatory risks associated with data breaches and non-compliance penalties.
Performance and Reliability: Comparing Cloud Models
Public cloud platforms offer high scalability and global accessibility but may face variability in performance due to shared resources. Hybrid cloud models enhance reliability by combining on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services, enabling more consistent performance and greater control over critical workloads. Enterprises leverage hybrid clouds to optimize resource allocation, balancing flexibility with enhanced security and reduced latency for mission-critical applications.
Integration with Legacy Systems: Public Cloud or Hybrid Cloud?
Hybrid cloud offers superior integration with legacy systems by combining on-premises infrastructure and public cloud resources, allowing seamless data and application interoperability. Public cloud environments often face challenges connecting with older enterprise systems due to compatibility and security constraints. Organizations seeking to modernize IT while preserving existing investments prefer hybrid cloud solutions for flexible, scalable, and secure integration capabilities.
Use Cases: When to Choose Public Cloud or Hybrid Cloud
Public cloud is ideal for workloads requiring rapid scalability, cost efficiency, and broad accessibility, such as web hosting, development environments, and big data analytics. Hybrid cloud suits enterprises needing data sovereignty, regulatory compliance, or seamless integration between on-premises infrastructure and cloud resources, common in finance, healthcare, and government sectors. Choosing between public and hybrid cloud depends on factors like security requirements, workload variability, and integration complexity.
Future Trends in Cloud Adoption: Public vs Hybrid Cloud
Public cloud adoption continues to accelerate due to scalability, cost-efficiency, and seamless integration with AI and IoT technologies, driving enterprises to leverage its vast infrastructure for innovation. Hybrid cloud gains momentum as organizations prioritize data security, regulatory compliance, and workload flexibility by combining on-premises resources with public cloud services. Future trends indicate a convergence where hybrid cloud environments will increasingly incorporate advanced automation, edge computing, and multi-cloud management tools to optimize performance and agility.
Public cloud vs Hybrid cloud Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com