Cat7 cables offer improved shielding and higher bandwidth capacity compared to Cat6, making them ideal for demanding network environments requiring speeds up to 10 Gbps over longer distances. Cat6 cables, widely used for home and office setups, support up to 1 Gbps with less stringent shielding, which suits most standard internet and smart pet device connections. Choosing Cat7 ensures better future-proofing and reduced interference, beneficial for seamless connectivity in tech-savvy pet monitoring systems.
Table of Comparison
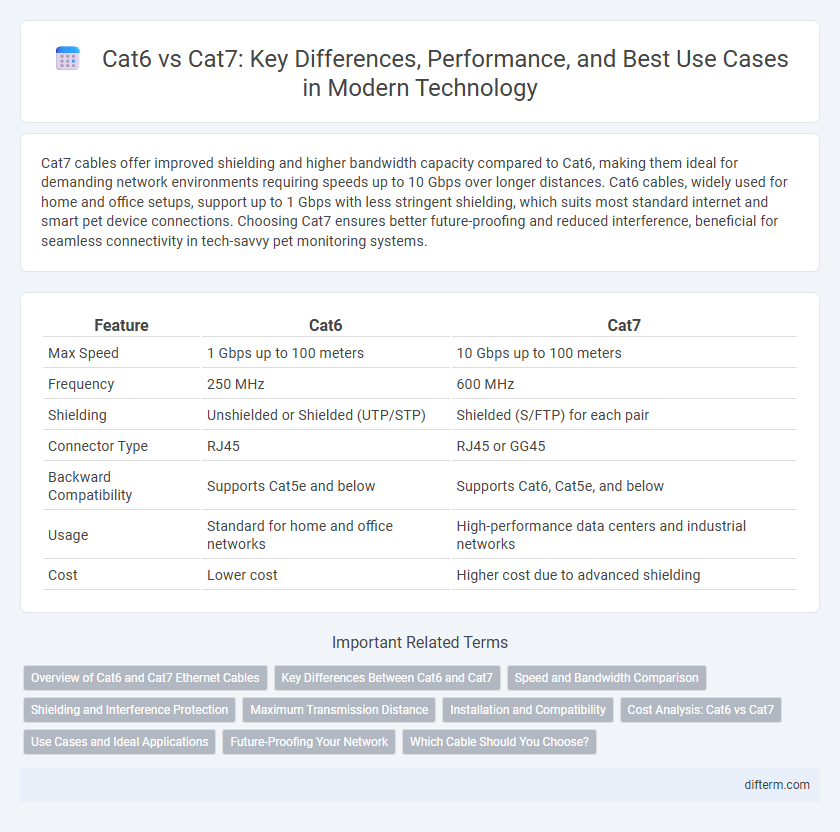
| Feature | Cat6 | Cat7 |
|---|---|---|
| Max Speed | 1 Gbps up to 100 meters | 10 Gbps up to 100 meters |
| Frequency | 250 MHz | 600 MHz |
| Shielding | Unshielded or Shielded (UTP/STP) | Shielded (S/FTP) for each pair |
| Connector Type | RJ45 | RJ45 or GG45 |
| Backward Compatibility | Supports Cat5e and below | Supports Cat6, Cat5e, and below |
| Usage | Standard for home and office networks | High-performance data centers and industrial networks |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to advanced shielding |
Overview of Cat6 and Cat7 Ethernet Cables
Cat6 Ethernet cables support speeds up to 10 Gbps over distances of up to 55 meters, featuring a bandwidth of 250 MHz, making them suitable for most home and office networks. Cat7 cables offer enhanced shielding and can handle frequencies up to 600 MHz, enabling 10 Gbps speeds over 100 meters with improved resistance to crosstalk and electromagnetic interference. The advanced shielding in Cat7 cables makes them ideal for high-demand data centers and industrial environments requiring maximum performance and reliability.
Key Differences Between Cat6 and Cat7
Cat6 cables support speeds up to 10 Gbps at 55 meters with a bandwidth of 250 MHz, while Cat7 cables offer up to 10 Gbps at 100 meters and a higher bandwidth of 600 MHz, enhancing overall performance. Cat7 features individually shielded pairs (S/FTP) that reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic interference compared to the unshielded or shielded twisted pairs in Cat6. Connector compatibility also differs as Cat7 uses GG45 or TERA connectors, which provide superior shielding but are less common than the RJ45 connectors used in Cat6 installations.
Speed and Bandwidth Comparison
Cat7 cables support speeds up to 10 Gbps over 100 meters and offer a bandwidth of 600 MHz, outperforming Cat6 which supports speeds up to 1 Gbps and bandwidth of 250 MHz over the same distance. Cat7's shielding reduces interference, ensuring higher data transfer rates in environments with heavy electromagnetic noise. For high-speed network applications requiring enhanced bandwidth and minimal crosstalk, Cat7 delivers superior performance compared to Cat6.
Shielding and Interference Protection
Cat7 cables feature superior shielding with individually shielded pairs and an overall braided shield, effectively minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI) compared to Cat6 cables, which typically use unshielded or foil-shielded pairs. This enhanced shielding in Cat7 provides better protection against crosstalk and external interference, making it ideal for high-density or industrial environments. The improved interference protection ensures more reliable data transmission and reduces signal degradation over longer distances.
Maximum Transmission Distance
Cat6 cables support a maximum transmission distance of 55 meters at 10 Gbps, while maintaining up to 100 meters for slower speeds. Cat7 cables can reliably transmit data up to 100 meters at 10 Gbps and higher frequencies, offering improved shielding and reduced crosstalk. The enhanced shielding in Cat7 enables longer maximum transmission distances without signal degradation compared to Cat6.
Installation and Compatibility
Cat6 cables support up to 10 Gbps speeds over 55 meters and are widely compatible with most networking devices, making installation straightforward and cost-effective. Cat7 cables, designed for higher frequencies up to 600 MHz, require specialized connectors like GG45 or TERA, which can complicate installation and limit backward compatibility. Choosing Cat6 is practical for standard office setups, while Cat7 suits high-performance environments needing shielded cabling and enhanced noise reduction.
Cost Analysis: Cat6 vs Cat7
Cat6 cables typically cost between $0.10 to $0.40 per foot, making them a budget-friendly option for most home and office networks, while Cat7 cables range from $0.90 to $3.00 per foot due to enhanced shielding and higher bandwidth capacity. Investing in Cat7 can lead to long-term savings in high-demand environments by supporting 10 Gbps speeds over longer distances and reducing signal interference. Evaluating network requirements and future-proofing needs is essential when considering the cost-benefit ratio of Cat6 versus Cat7 cabling solutions.
Use Cases and Ideal Applications
Cat6 cables are ideal for residential and small office networks, supporting speeds up to 10 Gbps over distances up to 55 meters, making them suitable for everyday internet browsing, streaming, and gaming. Cat7 cables, offering shielded twisted pairs and transmission speeds up to 10 Gbps over 100 meters, excel in data centers and large enterprise environments where interference reduction and higher bandwidth are critical. Choosing between Cat6 and Cat7 depends on network size, interference levels, and future-proofing requirements for high-speed data transmission.
Future-Proofing Your Network
Cat7 cables offer superior shielding and higher frequency support up to 600 MHz compared to Cat6's 250 MHz, making them more suitable for future-proofing your network. With Cat7, you can achieve faster data transfer rates up to 10 Gbps over longer distances, ensuring compatibility with next-generation networking standards. Investing in Cat7 infrastructure provides enhanced durability and reduced interference, minimizing upgrade needs as network demands evolve.
Which Cable Should You Choose?
Choose Cat7 cable for superior shielding and bandwidth capabilities, supporting frequencies up to 600 MHz and data rates up to 10 Gbps over longer distances. Cat6 cables remain a cost-effective option for standard Ethernet connections, handling frequencies up to 250 MHz with reliable performance for up to 55 meters. Select Cat7 for future-proofing high-speed network infrastructures, while Cat6 suits typical home or office environments with moderate data demands.
Cat6 vs Cat7 Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com