Bluetooth Classic offers higher data transfer rates and better support for continuous streaming applications such as audio, making it suitable for devices like wireless headphones and speakers. In contrast, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) prioritizes power efficiency and is ideal for battery-operated devices requiring intermittent data transmission, such as fitness trackers and smart sensors. The choice between Bluetooth Classic and BLE depends on the specific application requirements regarding data throughput and energy consumption.
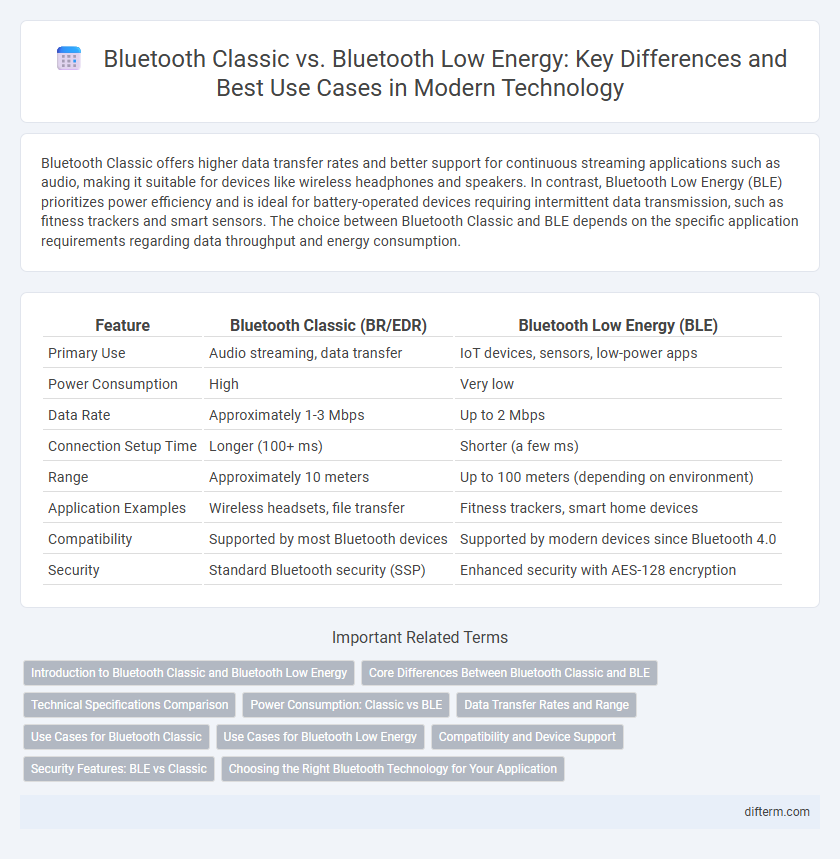
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bluetooth Classic (BR/EDR) | Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Audio streaming, data transfer | IoT devices, sensors, low-power apps |
| Power Consumption | High | Very low |
| Data Rate | Approximately 1-3 Mbps | Up to 2 Mbps |
| Connection Setup Time | Longer (100+ ms) | Shorter (a few ms) |
| Range | Approximately 10 meters | Up to 100 meters (depending on environment) |
| Application Examples | Wireless headsets, file transfer | Fitness trackers, smart home devices |
| Compatibility | Supported by most Bluetooth devices | Supported by modern devices since Bluetooth 4.0 |
| Security | Standard Bluetooth security (SSP) | Enhanced security with AES-128 encryption |
Introduction to Bluetooth Classic and Bluetooth Low Energy
Bluetooth Classic operates on the 2.4 GHz ISM band, delivering continuous, high-speed data transfer suitable for audio streaming and file exchange. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), also on the 2.4 GHz band, prioritizes minimal power consumption and intermittent data transmission, making it ideal for IoT devices and wearable technology. Both protocols use frequency hopping spread spectrum to reduce interference, but BLE's optimized design extends battery life significantly compared to Bluetooth Classic.
Core Differences Between Bluetooth Classic and BLE
Bluetooth Classic supports continuous, high data rate connections ideal for streaming audio and video, whereas Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is engineered for intermittent, low-power data transfer suited for sensor and IoT devices. Classic Bluetooth operates at higher energy consumption, maintaining constant connections for extended periods, while BLE optimizes power efficiency through short, periodic data exchanges. The core protocol differences include data throughput, connection intervals, and power utilization, making Bluetooth Classic preferable for bandwidth-intensive applications and BLE optimal for energy-sensitive communications.
Technical Specifications Comparison
Bluetooth Classic operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band with data rates up to 3 Mbps using Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) technology, making it suitable for continuous, high-throughput applications. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), also in the 2.4 GHz ISM band, prioritizes ultra-low power consumption with data rates up to 2 Mbps using the LE 2M PHY, ideal for battery-powered devices requiring intermittent data transfer. BLE employs a different modulation scheme (GFSK) and shorter connection intervals compared to Bluetooth Classic's adaptive frequency hopping, optimizing it for energy efficiency in Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
Power Consumption: Classic vs BLE
Bluetooth Classic consumes significantly more power than Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), making BLE the preferred choice for battery-operated devices. BLE is designed to reduce power usage by using short, infrequent data transmissions and optimized sleep modes. This efficiency enables longer battery life in wearable technology, medical devices, and IoT applications compared to Bluetooth Classic.
Data Transfer Rates and Range
Bluetooth Classic offers data transfer rates up to 3 Mbps with an effective range of approximately 100 meters, making it suitable for continuous streaming and high-bandwidth applications. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) supports lower data rates, typically around 1 Mbps, but excels in power efficiency and extends range up to 300 meters under ideal conditions. The choice between Bluetooth Classic and BLE depends on the specific application requirements for speed and connectivity distance.
Use Cases for Bluetooth Classic
Bluetooth Classic excels in audio streaming applications such as wireless headphones, speakers, and in-car entertainment systems due to its higher data transfer rates and robust connection stability. It is preferred for continuous data exchange in devices like gaming controllers and hands-free calling systems where low latency is critical. Industrial equipment and medical devices also utilize Bluetooth Classic for reliable, sustained communication in real-time monitoring and control scenarios.
Use Cases for Bluetooth Low Energy
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is ideal for use cases requiring long battery life and low data throughput, such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and health monitoring devices. Its energy-efficient protocol supports continuous data transmission in applications like proximity sensors, beacons, and wireless keyboards. BLE's ability to maintain persistent connections with minimal power consumption makes it a preferred choice for IoT devices and home automation systems.
Compatibility and Device Support
Bluetooth Classic offers broad compatibility with a wide range of devices, including smartphones, laptops, and audio peripherals, ensuring seamless connectivity and high data throughput. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is designed for modern IoT devices and wearables, providing lower power consumption but with limited support for older hardware. Device support for Bluetooth Classic remains dominant in legacy applications, while BLE is increasingly favored in smart home and fitness technology for efficient, long-lasting connections.
Security Features: BLE vs Classic
Bluetooth Classic employs robust security protocols such as Secure Simple Pairing (SSP) with Encryption and Authentication, ensuring strong protection for established connections. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) utilizes AES-128 encryption and supports features like LE Secure Connections introduced in Bluetooth 4.2, enhancing protection against passive eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. Despite BLE's energy-efficient design, both technologies offer scalable security levels, with BLE's recent advancements closing the gap on Classic Bluetooth's well-established security mechanisms.
Choosing the Right Bluetooth Technology for Your Application
Bluetooth Classic offers higher data transfer rates up to 3 Mbps, making it ideal for audio streaming and devices requiring continuous data exchange. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) prioritizes power efficiency with data rates up to 2 Mbps, perfect for battery-sensitive IoT devices and intermittent data transmission. Selecting the appropriate Bluetooth technology depends on balancing power consumption needs and data throughput requirements specific to your application.
Bluetooth Classic vs Bluetooth Low Energy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com