Fiber optic cables offer significantly higher data transmission speeds and greater bandwidth compared to copper cables, making them ideal for modern high-speed internet and communication networks. Unlike copper cable, fiber optics are immune to electromagnetic interference, ensuring more reliable and stable connections over longer distances. The lightweight, durable design of fiber optic cables also results in lower maintenance costs and enhanced future-proofing for technology infrastructures.
Table of Comparison
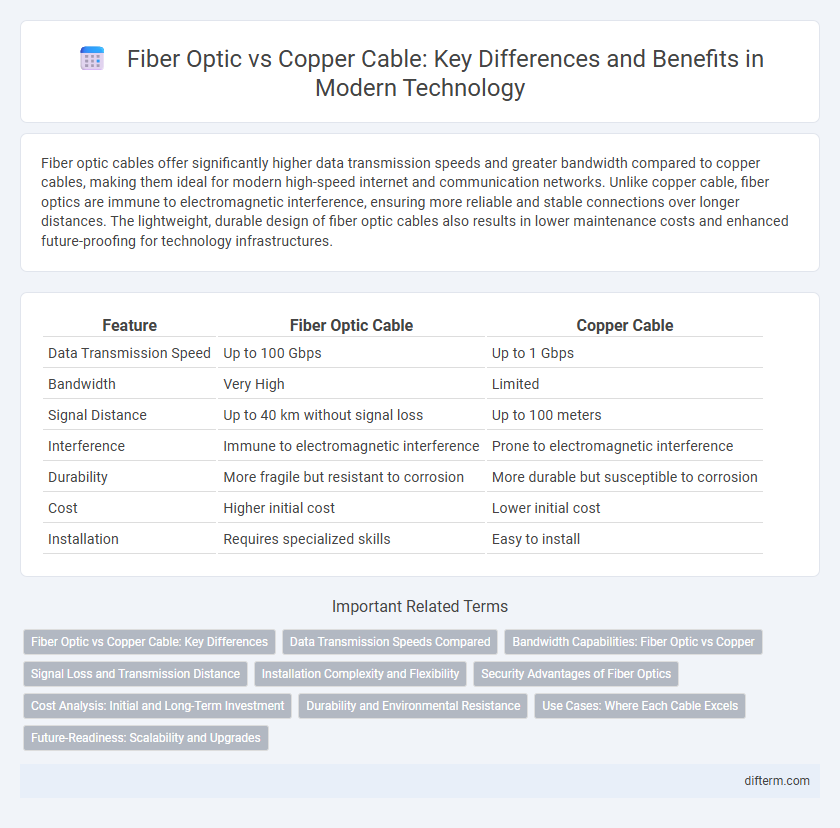
| Feature | Fiber Optic Cable | Copper Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transmission Speed | Up to 100 Gbps | Up to 1 Gbps |
| Bandwidth | Very High | Limited |
| Signal Distance | Up to 40 km without signal loss | Up to 100 meters |
| Interference | Immune to electromagnetic interference | Prone to electromagnetic interference |
| Durability | More fragile but resistant to corrosion | More durable but susceptible to corrosion |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Installation | Requires specialized skills | Easy to install |
Fiber Optic vs Copper Cable: Key Differences
Fiber optic cables transmit data using light signals through glass or plastic fibers, offering significantly higher bandwidth and faster speeds compared to copper cables, which rely on electrical signals. Fiber optics provide superior resistance to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation, enabling longer transmission distances without loss of quality. Copper cables, while more affordable and easier to install, suffer from limited bandwidth and are prone to signal attenuation and interference, making fiber optic technology the preferred choice for modern high-speed networks.
Data Transmission Speeds Compared
Fiber optic cables transmit data at speeds up to 100 Gbps or higher, significantly outperforming copper cables, which typically max out at 10 Gbps for common standards like Cat6a. The superior bandwidth capacity of fiber optics reduces latency and signal degradation over long distances, making it ideal for high-speed internet and data centers. Copper cables face electromagnetic interference and attenuation issues that limit their effective transmission distance and speed.
Bandwidth Capabilities: Fiber Optic vs Copper
Fiber optic cables offer significantly higher bandwidth capabilities compared to copper cables, supporting data transmission speeds up to 100 Gbps and beyond over long distances without signal degradation. Copper cables, such as twisted pair or coaxial, typically max out around 10 Gbps and experience increased attenuation and electromagnetic interference at higher frequencies. Fiber optics utilize light signals which enable greater data capacity and more reliable performance for modern high-speed networks.
Signal Loss and Transmission Distance
Fiber optic cables exhibit significantly lower signal loss compared to copper cables, with attenuation rates typically around 0.2 dB/km for single-mode fiber versus up to 10 dB/km for copper. This lower signal loss enables fiber optics to support much longer transmission distances, reaching up to 40 kilometers or more without the need for signal boosters. Copper cables, constrained by higher signal attenuation and electromagnetic interference, are generally limited to transmission lengths of 100 meters in standard Ethernet applications.
Installation Complexity and Flexibility
Fiber optic cables require specialized skill sets and precise handling during installation due to their fragility and sensitivity to bending, making the process more complex than copper cable installation. Copper cables offer greater flexibility in physical manipulation and easier termination, allowing quicker and less expensive deployment in varied environments. The choice between fiber optic and copper cables often depends on the balance between desired bandwidth capabilities and the installation environment's constraints.
Security Advantages of Fiber Optics
Fiber optic cables provide superior security advantages over copper cables due to their resistance to electromagnetic interference and signal tapping, making data interception extremely difficult. Unlike copper cables, fiber optic technology transmits data as light pulses, which do not emit signals that can be easily tapped or monitored. This intrinsic security feature makes fiber optics ideal for sensitive communications in sectors such as finance, government, and healthcare.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term Investment
Fiber optic cables typically involve higher initial installation costs due to expensive materials and specialized labor, while copper cables offer lower upfront expenses. Over the long term, fiber optics prove more cost-effective with reduced maintenance, lower signal degradation, and greater bandwidth capacity that supports future technology upgrades. Copper cables incur higher operational costs from frequent repairs, electrical interference issues, and limited data transmission capabilities.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Fiber optic cables exhibit superior durability and environmental resistance compared to copper cables due to their immunity to electromagnetic interference, corrosion, and moisture damage. Unlike copper cables, fiber optics maintain signal integrity over longer distances and extreme temperature fluctuations, ensuring reliable performance in harsh environments. The lightweight, non-metallic construction of fiber optic cabling further enhances its resilience against physical stress and chemical exposure.
Use Cases: Where Each Cable Excels
Fiber optic cables excel in high-speed data transmission over long distances, making them ideal for internet backbones, data centers, and telecommunications networks where low latency and high bandwidth are critical. Copper cables are better suited for shorter distances in residential wiring, office LANs, and Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications due to their lower cost and easier installation. Fiber optic technology supports future-proof infrastructures with greater immunity to electromagnetic interference, while copper remains practical for legacy systems and cost-sensitive environments.
Future-Readiness: Scalability and Upgrades
Fiber optic cables offer superior future-readiness through higher bandwidth capacity and easier scalability compared to copper cables, supporting the increasing data demands of emerging technologies such as 5G and IoT. Upgrading fiber networks often involves minimal physical changes, primarily focusing on terminal equipment enhancements, whereas copper cabling typically requires extensive infrastructure replacement to achieve comparable speed improvements. This makes fiber optics the preferred choice for scalable, high-performance network infrastructures that accommodate rapid technological advancements.
Fiber Optic vs Copper Cable Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com