Static websites offer fast loading times and enhanced security by delivering fixed content with minimal server-side processing. Dynamic websites generate content in real-time, enabling personalized user experiences and interactive features through databases and server-side scripting. Choosing between static and dynamic depends on the need for simplicity and speed versus flexibility and user engagement.
Table of Comparison
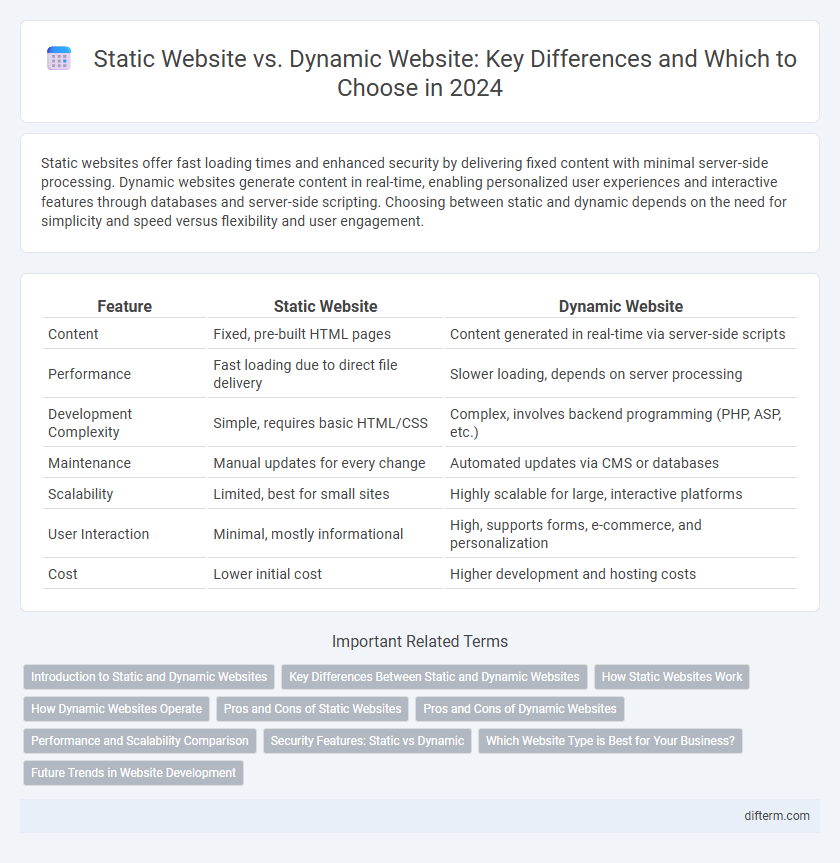
| Feature | Static Website | Dynamic Website |
|---|---|---|
| Content | Fixed, pre-built HTML pages | Content generated in real-time via server-side scripts |
| Performance | Fast loading due to direct file delivery | Slower loading, depends on server processing |
| Development Complexity | Simple, requires basic HTML/CSS | Complex, involves backend programming (PHP, ASP, etc.) |
| Maintenance | Manual updates for every change | Automated updates via CMS or databases |
| Scalability | Limited, best for small sites | Highly scalable for large, interactive platforms |
| User Interaction | Minimal, mostly informational | High, supports forms, e-commerce, and personalization |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher development and hosting costs |
Introduction to Static and Dynamic Websites
Static websites consist of fixed content delivered directly from the server to the user's browser, typically built using HTML and CSS without server-side processing. Dynamic websites generate content in real time using server-side languages like PHP, Python, or JavaScript frameworks, allowing for personalized and interactive user experiences. Understanding the differences in structure and functionality between static and dynamic sites is crucial for selecting the appropriate web development approach.
Key Differences Between Static and Dynamic Websites
Static websites deliver fixed content directly from the server to the user's browser, ensuring faster load times and simpler hosting requirements. Dynamic websites generate content on-the-fly using server-side scripts like PHP, Python, or JavaScript frameworks, enabling personalized user experiences and easier content management through databases. Key differences include flexibility, scalability, maintenance complexity, and interactivity, with dynamic sites supporting features such as user authentication and content updates, unlike static sites that are best suited for simple, informational purposes.
How Static Websites Work
Static websites deliver fixed content through HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files stored on a server and sent directly to the user's browser without server-side processing. Each request retrieves the exact same files, ensuring fast load times and consistent content display. This simplicity makes static websites ideal for small businesses, portfolios, and landing pages with infrequent content updates.
How Dynamic Websites Operate
Dynamic websites operate by generating content in real-time using server-side scripting languages like PHP, Python, or JavaScript frameworks, allowing for personalized user experiences and interactive features. These websites rely on databases such as MySQL or MongoDB to store and retrieve information dynamically, enabling content updates without altering the underlying code. The server processes user requests, executes relevant scripts, and delivers customized pages that respond to input, transaction, or behavior, contrasting with static sites where content remains fixed and unchanging.
Pros and Cons of Static Websites
Static websites offer fast loading times and enhanced security due to their fixed content and lack of server-side processing. They are cost-effective and easier to host, requiring minimal resources and maintenance compared to dynamic websites. However, static sites lack interactivity and scalability, making content updates and customization more labor-intensive without automated backend systems.
Pros and Cons of Dynamic Websites
Dynamic websites offer the advantage of real-time content updates and personalized user experiences, making them ideal for e-commerce platforms and social media sites. They require server-side scripting languages like PHP, ASP.NET, or JavaScript frameworks, which can increase development complexity and hosting costs. However, dynamic websites enable seamless content management, user interactivity, and scalability, outweighing the challenges for businesses needing frequent content changes and user engagement.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
Static websites deliver faster load times and improved performance due to pre-rendered HTML files served directly from the server, minimizing server processing and database queries. Dynamic websites, while slower because they generate content on-the-fly using server-side scripting and databases, offer superior scalability by supporting complex user interactions and real-time content updates. Optimizing caching strategies and leveraging CDNs can enhance both static and dynamic website performance and scalability across varying traffic volumes.
Security Features: Static vs Dynamic
Static websites offer enhanced security due to their fixed content and lack of server-side processing, minimizing vulnerabilities to common attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Dynamic websites, while providing interactive features, require frequent updates and robust security measures such as firewalls, input validation, and secure authentication to mitigate risks inherent in server-side coding. Choosing static websites can significantly reduce the attack surface, making them a preferred option for security-conscious applications with limited user interactions.
Which Website Type is Best for Your Business?
Static websites offer fast loading times and lower hosting costs, making them ideal for small businesses with minimal content updates. Dynamic websites provide interactive features and easy content management, suitable for growing businesses requiring frequent updates and user engagement. Choosing the best website type depends on your business goals, budget, and need for scalability.
Future Trends in Website Development
Static websites offer simplicity and faster load times, making them ideal for small-scale projects, but dynamic websites dominate with their ability to deliver personalized user experiences and real-time content updates. Future trends in website development emphasize progressive web apps (PWAs), artificial intelligence integration for adaptive interfaces, and enhanced security protocols, favoring dynamic frameworks powered by technologies like React, Angular, and serverless architectures. As web performance and user engagement become critical, developers increasingly adopt headless CMS and API-driven designs to create scalable, responsive, and easily maintainable websites.
Static website vs Dynamic website Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com