Zero-day vulnerabilities represent unknown security flaws that hackers can exploit before developers have a chance to create patches, posing a significant risk in cybersecurity. In contrast, N-day vulnerabilities are known issues with available fixes or workarounds, allowing organizations to protect their systems effectively by applying timely updates. Understanding the difference between zero-day and N-day threats is crucial for developing proactive security strategies and minimizing potential breaches.
Table of Comparison
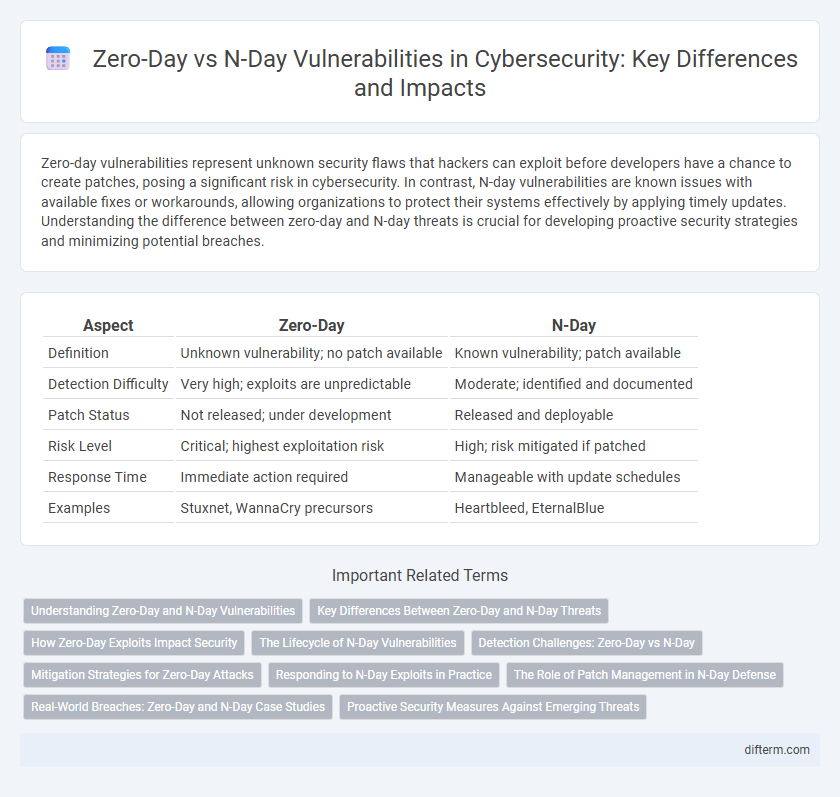
| Aspect | Zero-Day | N-Day |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unknown vulnerability; no patch available | Known vulnerability; patch available |
| Detection Difficulty | Very high; exploits are unpredictable | Moderate; identified and documented |
| Patch Status | Not released; under development | Released and deployable |
| Risk Level | Critical; highest exploitation risk | High; risk mitigated if patched |
| Response Time | Immediate action required | Manageable with update schedules |
| Examples | Stuxnet, WannaCry precursors | Heartbleed, EternalBlue |
Understanding Zero-Day and N-Day Vulnerabilities
Zero-day vulnerabilities are security flaws unknown to software vendors and remain unpatched, making them highly exploitable by attackers. N-day vulnerabilities refer to known security weaknesses with available patches that organizations may not have applied, increasing their risk exposure. Effective vulnerability management requires distinguishing between zero-day threats, which demand proactive threat intelligence, and N-day risks that rely on timely patch deployment.
Key Differences Between Zero-Day and N-Day Threats
Zero-Day threats exploit previously unknown vulnerabilities, leaving no time for developers to create patches, while N-Day threats target vulnerabilities already identified and patched by security teams. Zero-Day attacks carry higher risks due to the lack of available defenses, whereas N-Day exploits rely on delayed patching or incomplete security measures. Effective cybersecurity strategies prioritize rapid patch management and real-time threat intelligence to mitigate both types of risks.
How Zero-Day Exploits Impact Security
Zero-Day exploits significantly impact security by targeting software vulnerabilities unknown to developers, allowing attackers to infiltrate systems before patches are available. Unlike N-Day vulnerabilities, which have known fixes, Zero-Day attacks leave organizations defenseless, increasing the risk of data breaches, system compromise, and financial loss. Rapid detection and advanced threat intelligence are critical to mitigate the damage caused by Zero-Day exploits.
The Lifecycle of N-Day Vulnerabilities
N-Day vulnerabilities refer to security flaws that have been publicly disclosed and for which patches or mitigations are available, marking them as known threats within the cybersecurity community. Their lifecycle begins at disclosure, followed by rapid exploitation by threat actors if systems remain unpatched, emphasizing the critical importance of timely vulnerability management and patch deployment. Continuous monitoring and updating of security infrastructures reduce the risk posed by N-Day exploits, contrasting the unpredictable nature of Zero-Day attacks.
Detection Challenges: Zero-Day vs N-Day
Zero-Day vulnerabilities pose significant detection challenges due to the absence of prior knowledge or signatures, making traditional antivirus and intrusion detection systems less effective. N-Day exploits, by contrast, are identifiable through known patterns and patches, enabling quicker detection and mitigation. Effective security strategies require advanced behavioral analysis and threat intelligence integration to identify zero-day threats before exploitation.
Mitigation Strategies for Zero-Day Attacks
Zero-Day attacks exploit unknown vulnerabilities, making traditional patch-based defenses ineffective, so mitigation strategies focus on behavior-based anomaly detection and network segmentation to limit attack impact. Implementing advanced threat intelligence and proactive threat hunting enables early identification of exploitation patterns before patches are available. Employing endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools and regular security training further strengthens resilience against zero-day threats.
Responding to N-Day Exploits in Practice
Responding to N-Day exploits involves swiftly deploying patches and updates for known vulnerabilities, leveraging threat intelligence feeds to identify active exploits, and conducting thorough system audits to ensure comprehensive remediation. Security teams prioritize vulnerability management tools and incident response plans tailored to address the specific characteristics of N-Day threats. Effective N-Day exploit response reduces exposure time and mitigates potential damage by utilizing established update channels and proactive monitoring systems.
The Role of Patch Management in N-Day Defense
Effective patch management plays a critical role in N-Day defense by rapidly deploying fixes for known vulnerabilities, thereby minimizing the window of exposure. Organizations that maintain automated patching systems can reduce the risk of exploitation from publicly disclosed security flaws. Continuous vulnerability assessment combined with timely patch application strengthens overall cybersecurity posture against N-Day threats.
Real-World Breaches: Zero-Day and N-Day Case Studies
Real-world breaches reveal the critical distinctions between Zero-Day and N-Day vulnerabilities, with Zero-Day exploits often enabling attackers to infiltrate systems before patches are available, exemplified by the Stuxnet attack targeting Iranian nuclear facilities. N-Day exploits capitalize on publicly disclosed vulnerabilities with existing patches, like the WannaCry ransomware leveraging the EternalBlue exploit months after patches were released but organizations failed to update. These case studies emphasize the importance of timely patch management and proactive threat intelligence to mitigate both Zero-Day and N-Day risks effectively.
Proactive Security Measures Against Emerging Threats
Zero-Day vulnerabilities expose systems to unknown exploits before patches are available, demanding proactive security measures such as threat intelligence, behavior-based detection, and rigorous vulnerability assessments. N-Day vulnerabilities involve known security flaws with publicly available patches, emphasizing efficient patch management and continuous system updates to mitigate risks. Implementing advanced endpoint protection and comprehensive intrusion detection systems strengthens defenses against both Zero-Day and N-Day threats, enhancing overall cybersecurity resilience.
Zero-Day vs N-Day Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com