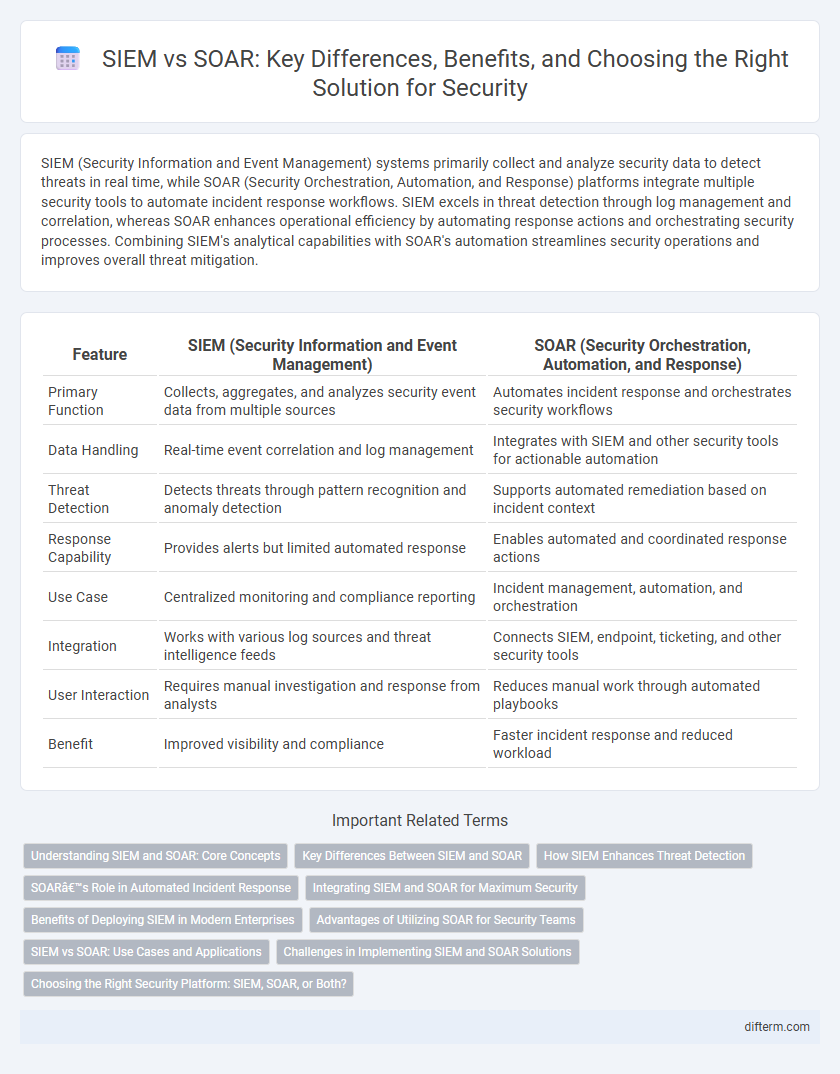
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems primarily collect and analyze security data to detect threats in real time, while SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) platforms integrate multiple security tools to automate incident response workflows. SIEM excels in threat detection through log management and correlation, whereas SOAR enhances operational efficiency by automating response actions and orchestrating security processes. Combining SIEM's analytical capabilities with SOAR's automation streamlines security operations and improves overall threat mitigation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) | SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Collects, aggregates, and analyzes security event data from multiple sources | Automates incident response and orchestrates security workflows |
| Data Handling | Real-time event correlation and log management | Integrates with SIEM and other security tools for actionable automation |
| Threat Detection | Detects threats through pattern recognition and anomaly detection | Supports automated remediation based on incident context |
| Response Capability | Provides alerts but limited automated response | Enables automated and coordinated response actions |
| Use Case | Centralized monitoring and compliance reporting | Incident management, automation, and orchestration |
| Integration | Works with various log sources and threat intelligence feeds | Connects SIEM, endpoint, ticketing, and other security tools |
| User Interaction | Requires manual investigation and response from analysts | Reduces manual work through automated playbooks |
| Benefit | Improved visibility and compliance | Faster incident response and reduced workload |
Understanding SIEM and SOAR: Core Concepts
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) collects and analyzes security data from multiple sources to detect and respond to potential threats in real time. SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) integrates with SIEM to automate incident response workflows, streamline threat investigation, and coordinate security tools for faster remediation. Understanding the core concepts of SIEM and SOAR enables organizations to strengthen their cybersecurity defenses through improved threat detection, efficient response, and comprehensive security management.
Key Differences Between SIEM and SOAR
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) specializes in collecting, correlating, and analyzing security event data to identify threats in real-time, whereas SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) focuses on automating incident response workflows and integrating multiple security tools for efficient threat mitigation. SIEM systems excel at providing comprehensive visibility and alerts from logs and network data, while SOAR platforms enhance operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and coordinating actions across security teams. The primary difference lies in SIEM's role in threat detection and analysis versus SOAR's emphasis on response automation and incident management orchestration.
How SIEM Enhances Threat Detection
SIEM enhances threat detection by aggregating and correlating security data from diverse sources in real-time, enabling rapid identification of anomalies and potential breaches. Its advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities improve the accuracy of threat detection by reducing false positives and prioritizing critical alerts. By providing comprehensive visibility into network activities and facilitating in-depth forensic analysis, SIEM empowers security teams to respond swiftly and effectively to cyber threats.
SOAR’s Role in Automated Incident Response
SOAR platforms enhance automated incident response by integrating threat intelligence, workflow automation, and case management to accelerate detection and mitigation processes. By orchestrating security tools and automating repetitive tasks, SOAR reduces response times and improves accuracy in handling complex security incidents. This automation enables security teams to focus on strategic threat analysis while ensuring consistent and efficient incident resolution.
Integrating SIEM and SOAR for Maximum Security
Integrating SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) and SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) enhances threat detection and accelerates incident response by combining real-time data analysis with automated workflows. SIEM aggregates and correlates security events from diverse sources to identify potential threats, while SOAR streamlines alert triage, investigation, and remediation processes through automation. This synergy minimizes response times, reduces analyst fatigue, and strengthens overall organizational cybersecurity posture.
Benefits of Deploying SIEM in Modern Enterprises
Deploying SIEM in modern enterprises enhances real-time threat detection by aggregating and analyzing security data from multiple sources, enabling quicker incident response. SIEM improves compliance management through comprehensive log collection and reporting tailored to regulatory standards such as GDPR and HIPAA. Integrating SIEM with advanced analytics provides actionable insights, reducing the risk of data breaches and optimizing security operations efficiency.
Advantages of Utilizing SOAR for Security Teams
SOAR platforms enhance security operations by automating incident response workflows, significantly reducing response time and human error. They provide advanced orchestration capabilities that integrate diverse security tools, enabling seamless data correlation and improved threat detection accuracy. By centralizing case management and offering playbook-driven processes, SOAR boosts team efficiency and enables proactive threat mitigation.
SIEM vs SOAR: Use Cases and Applications
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems excel in real-time monitoring, log aggregation, and threat detection by collecting data from various sources to identify suspicious activities. SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) platforms enhance incident response through automation, integrating workflows and enabling faster remediation by coordinating diverse security tools. Organizations use SIEM primarily for compliance reporting and alerting, while SOAR is applied to streamline threat investigation and accelerate response times in complex security environments.
Challenges in Implementing SIEM and SOAR Solutions
Implementing SIEM and SOAR solutions presents challenges including high complexity in integration with existing security infrastructure and the need for continuous tuning to reduce false positives. Organizations often face resource constraints for skilled personnel capable of managing these platforms effectively, which impacts incident response time and accuracy. Furthermore, data overload and lack of interoperability between different tools hinder seamless automation and comprehensive threat visibility.
Choosing the Right Security Platform: SIEM, SOAR, or Both?
Selecting the right security platform depends on organizational needs: SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) excels in real-time security event monitoring and log management, offering comprehensive data aggregation and threat detection. SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) enhances incident response by automating workflows, integrating threat intelligence, and coordinating security operations across multiple tools. Combining SIEM and SOAR platforms provides a robust security posture by merging deep visibility with efficient, automated incident remediation.
SIEM vs SOAR Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com