Endpoint security protects individual devices like laptops and smartphones by directly monitoring and controlling access, while perimeter security focuses on defending the network boundary through firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Effective cybersecurity requires integrating endpoint security measures with perimeter defenses to prevent breaches both at entry points and within the network. Endpoint solutions address threats that bypass perimeter controls, providing a critical layer of protection against malware, unauthorized access, and data leaks.
Table of Comparison
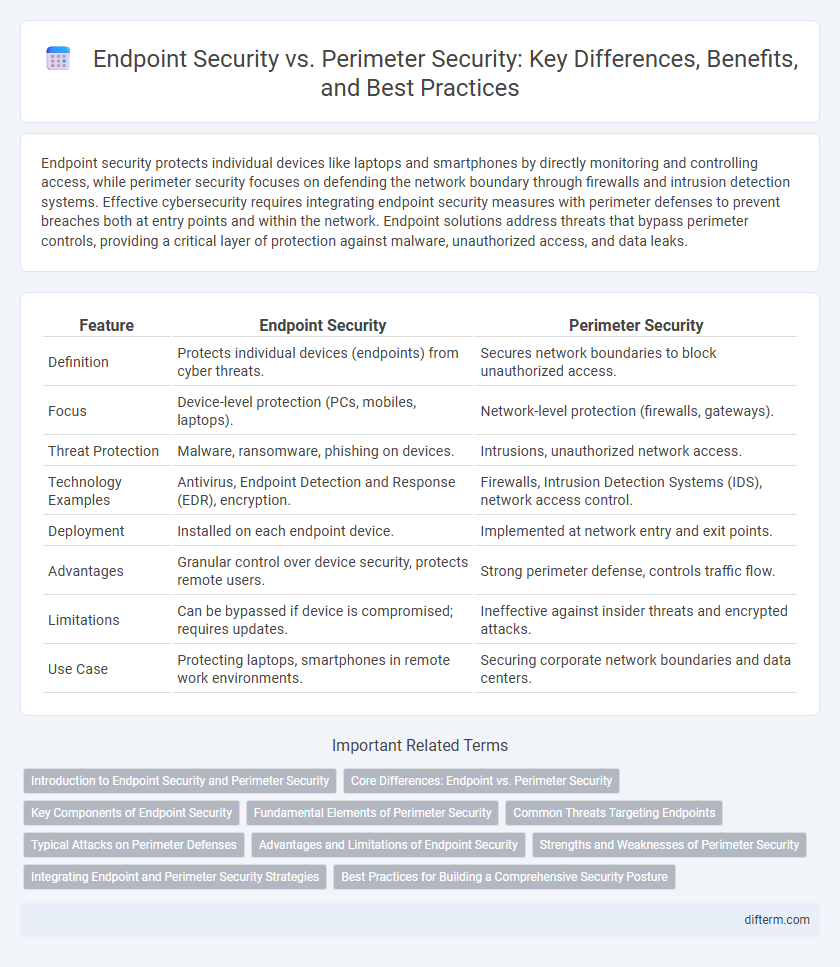
| Feature | Endpoint Security | Perimeter Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protects individual devices (endpoints) from cyber threats. | Secures network boundaries to block unauthorized access. |
| Focus | Device-level protection (PCs, mobiles, laptops). | Network-level protection (firewalls, gateways). |
| Threat Protection | Malware, ransomware, phishing on devices. | Intrusions, unauthorized network access. |
| Technology Examples | Antivirus, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), encryption. | Firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), network access control. |
| Deployment | Installed on each endpoint device. | Implemented at network entry and exit points. |
| Advantages | Granular control over device security, protects remote users. | Strong perimeter defense, controls traffic flow. |
| Limitations | Can be bypassed if device is compromised; requires updates. | Ineffective against insider threats and encrypted attacks. |
| Use Case | Protecting laptops, smartphones in remote work environments. | Securing corporate network boundaries and data centers. |
Introduction to Endpoint Security and Perimeter Security
Endpoint security protects individual devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets by securing access points that connect to a network, preventing malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches. Perimeter security focuses on defending the boundary of a network using firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and VPNs to control and monitor traffic entering and exiting the network. Both approaches are essential in a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy to safeguard organizational assets against evolving cyber threats.
Core Differences: Endpoint vs. Perimeter Security
Endpoint security focuses on protecting individual devices such as laptops, smartphones, and desktops from cyber threats by implementing antivirus software, encryption, and intrusion detection systems directly on the device. Perimeter security, on the other hand, secures the network boundary using firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion prevention systems to block unauthorized access before threats reach internal resources. The core difference lies in endpoint security's device-centric protection versus perimeter security's focus on controlling access at the network edge.
Key Components of Endpoint Security
Endpoint security focuses on protecting individual devices such as laptops, smartphones, and desktops through key components including antivirus software, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and device encryption. Advanced endpoint protection platforms (EPP) integrate threat prevention, detection, and response capabilities to safeguard against malware, ransomware, and zero-day attacks. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools provide continuous monitoring and real-time analysis to quickly identify and mitigate security threats at the device level.
Fundamental Elements of Perimeter Security
Perimeter security fundamentally relies on physical barriers such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and network access controls to establish a controlled boundary between trusted internal networks and untrusted external environments. It emphasizes monitoring and filtering incoming and outgoing traffic at network gateways to prevent unauthorized access and cyber threats. Effective perimeter security integrates continuous threat intelligence and real-time analytics to dynamically adapt to evolving attack vectors.
Common Threats Targeting Endpoints
Common threats targeting endpoints include malware infections, ransomware attacks, phishing schemes, and unauthorized access attempts exploiting vulnerabilities in devices. Endpoint security solutions use advanced threat detection, behavior analysis, and continuous monitoring to prevent data breaches caused by compromised laptops, desktops, and mobile devices. These protections are essential as endpoints serve as primary entry points for cyberattacks often bypassing traditional perimeter defenses.
Typical Attacks on Perimeter Defenses
Typical attacks on perimeter defenses include Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, firewall evasion techniques, and intrusion attempts exploiting vulnerabilities in VPNs or proxy servers. Cybercriminals often target perimeter security through phishing campaigns and sophisticated malware designed to bypass external filters and gain unauthorized network access. These attacks highlight the limitations of perimeter security alone and emphasize the need for integrated endpoint security measures to detect and respond to threats within the network.
Advantages and Limitations of Endpoint Security
Endpoint security provides granular protection by securing individual devices such as laptops, smartphones, and IoT devices, reducing the risk of threats bypassing network defenses. It enables real-time threat detection and response directly on endpoints, improving the ability to identify malware, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access quickly. However, endpoint security relies heavily on the continuous updating of software and user compliance, and it can be resource-intensive to manage across large, diverse device environments.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Perimeter Security
Perimeter security excels at creating a strong initial barrier to prevent unauthorized access by controlling network entry points through firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls. Its primary weakness lies in its limited effectiveness against insider threats and sophisticated attacks that bypass traditional boundaries, such as phishing or malware infiltrating trusted devices. Relying solely on perimeter security can leave internal systems vulnerable, emphasizing the need for complementary endpoint security measures to safeguard individual devices and data.
Integrating Endpoint and Perimeter Security Strategies
Integrating endpoint security and perimeter security strategies enhances overall cybersecurity posture by providing a multi-layered defense against threats targeting both network edges and individual devices. Endpoint security protects devices like laptops and smartphones from malware and unauthorized access, while perimeter security safeguards network boundaries through firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Combining these approaches enables real-time threat detection, seamless policy enforcement, and improved incident response across distributed environments.
Best Practices for Building a Comprehensive Security Posture
Endpoint security involves protecting individual devices through antivirus software, endpoint detection, and response solutions, while perimeter security focuses on safeguarding the network boundary using firewalls and intrusion prevention systems. Best practices for building a comprehensive security posture include integrating endpoint detection and response (EDR) with next-generation firewalls to achieve real-time threat detection and containment. Implementing multi-layered defenses that combine zero-trust principles, continuous monitoring, and regular patch management enhances resilience against sophisticated cyber threats targeting both endpoints and network perimeters.
Endpoint Security vs Perimeter Security Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com