A Purchase Agreement is a legally binding contract where the buyer agrees to purchase a property under specified terms, securing ownership upon closing. An Option Agreement grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase the property within a set timeframe, often requiring a fee for this privilege. Understanding the differences helps investors and homeowners choose the best contract type for flexibility or commitment in real estate transactions.
Table of Comparison
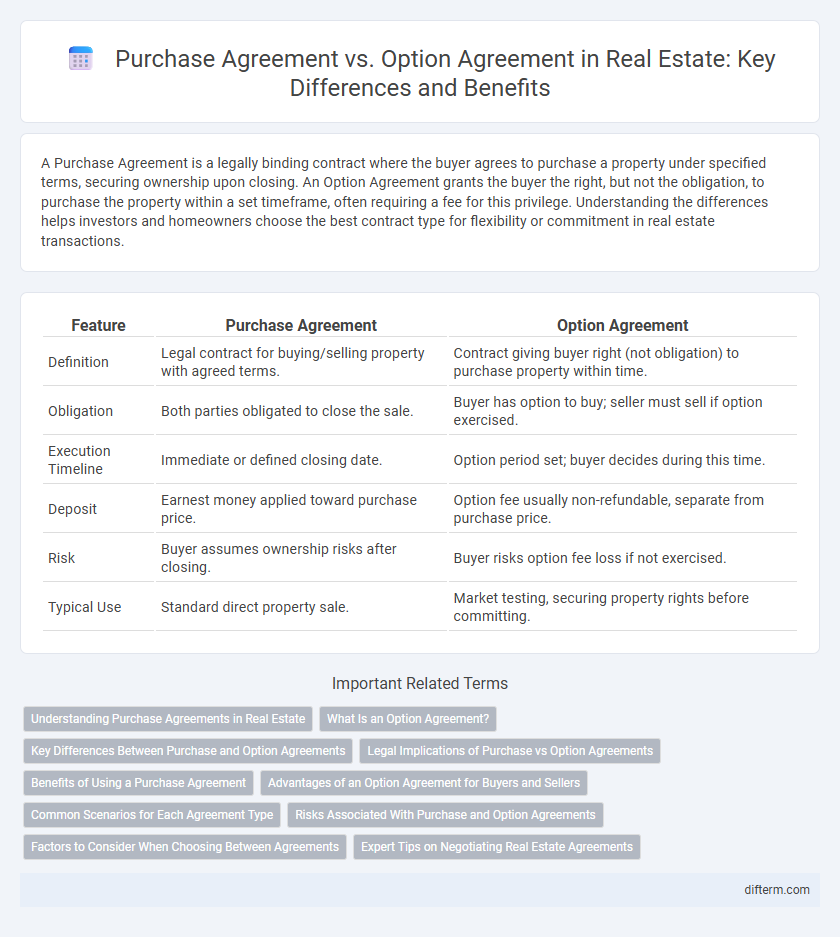
| Feature | Purchase Agreement | Option Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal contract for buying/selling property with agreed terms. | Contract giving buyer right (not obligation) to purchase property within time. |
| Obligation | Both parties obligated to close the sale. | Buyer has option to buy; seller must sell if option exercised. |
| Execution Timeline | Immediate or defined closing date. | Option period set; buyer decides during this time. |
| Deposit | Earnest money applied toward purchase price. | Option fee usually non-refundable, separate from purchase price. |
| Risk | Buyer assumes ownership risks after closing. | Buyer risks option fee loss if not exercised. |
| Typical Use | Standard direct property sale. | Market testing, securing property rights before committing. |
Understanding Purchase Agreements in Real Estate
A Purchase Agreement in real estate is a legally binding contract outlining the terms and conditions between a buyer and seller for transferring property ownership. It specifies crucial details such as purchase price, property description, contingencies, closing date, and obligations of both parties, ensuring clarity and protection throughout the transaction. Understanding the Purchase Agreement is essential for navigating due diligence, financing, inspections, and closing procedures effectively.
What Is an Option Agreement?
An Option Agreement in real estate grants a potential buyer the exclusive right to purchase a property within a specified timeframe without the obligation to do so. This agreement typically involves an option fee paid upfront, which may be applied to the purchase price if the option is exercised. Unlike a Purchase Agreement, an Option Agreement provides flexibility and control over the property while allowing the buyer to evaluate the investment before committing.
Key Differences Between Purchase and Option Agreements
A Purchase Agreement is a binding contract outlining the terms for transferring property ownership upon closing, while an Option Agreement grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase within a specified timeframe. Purchase Agreements typically require a deposit and set closing dates, whereas Option Agreements involve paying an option fee for exclusive purchasing rights without immediate transfer of ownership. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for investors seeking flexibility in property acquisition versus committing to a definite sale.
Legal Implications of Purchase vs Option Agreements
A Purchase Agreement legally binds both buyer and seller to complete a real estate transaction under agreed terms, ensuring enforceability and clear title transfer upon closing. An Option Agreement grants the buyer the exclusive right, but not the obligation, to purchase the property within a specified period, providing flexibility but limited immediate rights. Legal implications differ significantly; Purchase Agreements create immediate contractual duties, whereas Option Agreements primarily provide potential future rights, affecting risk, enforceability, and remedies for breach.
Benefits of Using a Purchase Agreement
A Purchase Agreement provides a clear, legally binding contract that outlines the terms and conditions of the real estate transaction, offering both buyer and seller certainty and protection. This agreement typically includes details such as purchase price, closing date, and contingencies, which help prevent misunderstandings and disputes. Using a Purchase Agreement facilitates a smoother transaction process by ensuring all parties commit to the sale, reducing the risk of unexpected changes or cancellations.
Advantages of an Option Agreement for Buyers and Sellers
An Option Agreement provides buyers with the exclusive right to purchase a property within a specified timeframe, allowing them to secure the opportunity without immediate commitment, which reduces upfront risk and enhances investment flexibility. Sellers benefit from Option Agreements by receiving non-refundable option fees upfront, creating a steady income stream while maintaining control over the property's sale timeline. This arrangement also attracts committed buyers and potentially increases the final sale price due to the buyer's secured interest.
Common Scenarios for Each Agreement Type
Purchase agreements are commonly used in straightforward real estate transactions where the buyer commits to purchasing the property under agreed terms and conditions, often involving financing and inspection contingencies. Option agreements frequently appear in scenarios where a buyer wants to secure the right to purchase the property within a specified period without an immediate obligation, providing flexibility for investment analysis or market conditions. Investors and developers often utilize option agreements to control properties while minimizing upfront risk before deciding on full acquisition via a purchase agreement.
Risks Associated With Purchase and Option Agreements
Purchase agreements carry risks such as binding commitments that may expose buyers to financial loss if they fail to close, while sellers face potential liability for contract breach. Option agreements mitigate some risk by granting the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase property within a specified period, although option fees may be non-refundable. Both agreements require careful review of terms related to contingencies, deadlines, and default consequences to minimize legal and financial exposure.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Agreements
When deciding between a Purchase Agreement and an Option Agreement in real estate, consider factors such as commitment level, financial risk, and flexibility. A Purchase Agreement binds the buyer to complete the transaction under specified terms, while an Option Agreement grants the buyer the right--but not the obligation--to purchase within a set timeframe, providing more control over timing. Assess the buyer's readiness, market conditions, and negotiation goals to determine which agreement aligns best with investment strategy and risk tolerance.
Expert Tips on Negotiating Real Estate Agreements
Negotiating real estate agreements requires precise understanding of Purchase Agreements and Option Agreements to protect buyers and sellers. Purchase Agreements create binding commitments for property transfer, while Option Agreements grant the right to buy without obligation, allowing flexible negotiation. Expert tips emphasize clear terms on contingencies, deadlines, and consideration to minimize disputes and secure favorable deal outcomes.
Purchase Agreement vs Option Agreement Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com