Fee simple ownership grants the property owner full rights to use, sell, or transfer the property indefinitely, providing the highest level of control. Life estate ownership allows a person to use and benefit from the property for the duration of their life, after which ownership passes to a predetermined beneficiary. Understanding these distinctions helps buyers and sellers navigate property rights, inheritance, and long-term investment strategies effectively.
Table of Comparison
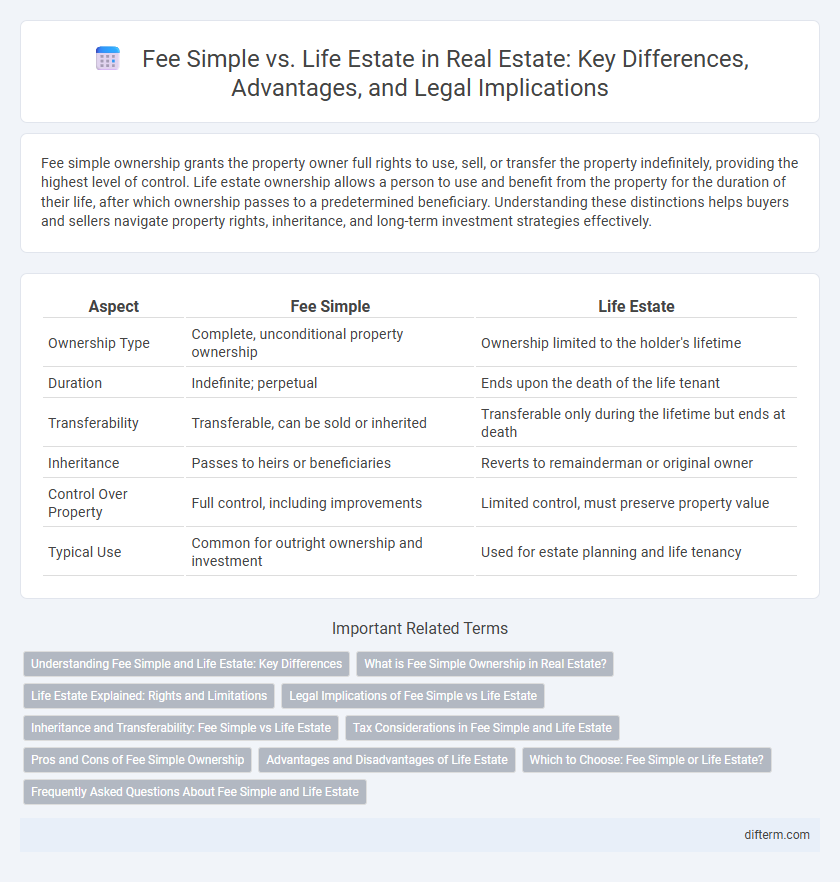
| Aspect | Fee Simple | Life Estate |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership Type | Complete, unconditional property ownership | Ownership limited to the holder's lifetime |
| Duration | Indefinite; perpetual | Ends upon the death of the life tenant |
| Transferability | Transferable, can be sold or inherited | Transferable only during the lifetime but ends at death |
| Inheritance | Passes to heirs or beneficiaries | Reverts to remainderman or original owner |
| Control Over Property | Full control, including improvements | Limited control, must preserve property value |
| Typical Use | Common for outright ownership and investment | Used for estate planning and life tenancy |
Understanding Fee Simple and Life Estate: Key Differences
Fee simple ownership grants the holder absolute property rights, including the ability to sell, lease, or bequeath the property without limitations, making it the most complete form of real estate ownership. In contrast, a life estate provides ownership rights only for the duration of an individual's life, after which the property automatically transfers to a designated remainderman or reverts to the original owner. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for property planning, as fee simple ensures perpetual control, while life estates limit ownership to a lifetime with conditional future interests.
What is Fee Simple Ownership in Real Estate?
Fee simple ownership in real estate represents the most complete form of property ownership, granting the owner absolute and indefinite rights to use, sell, lease, or bequeath the property. This estate includes full control over the land and any structures on it, subject only to local laws, zoning regulations, and easements. Unlike life estates, fee simple ownership is not limited by the owner's lifetime and transfers with full title upon sale or inheritance.
Life Estate Explained: Rights and Limitations
A life estate grants an individual the right to use and occupy a property during their lifetime, with ownership reverting to a designated remainderman upon their death. The life tenant can derive benefits such as living in or leasing the property but cannot sell or bequeath the estate beyond their lifetime. Restrictions often include limitations on making significant alterations or committing waste that diminishes the property's value for future owners.
Legal Implications of Fee Simple vs Life Estate
Fee simple ownership grants absolute property rights, allowing the owner to sell, lease, or bequeath the property without restrictions. In contrast, a life estate limits ownership to the duration of the life tenant's lifetime, after which the property reverts to the remainderman or original grantor. Legal implications include potential disputes over property use, transfer rights, and responsibilities for property taxes and maintenance during the life estate period.
Inheritance and Transferability: Fee Simple vs Life Estate
Fee simple estate offers complete ownership with full inheritance rights, allowing the property to be freely transferred or sold without restrictions. In contrast, a life estate grants ownership rights only for the duration of the life tenant, after which the property automatically passes to the remainderman or revert to the original grantor, limiting transferability. This distinction is crucial in estate planning and property succession, impacting how assets are inherited and managed post-mortem.
Tax Considerations in Fee Simple and Life Estate
Fee simple ownership provides greater tax benefits due to the ability to claim property tax deductions, depreciation, and full capital gains exclusion upon sale. Life estate holders have limited tax advantages since their interest is considered a future interest, often leading to complex valuation for estate and gift tax purposes. Property taxes in life estate arrangements are typically paid by the life tenant, but the remainderman's potential tax liabilities can arise upon transfer or death.
Pros and Cons of Fee Simple Ownership
Fee simple ownership grants the most complete control over a property, allowing owners to sell, lease, or bequeath the asset without restrictions, which maximizes investment flexibility and long-term value. However, it also carries full responsibility for property taxes, maintenance costs, and liability, potentially leading to significant financial burdens. This form of ownership is ideal for those seeking permanent, unrestricted property rights but may be less suitable for individuals needing temporary or conditional interests in real estate.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Life Estate
A life estate grants ownership rights for the duration of an individual's life, enabling control and use of the property without transferring full ownership, which can simplify estate planning and reduce probate costs. However, the life tenant cannot sell or encumber the property beyond their lifetime, limiting financial flexibility and potentially causing conflicts with remaindermen who hold future interests. The property also may lack marketability and can complicate inheritance since the life estate terminates upon the tenant's death, returning possession to the designated remainderman.
Which to Choose: Fee Simple or Life Estate?
Choosing between fee simple and life estate depends on your long-term ownership goals and control preferences. Fee simple offers full ownership with unlimited duration and the ability to sell or transfer the property, while a life estate grants usage rights only for the duration of a person's lifetime, reverting to another party afterward. For maximum control and investable value, fee simple is ideal; for estate planning or ensuring a property's future transition, a life estate may be more suitable.
Frequently Asked Questions About Fee Simple and Life Estate
Fee simple ownership grants the most complete property rights, allowing the owner to sell, lease, or bequeath the property indefinitely. A life estate provides ownership for the duration of an individual's life, after which the property passes to a remainderman or reverts to the original grantor. Common questions include differences in transferability, tax implications, and what happens to the property after the life tenant's death.
fee simple vs life estate Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com