The Eisenhower matrix categorizes tasks by urgency and importance to prioritize effectively, helping users focus on what requires immediate attention and what can be delegated or deferred. Pareto analysis identifies the 20% of tasks or efforts that yield 80% of the results, guiding users to maximize productivity by concentrating on high-impact activities. Combining both methods enhances decision-making, ensuring tasks are not only significant but also aligned with optimal resource allocation.
Table of Comparison
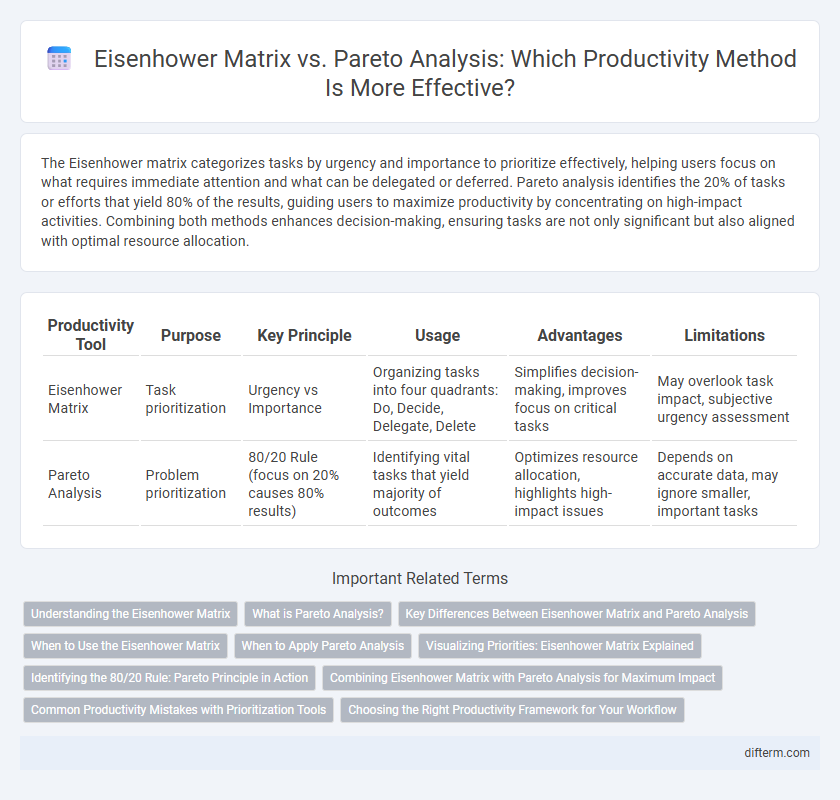
| Productivity Tool | Purpose | Key Principle | Usage | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eisenhower Matrix | Task prioritization | Urgency vs Importance | Organizing tasks into four quadrants: Do, Decide, Delegate, Delete | Simplifies decision-making, improves focus on critical tasks | May overlook task impact, subjective urgency assessment |
| Pareto Analysis | Problem prioritization | 80/20 Rule (focus on 20% causes 80% results) | Identifying vital tasks that yield majority of outcomes | Optimizes resource allocation, highlights high-impact issues | Depends on accurate data, may ignore smaller, important tasks |
Understanding the Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix categorizes tasks into four quadrants based on urgency and importance, enabling effective prioritization to enhance productivity. By distinguishing between what needs immediate attention and what can be delegated or deferred, this method streamlines decision-making and time management. Its contrast with Pareto analysis lies in focusing on task urgency rather than solely on impact distribution, making it essential for daily task prioritization.
What is Pareto Analysis?
Pareto Analysis is a decision-making tool that identifies the most significant factors contributing to a problem by applying the 80/20 rule, which states that roughly 80% of effects come from 20% of causes. It helps prioritize tasks by focusing on the critical few that will yield the greatest impact on productivity. Unlike the Eisenhower Matrix, which categorizes tasks by urgency and importance, Pareto Analysis emphasizes resource allocation to optimize results efficiently.
Key Differences Between Eisenhower Matrix and Pareto Analysis
The Eisenhower Matrix categorizes tasks based on urgency and importance, enabling prioritization through four quadrants, while Pareto Analysis focuses on identifying the vital 20% of causes that generate 80% of the results. The matrix emphasizes time management and decision-making for immediate action, whereas Pareto Analysis targets resource allocation to maximize overall impact. Both tools enhance productivity but differ in approach: Eisenhower Matrix guides task execution sequence, Pareto Analysis drives strategic focus on high-impact factors.
When to Use the Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix is ideal for managing urgent and important tasks by categorizing activities into four quadrants based on urgency and importance, helping prioritize work effectively. Use it when facing a high volume of diverse tasks that require quick decision-making to avoid procrastination and ensure critical deadlines are met. This method excels in daily task management, especially for professionals balancing immediate responsibilities with long-term goals.
When to Apply Pareto Analysis
Pareto analysis is most effective when identifying the 20% of tasks or issues responsible for 80% of the results or problems, making it ideal for prioritizing workload in complex projects. Use Pareto analysis during project reviews to isolate major bottlenecks or when resource allocation must maximize impact. Applying Pareto analysis helps focus efforts on key tasks that drive the greatest productivity gains, complementing the Eisenhower matrix's focus on urgency and importance.
Visualizing Priorities: Eisenhower Matrix Explained
The Eisenhower Matrix categorizes tasks into four quadrants based on urgency and importance, enabling clear visualization of priorities for effective time management. By distinguishing between urgent-important and non-urgent-important tasks, it helps users focus on strategic activities that drive long-term productivity. In comparison, Pareto analysis emphasizes identifying the critical 20% of tasks that yield 80% of results but lacks the visual structure for immediate prioritization present in the Eisenhower Matrix.
Identifying the 80/20 Rule: Pareto Principle in Action
The Eisenhower Matrix prioritizes tasks based on urgency and importance, while Pareto Analysis focuses on identifying the critical 20% of tasks that generate 80% of results, exemplifying the 80/20 Rule. Pareto Principle in practice helps individuals and businesses concentrate efforts on high-impact activities to maximize productivity and efficiency. By integrating Pareto Analysis with time management methods, users can streamline decision-making and optimize resource allocation for better outcomes.
Combining Eisenhower Matrix with Pareto Analysis for Maximum Impact
Combining the Eisenhower Matrix with Pareto Analysis enhances productivity by prioritizing tasks based on urgency, importance, and impact, enabling focused decision-making on high-value activities. The Eisenhower Matrix categorizes tasks into four quadrants, while Pareto Analysis identifies the 20% of tasks that generate 80% of results; integrating both tools streamlines task management and resource allocation. This strategic approach maximizes efficiency, reduces time wasted on low-priority work, and drives significant progress toward key goals.
Common Productivity Mistakes with Prioritization Tools
Misapplication of the Eisenhower matrix often leads to overemphasizing urgent tasks over important ones, causing inefficient prioritization. Pareto analysis can be misleading if users focus solely on the 20% of tasks that seem impactful without re-evaluating task relevance periodically. Common productivity mistakes include neglecting task context and failing to integrate these tools with broader time management strategies.
Choosing the Right Productivity Framework for Your Workflow
The Eisenhower Matrix prioritizes tasks by urgency and importance, helping users focus on critical activities and avoid time-wasting distractions. Pareto Analysis identifies the 20% of tasks that generate 80% of results, optimizing efforts for maximum impact. Selecting between these productivity frameworks depends on whether your workflow benefits more from time-sensitive task management or impact-driven prioritization.
Eisenhower matrix vs Pareto analysis Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com