Bullet Journal offers a customizable analog system ideal for visual thinkers who prefer tracking tasks, events, and notes in one place. GTD (Getting Things Done) emphasizes a structured, digital-friendly approach to capturing, clarifying, and organizing actionable items to reduce mental clutter. Choosing between Bullet Journal and GTD depends on whether you value creative flexibility or systematic efficiency in managing productivity.
Table of Comparison
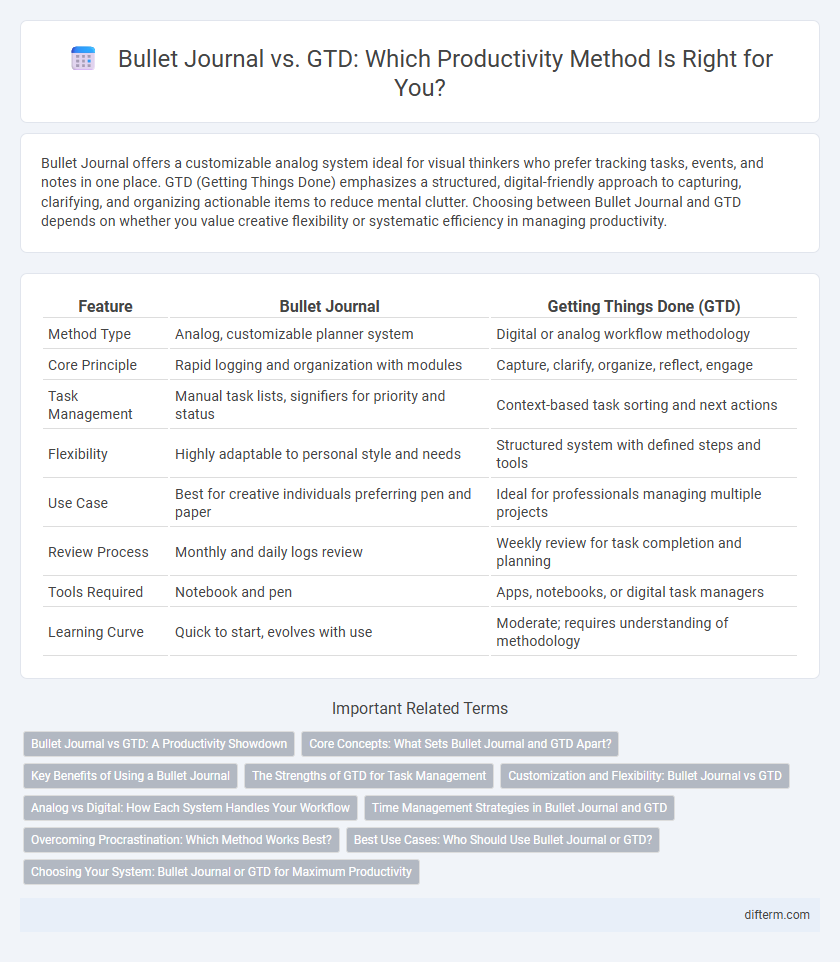
| Feature | Bullet Journal | Getting Things Done (GTD) |
|---|---|---|
| Method Type | Analog, customizable planner system | Digital or analog workflow methodology |
| Core Principle | Rapid logging and organization with modules | Capture, clarify, organize, reflect, engage |
| Task Management | Manual task lists, signifiers for priority and status | Context-based task sorting and next actions |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to personal style and needs | Structured system with defined steps and tools |
| Use Case | Best for creative individuals preferring pen and paper | Ideal for professionals managing multiple projects |
| Review Process | Monthly and daily logs review | Weekly review for task completion and planning |
| Tools Required | Notebook and pen | Apps, notebooks, or digital task managers |
| Learning Curve | Quick to start, evolves with use | Moderate; requires understanding of methodology |
Bullet Journal vs GTD: A Productivity Showdown
Bullet Journal offers a customizable, analog system that combines task management, note-taking, and personal reflection to boost productivity, while GTD (Getting Things Done) provides a structured, digital-friendly framework emphasizing clear action lists and project tracking. Bullet Journal's flexibility appeals to creative users who prefer a visual and tactile approach, whereas GTD delivers a standardized, methodology-driven process favored by professionals seeking efficiency and consistency. Choosing between Bullet Journal vs GTD depends on individual workflow preferences, with Bullet Journal excelling in personalization and GTD in systematic task execution.
Core Concepts: What Sets Bullet Journal and GTD Apart?
Bullet Journal emphasizes a customizable, analog system combining rapid logging, migration, and reflection to capture tasks, events, and notes in one place, fostering mindfulness and creativity. GTD (Getting Things Done) is a digital-friendly method centered on capturing all commitments externally, clarifying next actions, organizing by context, and regularly reviewing to increase workflow efficiency and reduce mental clutter. The core difference lies in Bullet Journal's fluid, personalized format versus GTD's structured, process-driven approach to task management.
Key Benefits of Using a Bullet Journal
Bullet Journals enhance productivity by offering customizable organization tailored to individual workflows, allowing users to track tasks, goals, and habits in one streamlined system. The analog format promotes mindfulness and reduces digital distractions, helping users maintain focus and prioritize effectively. Rapid logging and flexible layouts enable quick adjustments, fostering continuous improvement in task management and time allocation.
The Strengths of GTD for Task Management
GTD (Getting Things Done) excels in task management by providing a clear, structured workflow that captures, clarifies, organizes, reflects, and engages with tasks efficiently. Its strength lies in breaking down complex projects into actionable next steps, reducing mental clutter and increasing focus on priority tasks. The system's emphasis on regular reviews supports adaptive planning and ensures consistent progress toward goals.
Customization and Flexibility: Bullet Journal vs GTD
Bullet Journal offers unparalleled customization, allowing users to design layouts, trackers, and notes tailored to their unique productivity needs, fostering creativity and adaptability. GTD (Getting Things Done) emphasizes a structured methodology with defined stages like capture, clarify, organize, reflect, and engage, providing a systematic framework but less flexibility in format. Users seeking a personalized, creative approach benefit from Bullet Journal's flexibility, while those preferring a standardized, process-driven system may gravitate towards GTD's consistent methodology.
Analog vs Digital: How Each System Handles Your Workflow
Bullet Journal leverages analog methods by using customizable notebooks that allow for flexible task management, habit tracking, and creative expression, enhancing memory retention through handwritten notes. GTD, often implemented digitally via apps like Todoist or Evernote, emphasizes a structured workflow with clear categorization, seamless syncing, and automated reminders to boost efficiency across devices. Analog Bullet Journals encourage mindfulness and personal reflection, while digital GTD systems prioritize speed, organization, and real-time updates for complex workflows.
Time Management Strategies in Bullet Journal and GTD
Bullet Journal employs customizable time management strategies that combine task lists, calendars, and habit tracking to enhance focus and flexibility. GTD (Getting Things Done) relies on a structured workflow of capturing, clarifying, organizing, reflecting, and engaging to efficiently process tasks and reduce mental clutter. Both methods optimize productivity by offering distinct approaches: Bullet Journal emphasizes creativity and adaptability, whereas GTD prioritizes systematic task management and consistent review cycles.
Overcoming Procrastination: Which Method Works Best?
Bullet Journal offers a tactile, customizable system that enhances mindfulness and accountability by visually tracking tasks, making it effective for overcoming procrastination through increased engagement. GTD (Getting Things Done) relies on a structured workflow that breaks down tasks into actionable steps, reducing overwhelm and enabling clearer prioritization to combat procrastination. Studies and user reports suggest combining Bullet Journal's reflective elements with GTD's task organization yields the most robust results in sustaining productivity and minimizing delay.
Best Use Cases: Who Should Use Bullet Journal or GTD?
Bullet Journal suits creative individuals who prefer a flexible, analog method for organizing tasks, ideas, and goals, offering customization and mindfulness benefits. GTD (Getting Things Done) is ideal for professionals managing high volumes of complex projects or tasks, emphasizing efficiency through a structured digital or physical workflow. Users seeking a blend of creativity and productivity may combine both systems to maximize personal organization and task execution.
Choosing Your System: Bullet Journal or GTD for Maximum Productivity
Choosing between Bullet Journal and Getting Things Done (GTD) hinges on your need for flexibility versus structure; Bullet Journal offers customizable layouts ideal for creative planners, while GTD provides a systematic framework designed to capture and process tasks efficiently. Bullet Journal's analog format enhances mindfulness and visual tracking, promoting deeper engagement with your daily goals, whereas GTD's digital-friendly system emphasizes clear next actions and project organization to minimize task overwhelm. Evaluating your productivity style and preference for tactile note-taking or digital task management ensures optimal system alignment for sustained focus and accomplishment.
Bullet Journal vs GTD (Getting Things Done) Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com