Single-tasking enhances focus by dedicating full attention to one task, reducing errors and improving quality. Serial tasking involves completing tasks one after another but may lead to mental fatigue as switching between different types of work can disrupt concentration. Prioritizing single-tasking over serial tasking boosts efficiency and promotes deeper cognitive engagement with each objective.
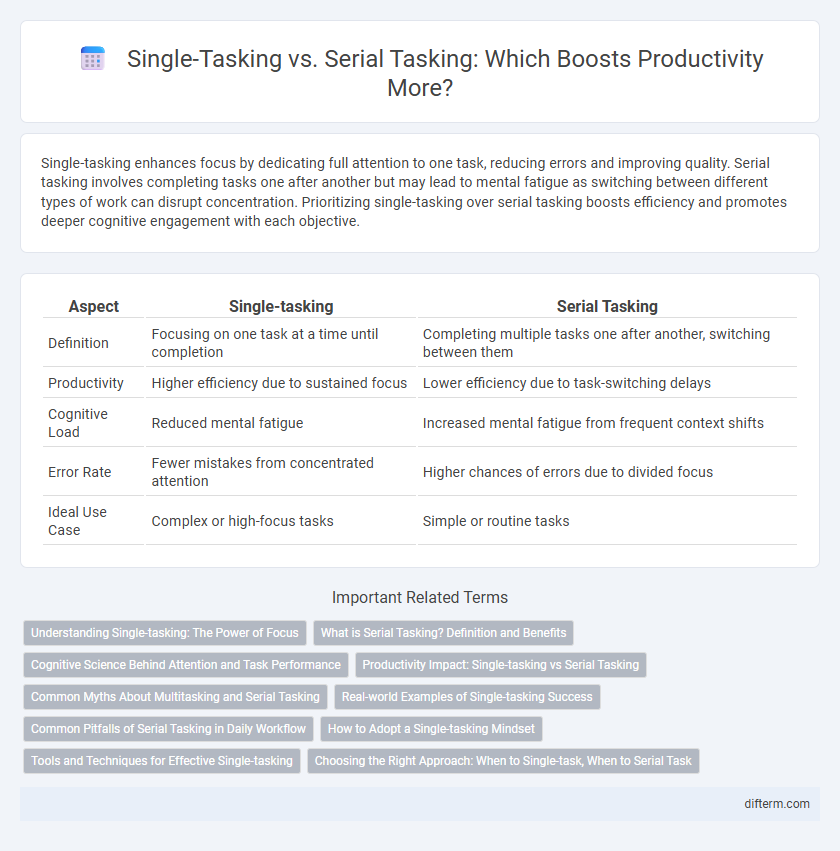
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Single-tasking | Serial Tasking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focusing on one task at a time until completion | Completing multiple tasks one after another, switching between them |
| Productivity | Higher efficiency due to sustained focus | Lower efficiency due to task-switching delays |
| Cognitive Load | Reduced mental fatigue | Increased mental fatigue from frequent context shifts |
| Error Rate | Fewer mistakes from concentrated attention | Higher chances of errors due to divided focus |
| Ideal Use Case | Complex or high-focus tasks | Simple or routine tasks |
Understanding Single-tasking: The Power of Focus
Single-tasking enhances productivity by allowing individuals to concentrate fully on one task, reducing cognitive overload and minimizing errors. Neuroscientific studies show that focused attention improves memory retention and task efficiency by activating deep work states. Prioritizing single-tasking over serial tasking leads to higher quality outcomes and faster completion times, as fragmented attention impairs information processing.
What is Serial Tasking? Definition and Benefits
Serial tasking refers to the process of completing tasks sequentially, one after another, rather than switching between multiple tasks simultaneously. This method reduces cognitive overload and minimizes mistakes by allowing full focus on each activity, enhancing overall efficiency and task accuracy. Benefits of serial tasking include improved concentration, better time management, and higher quality outcomes in professional and personal productivity.
Cognitive Science Behind Attention and Task Performance
Single-tasking enhances cognitive focus by reducing the mental load associated with task-switching, which often depletes working memory and impairs executive function as demonstrated in cognitive neuroscience studies. Serial tasking, or sequentially completing tasks one at a time without overlapping activities, optimizes sustained attention and minimizes interference effects, leading to improved task accuracy and response time efficiency. Research in cognitive psychology highlights that maintaining attentional control through single-task engagement activates the prefrontal cortex more effectively, promoting deeper information processing and stronger memory consolidation.
Productivity Impact: Single-tasking vs Serial Tasking
Single-tasking enhances productivity by allowing full concentration on one task, reducing cognitive switching costs and minimizing errors. Serial tasking, often confused with multitasking, involves completing tasks sequentially but can still induce mental fatigue if tasks are complex or prolonged. Studies show single-tasking improves focus and output quality, making it a preferred strategy for high-performance work environments.
Common Myths About Multitasking and Serial Tasking
Multitasking is often praised for efficiency, but studies show it reduces productivity by up to 40% due to frequent task switching impairing focus. Serial tasking, completing one task before moving to the next, enhances cognitive performance and lowers error rates, countering the myth that juggling multiple tasks saves time. Understanding that multitasking leads to mental fatigue and decreased accuracy can significantly improve work quality and overall productivity.
Real-world Examples of Single-tasking Success
Single-tasking enhances focus and efficiency, as exemplified by Apple CEO Tim Cook, who dedicates specific time blocks to individual tasks without multitasking interruptions. Studies show that employees who engage in single-tasking complete projects 25% faster with 50% fewer errors compared to those practicing serial tasking. Real-world applications in industries such as software development and creative design highlight single-tasking's role in boosting innovation and reducing cognitive overload.
Common Pitfalls of Serial Tasking in Daily Workflow
Serial tasking often leads to increased cognitive load and frequent context switching, which decreases overall efficiency and accuracy. Common pitfalls include prolonged task completion time and heightened stress levels due to disrupted focus. Maintaining a consistent focus on one task at a time significantly reduces errors and enhances productivity in daily workflows.
How to Adopt a Single-tasking Mindset
Adopting a single-tasking mindset requires consciously prioritizing one task at a time to maximize focus and efficiency. Techniques such as time blocking, minimizing digital distractions, and setting clear, specific goals help reinforce sustained attention on a single task, reducing cognitive overload. Consistent practice of these strategies improves mental clarity and increases overall productivity by leveraging deeper engagement with individual tasks over fragmented serial tasking.
Tools and Techniques for Effective Single-tasking
Effective single-tasking relies on tools like time-blocking apps, distraction blockers, and focus-enhancing techniques such as the Pomodoro method, which maximizes concentration by breaking work into intervals. Techniques including prioritization matrices and task batching help streamline workflows, reducing cognitive load and increasing productivity. Implementing these tools alongside mindfulness practices supports sustained attention, minimizing task-switching costs and enhancing overall work quality.
Choosing the Right Approach: When to Single-task, When to Serial Task
Single-tasking maximizes focus and efficiency on complex or high-priority tasks requiring deep concentration, making it ideal for problem-solving and creative work. Serial tasking suits scenarios involving multiple routine or low-cognitive-demand activities, allowing for structured task switching without sacrificing overall productivity. Recognizing task complexity and cognitive load helps determine the best approach, optimizing performance by aligning work style with the specific demands of each task.
Single-tasking vs Serial tasking Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com