Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, while prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for these bacteria, promoting their growth and activity. Incorporating both probiotics and prebiotics into the diet supports digestive health, enhances immune function, and improves nutrient absorption. A balanced intake of probiotics and prebiotics optimizes gut flora diversity and overall well-being.
Table of Comparison
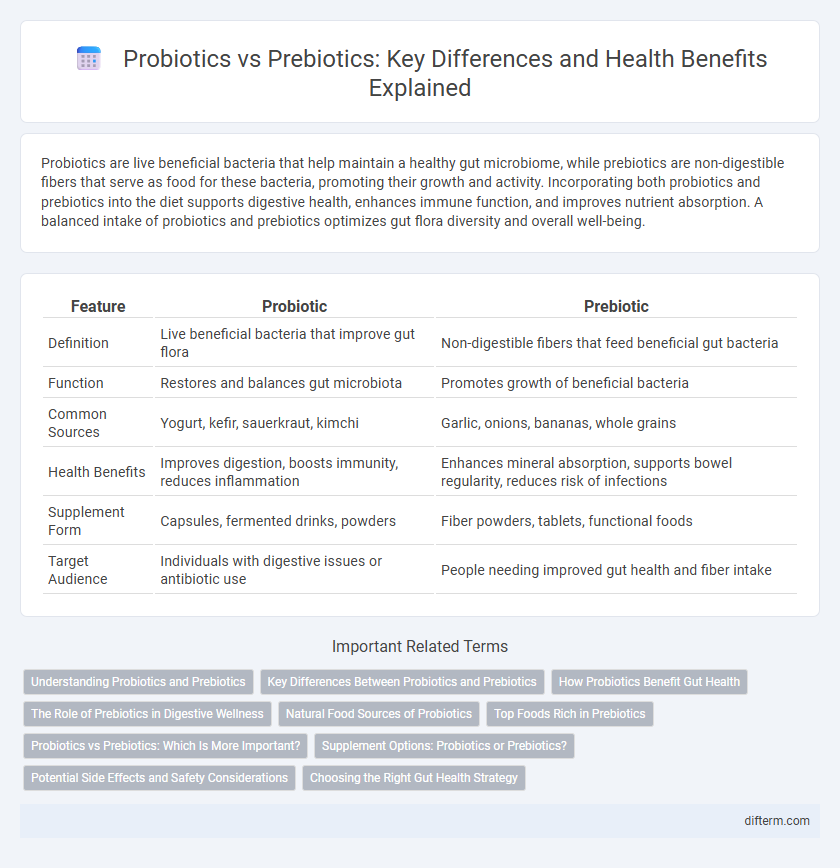
| Feature | Probiotic | Prebiotic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Live beneficial bacteria that improve gut flora | Non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial gut bacteria |
| Function | Restores and balances gut microbiota | Promotes growth of beneficial bacteria |
| Common Sources | Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi | Garlic, onions, bananas, whole grains |
| Health Benefits | Improves digestion, boosts immunity, reduces inflammation | Enhances mineral absorption, supports bowel regularity, reduces risk of infections |
| Supplement Form | Capsules, fermented drinks, powders | Fiber powders, tablets, functional foods |
| Target Audience | Individuals with digestive issues or antibiotic use | People needing improved gut health and fiber intake |
Understanding Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that support gut health by enhancing the balance of microbiota and improving digestion. Prebiotics are non-digestible dietary fibers that feed these good bacteria, promoting their growth and activity. Understanding the symbiotic relationship between probiotics and prebiotics is essential for optimizing digestive health and immune function.
Key Differences Between Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that colonize the gut and improve digestive health, while prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for these bacteria, promoting their growth. Probiotics directly enhance the gut microbiota by introducing active microorganisms, whereas prebiotics indirectly support gut health by nourishing existing beneficial bacteria. The key difference lies in their function: probiotics add live bacteria, and prebiotics stimulate and sustain these bacterial populations.
How Probiotics Benefit Gut Health
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that enhance gut health by restoring the natural balance of gut microbiota, which can be disrupted by factors like antibiotics or poor diet. These microorganisms improve digestion, boost immune function, and reduce symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome and diarrhea. Scientific studies show that regular consumption of probiotic-rich foods or supplements supports the growth of healthy bacteria, promoting overall digestive wellness and reducing inflammation in the gut.
The Role of Prebiotics in Digestive Wellness
Prebiotics serve as essential dietary fibers that selectively nourish beneficial gut bacteria, enhancing digestive health by promoting a balanced microbiome. These compounds, found in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas, stimulate the growth of probiotics, improving nutrient absorption and reducing inflammation in the digestive tract. Incorporating prebiotics supports regular bowel movements, strengthens gut barrier function, and contributes to overall gastrointestinal wellness.
Natural Food Sources of Probiotics
Natural food sources of probiotics include fermented products such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and miso, which contain live beneficial bacteria that support gut health. Consuming these foods regularly can enhance the diversity and balance of the gut microbiome, improving digestion and immune function. Unlike prebiotics, which are non-digestible fibers that feed gut bacteria, probiotics directly introduce beneficial microorganisms into the digestive system.
Top Foods Rich in Prebiotics
Top foods rich in prebiotics include chicory root, garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, and bananas, which promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. These prebiotic fibers nourish probiotics and improve digestive health by enhancing nutrient absorption and supporting immune function. Incorporating a variety of these prebiotic-rich foods helps maintain a balanced microbiome and reduces gastrointestinal disorders.
Probiotics vs Prebiotics: Which Is More Important?
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that directly improve gut flora and support digestion, while prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that nourish these bacteria, enhancing their growth and activity. Both play crucial roles in maintaining digestive health, immune function, and nutrient absorption, but probiotics provide immediate microbial balance, whereas prebiotics sustain long-term gut ecosystem stability. Prioritizing a balanced intake of probiotics and prebiotics optimizes gut health by combining microbial restoration with supportive nourishment.
Supplement Options: Probiotics or Prebiotics?
Probiotic supplements contain live beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains that help restore gut flora balance and improve digestion. Prebiotic supplements provide non-digestible fibers like inulin and fructooligosaccharides, which feed and stimulate the growth of healthy gut bacteria. Choosing between probiotics or prebiotics depends on individual gut health needs, with many experts recommending a combination for optimal microbiome support.
Potential Side Effects and Safety Considerations
Probiotics may cause mild digestive issues such as gas, bloating, or upset stomach, particularly during initial use, and immunocompromised individuals should exercise caution due to rare risks of infections. Prebiotics commonly lead to symptoms like bloating, gas, and abdominal discomfort when consumed in excess, especially in those with sensitive digestive systems or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Both supplements require careful dosage adherence and consultation with healthcare professionals to minimize adverse effects and ensure safe integration into dietary routines.
Choosing the Right Gut Health Strategy
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that directly replenish the gut microbiome, while prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that nourish existing gut bacteria to promote their growth. Choosing the right gut health strategy depends on individual digestive needs, with probiotics offering immediate microbiome support and prebiotics fostering long-term microbial balance. Combining both can enhance gut diversity, improve digestion, and support immune function more effectively than either approach alone.
Probiotic vs Prebiotic Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com