Prophylaxis involves preventive measures taken to reduce the risk of disease onset, emphasizing early intervention to maintain health. Treatment focuses on managing and curing diagnosed conditions, aiming to alleviate symptoms and restore normal function. Prioritizing prophylaxis can reduce healthcare costs and improve patient outcomes by minimizing the need for extensive therapeutic interventions.
Table of Comparison
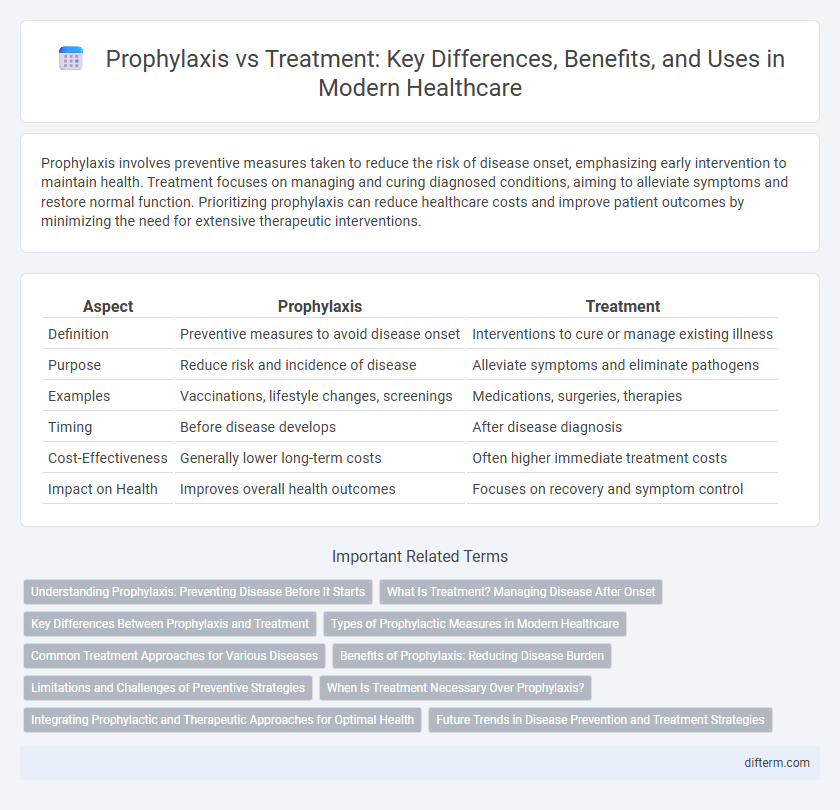
| Aspect | Prophylaxis | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preventive measures to avoid disease onset | Interventions to cure or manage existing illness |
| Purpose | Reduce risk and incidence of disease | Alleviate symptoms and eliminate pathogens |
| Examples | Vaccinations, lifestyle changes, screenings | Medications, surgeries, therapies |
| Timing | Before disease develops | After disease diagnosis |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Generally lower long-term costs | Often higher immediate treatment costs |
| Impact on Health | Improves overall health outcomes | Focuses on recovery and symptom control |
Understanding Prophylaxis: Preventing Disease Before It Starts
Prophylaxis involves preventive measures designed to stop diseases from developing, such as vaccinations, lifestyle modifications, and chemoprophylaxis. By targeting the causative agents or risk factors before symptoms appear, prophylaxis reduces disease incidence and healthcare costs. This approach contrasts with treatment, which focuses on managing symptoms and curing existing conditions after diagnosis.
What Is Treatment? Managing Disease After Onset
Treatment involves interventions aimed at managing and alleviating symptoms after a disease has manifested, often including medications, therapies, or surgical procedures tailored to the specific condition. Effective treatment strategies focus on eliminating the cause, controlling progression, and improving patient quality of life through ongoing medical supervision and personalized care plans. Understanding treatment protocols for diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and infections is essential for achieving optimal health outcomes and preventing complications.
Key Differences Between Prophylaxis and Treatment
Prophylaxis involves preventive measures aimed at stopping diseases before they occur, such as vaccinations and lifestyle modifications, whereas treatment focuses on managing and curing existing health conditions through medications, therapies, or surgeries. Prophylaxis reduces disease incidence and complications, while treatment addresses symptoms and aims to restore health after onset. Understanding the distinction aids in optimizing healthcare strategies for disease control and patient outcomes.
Types of Prophylactic Measures in Modern Healthcare
Prophylactic measures in modern healthcare include immunizations, chemoprophylaxis, and lifestyle modifications aimed at preventing disease onset. Vaccinations stimulate the immune system to build resistance against specific pathogens, while chemoprophylaxis uses medications to prevent infections or disease progression. Public health initiatives also promote behavioral changes like smoking cessation and balanced nutrition to reduce the risk of chronic conditions.
Common Treatment Approaches for Various Diseases
Common treatment approaches for various diseases include pharmacotherapy, which involves the use of medications to manage symptoms or eradicate pathogens, and physical therapy, aimed at restoring mobility and function. Surgical interventions are employed for conditions requiring anatomical correction or removal of diseased tissue. Supportive care, encompassing nutritional support and symptom relief, is integral in managing chronic and acute illnesses effectively.
Benefits of Prophylaxis: Reducing Disease Burden
Prophylaxis significantly reduces disease burden by preventing the onset of illness, thereby lowering healthcare costs and minimizing hospital admissions. Vaccinations, regular screenings, and lifestyle modifications contribute to decreased disease incidence and improve population health outcomes. Early preventive measures strengthen immunity and reduce transmission rates, enhancing overall community well-being.
Limitations and Challenges of Preventive Strategies
Preventive strategies in health face limitations such as varying individual responses to vaccines and behavioral interventions, which can reduce overall efficacy. Challenges include resource allocation for widespread implementation and overcoming socio-cultural barriers that impede compliance. Additionally, preventive measures may not address all risk factors, necessitating continued reliance on treatment options.
When Is Treatment Necessary Over Prophylaxis?
Treatment becomes necessary over prophylaxis when an active infection or disease manifests symptoms, requiring immediate medical intervention to prevent complications and progression. Prophylaxis serves primarily to reduce the risk of disease onset, but once pathological signs are evident, targeted therapies such as antibiotics, antivirals, or other medications are essential. Clinical guidelines recommend prompt treatment initiation for confirmed cases to optimize patient outcomes and reduce morbidity.
Integrating Prophylactic and Therapeutic Approaches for Optimal Health
Integrating prophylactic and therapeutic approaches maximizes health outcomes by preventing disease onset while effectively managing existing conditions. Prophylaxis includes vaccinations, lifestyle modifications, and regular screenings that reduce risk factors, complementing treatments such as medications, surgeries, and rehabilitation. A combined strategy enhances patient resilience, decreases healthcare costs, and improves long-term quality of life.
Future Trends in Disease Prevention and Treatment Strategies
Emerging trends in disease prevention prioritize personalized prophylaxis through advancements in genomics and immunotherapy, allowing targeted intervention before disease onset. Future treatment strategies emphasize integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance diagnostic accuracy and develop precision medicine approaches tailored to individual patient profiles. Innovations in vaccine technology and wearable health monitoring devices also play a crucial role in reshaping the landscape of prophylaxis and disease management.
Prophylaxis vs Treatment Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com