Sleep latency, the time it takes to transition from full wakefulness to sleep, directly influences overall sleep efficiency, which measures the percentage of time spent asleep while in bed. Shorter sleep latency typically enhances sleep efficiency, leading to more restorative rest and better cognitive function. Monitoring and improving these metrics can significantly impact overall health and wellbeing.
Table of Comparison
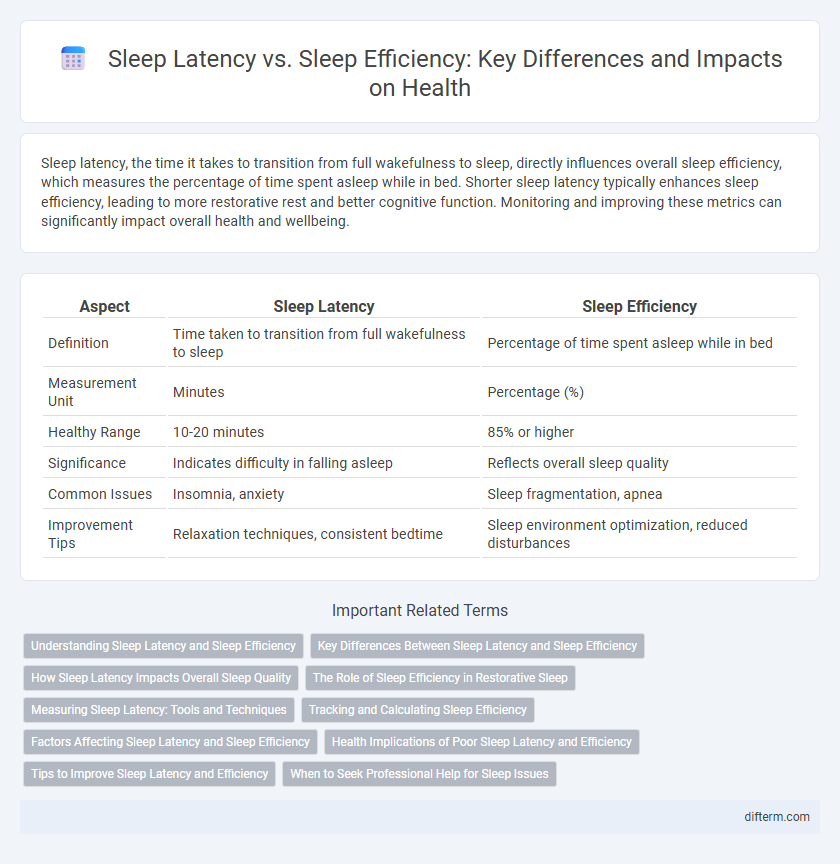
| Aspect | Sleep Latency | Sleep Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Time taken to transition from full wakefulness to sleep | Percentage of time spent asleep while in bed |
| Measurement Unit | Minutes | Percentage (%) |
| Healthy Range | 10-20 minutes | 85% or higher |
| Significance | Indicates difficulty in falling asleep | Reflects overall sleep quality |
| Common Issues | Insomnia, anxiety | Sleep fragmentation, apnea |
| Improvement Tips | Relaxation techniques, consistent bedtime | Sleep environment optimization, reduced disturbances |
Understanding Sleep Latency and Sleep Efficiency
Sleep latency refers to the time it takes to transition from full wakefulness to sleep, typically measured in minutes, while sleep efficiency indicates the percentage of time spent asleep during the total time spent in bed. A shorter sleep latency combined with higher sleep efficiency reflects better sleep quality, crucial for cognitive function and overall health. Tracking these metrics using polysomnography or wearable sleep trackers helps identify sleep disorders such as insomnia and guides effective treatment strategies.
Key Differences Between Sleep Latency and Sleep Efficiency
Sleep latency measures the time it takes to transition from full wakefulness to sleep, typically expressed in minutes, while sleep efficiency indicates the percentage of time spent asleep relative to the total time spent in bed. A shorter sleep latency generally reflects easier sleep onset, whereas higher sleep efficiency demonstrates uninterrupted, restorative sleep throughout the night. Both metrics are essential in diagnosing sleep disorders and optimizing overall sleep quality for better health outcomes.
How Sleep Latency Impacts Overall Sleep Quality
Sleep latency, the time it takes to transition from full wakefulness to sleep, directly influences sleep efficiency, which measures the percentage of time spent asleep while in bed. Prolonged sleep latency often reduces sleep efficiency, indicating fragmented or less restorative sleep, which can impair cognitive function and overall health. Improving sleep latency through consistent routines or environmental adjustments enhances sleep efficiency and promotes better sleep quality.
The Role of Sleep Efficiency in Restorative Sleep
Sleep efficiency, defined as the ratio of total sleep time to time spent in bed, plays a critical role in restorative sleep by indicating the quality and continuity of rest. High sleep efficiency correlates with effective restoration of cognitive and physical functions, while low sleep efficiency often signals fragmented sleep and reduced recovery. Monitoring sleep efficiency provides valuable insights into sleep disorders and guides interventions to enhance overall health and well-being.
Measuring Sleep Latency: Tools and Techniques
Measuring sleep latency accurately involves tools such as polysomnography, which records brain waves, eye movements, and muscle activity to determine the transition from wakefulness to sleep. Actigraphy devices, worn like wristwatches, provide non-invasive, long-term monitoring by tracking movement patterns indicative of sleep onset. Subjective methods like sleep diaries complement these tools by capturing individual perceptions of time taken to fall asleep, enhancing the comprehensive assessment of sleep latency.
Tracking and Calculating Sleep Efficiency
Sleep efficiency is calculated by dividing total sleep time by the time spent in bed, expressed as a percentage, and can be tracked using wearable devices or sleep diaries to monitor sleep quality accurately. Sleep latency, the time taken to fall asleep, influences sleep efficiency by reducing total sleep time if latency is prolonged. Accurate measurement of both sleep latency and sleep efficiency provides valuable data for diagnosing sleep disorders and improving overall health.
Factors Affecting Sleep Latency and Sleep Efficiency
Sleep latency, the time it takes to fall asleep, is influenced by factors such as stress levels, caffeine intake, and bedtime routine consistency, which directly impact sleep efficiency or the percentage of time spent asleep while in bed. Environmental elements like noise, light exposure, and room temperature can disrupt both sleep latency and efficiency by causing awakenings and prolonged sleep onset. Medical conditions including insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless leg syndrome often lead to increased sleep latency and decreased sleep efficiency, reducing overall sleep quality.
Health Implications of Poor Sleep Latency and Efficiency
Poor sleep latency, characterized by prolonged time to fall asleep, often signals underlying stress or anxiety, negatively impacting overall sleep quality and daytime functioning. Reduced sleep efficiency, reflecting fragmented or insufficient restorative sleep, correlates strongly with increased risks of cardiovascular disease, obesity, and impaired immune response. Addressing these disturbances through behavioral interventions and sleep hygiene improvements is critical for preventing chronic health conditions and enhancing cognitive performance.
Tips to Improve Sleep Latency and Efficiency
Improving sleep latency and sleep efficiency involves establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine to signal the body that it's time to rest. Reducing exposure to screens and blue light at least an hour before bed enhances melatonin production, which aids in quicker sleep onset and more restorative sleep cycles. Incorporating regular physical activity and managing stress through mindfulness or meditation techniques also significantly boost sleep quality and overall efficiency.
When to Seek Professional Help for Sleep Issues
Prolonged sleep latency exceeding 30 minutes and consistently low sleep efficiency below 85% may indicate underlying sleep disorders requiring professional evaluation. Persistent difficulty falling asleep or maintaining restful sleep can contribute to daytime fatigue, impaired cognitive function, and reduced quality of life. Seeking consultation with a sleep specialist or healthcare provider is advised when sleep disturbances significantly disrupt daily activities or quality of sleep.
sleep latency vs sleep efficiency Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com