Personalized nutrition tailors dietary recommendations based on individual lifestyle, preferences, and health conditions, emphasizing a holistic approach. Precision nutrition leverages genetic, metabolic, and microbiome data to create highly specific dietary plans aimed at optimizing health outcomes. Both strategies improve health but differ in their depth of data integration and scientific complexity.
Table of Comparison
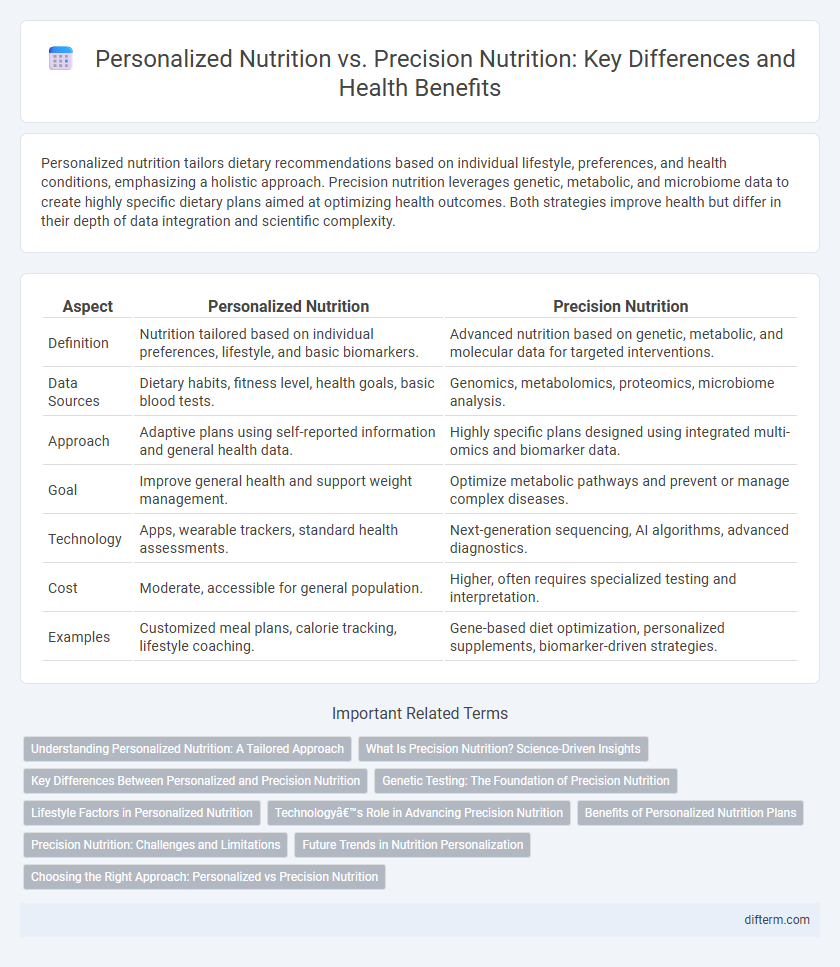
| Aspect | Personalized Nutrition | Precision Nutrition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Nutrition tailored based on individual preferences, lifestyle, and basic biomarkers. | Advanced nutrition based on genetic, metabolic, and molecular data for targeted interventions. |
| Data Sources | Dietary habits, fitness level, health goals, basic blood tests. | Genomics, metabolomics, proteomics, microbiome analysis. |
| Approach | Adaptive plans using self-reported information and general health data. | Highly specific plans designed using integrated multi-omics and biomarker data. |
| Goal | Improve general health and support weight management. | Optimize metabolic pathways and prevent or manage complex diseases. |
| Technology | Apps, wearable trackers, standard health assessments. | Next-generation sequencing, AI algorithms, advanced diagnostics. |
| Cost | Moderate, accessible for general population. | Higher, often requires specialized testing and interpretation. |
| Examples | Customized meal plans, calorie tracking, lifestyle coaching. | Gene-based diet optimization, personalized supplements, biomarker-driven strategies. |
Understanding Personalized Nutrition: A Tailored Approach
Personalized nutrition focuses on adapting dietary recommendations to individual characteristics such as age, lifestyle, and preferences, aiming to improve overall health outcomes. This approach utilizes data from self-reported behavior, medical history, and sometimes genetic information to create tailored nutritional plans. Understanding personalized nutrition emphasizes the importance of individual variability in metabolism and nutrient needs for effective dietary guidance.
What Is Precision Nutrition? Science-Driven Insights
Precision nutrition uses genetic, metabolic, and microbiome data to tailor dietary recommendations at an individual level, optimizing health outcomes through science-driven insights. This approach integrates biomarkers and lifestyle factors to design nutrition plans that address specific health risks and metabolic responses. By leveraging advanced technologies like genomic sequencing and metabolomics, precision nutrition offers a highly targeted strategy compared to broader personalized nutrition models.
Key Differences Between Personalized and Precision Nutrition
Personalized nutrition tailors dietary recommendations based on individual characteristics such as age, gender, lifestyle, and health status, focusing on practical adjustments that suit everyday needs. Precision nutrition uses advanced technologies like genomics, metabolomics, and microbiome analysis to create highly detailed, data-driven dietary plans targeting specific biological pathways. Key differences involve the depth of scientific data integration and the scale of customization, with precision nutrition offering a more granular approach rooted in molecular and genetic profiles.
Genetic Testing: The Foundation of Precision Nutrition
Genetic testing forms the cornerstone of precision nutrition by analyzing individual DNA variations to tailor dietary recommendations that optimize health outcomes. Unlike personalized nutrition, which often relies on generalized factors like age or lifestyle, precision nutrition integrates genetic insights to predict nutrient metabolism, disease risk, and response to dietary interventions. This approach enables the development of highly targeted nutrition plans that support disease prevention and personalized health management.
Lifestyle Factors in Personalized Nutrition
Personalized nutrition emphasizes tailoring dietary recommendations based on individual lifestyle factors such as physical activity, sleep patterns, and stress levels, which significantly influence nutritional needs. Unlike precision nutrition, which targets genetic and molecular data, personalized nutrition integrates behavioral and environmental variables to optimize health outcomes. Incorporating lifestyle factors ensures more practical and sustainable dietary interventions that align with personal habits and preferences.
Technology’s Role in Advancing Precision Nutrition
Advancements in technology have accelerated the development of precision nutrition by enabling detailed analysis of individual genetic, metabolic, and microbiome data, allowing tailored dietary recommendations beyond generalized guidelines. Cutting-edge tools such as AI-driven algorithms, wearable biosensors, and high-throughput sequencing provide real-time monitoring and adaptive nutrition plans, enhancing efficacy in disease prevention and management. This technological integration fosters a shift from personalized nutrition's broader customization to precision nutrition's data-intensive, scientifically grounded approach for optimal health outcomes.
Benefits of Personalized Nutrition Plans
Personalized nutrition plans leverage individual genetic, metabolic, and lifestyle data to optimize dietary recommendations, enhancing overall health outcomes. These plans improve nutrient absorption, reduce disease risk, and promote sustainable weight management by addressing unique personal needs. Tailoring nutrition in this way increases adherence and effectiveness compared to generalized dietary guidelines.
Precision Nutrition: Challenges and Limitations
Precision nutrition faces challenges such as the integration of complex multi-omics data, including genomics, metabolomics, and microbiomics, which requires advanced computational tools and expertise. Limitations arise from variability in individual responses to dietary interventions, influenced by environmental factors and lifestyle, complicating the development of universally effective personalized dietary recommendations. The need for large-scale, longitudinal studies to validate predictive biomarkers and ensure clinical applicability remains a significant hurdle in advancing precision nutrition.
Future Trends in Nutrition Personalization
Personalized nutrition tailors dietary recommendations based on individual preferences, lifestyle, and basic health metrics, while precision nutrition utilizes advanced data like genomics, metabolomics, and microbiome analysis for more targeted interventions. Future trends in nutrition personalization emphasize integrating artificial intelligence and big data analytics to refine dietary plans and improve health outcomes. Innovations in wearable technology and continuous biomarker monitoring will drive dynamic, real-time nutrition advice, enhancing the precision and adaptability of personalized diets.
Choosing the Right Approach: Personalized vs Precision Nutrition
Personalized nutrition tailors dietary recommendations based on individual preferences, lifestyle, and basic health metrics, enhancing adherence and long-term success. Precision nutrition uses genetic, metabolic, and microbiome data to create highly specific dietary plans targeting unique biological responses. Selecting the right approach depends on the depth of available data and the level of customization needed to optimize health outcomes effectively.
Personalized nutrition vs precision nutrition Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com