Leptin resistance impairs the ability of pets to regulate appetite and energy balance, often leading to obesity and related health issues. Ghrelin resistance disrupts hunger signals, causing abnormal feeding behaviors and metabolism problems in animals. Understanding the differences between leptin and ghrelin resistance is crucial for managing weight and promoting overall pet health.
Table of Comparison
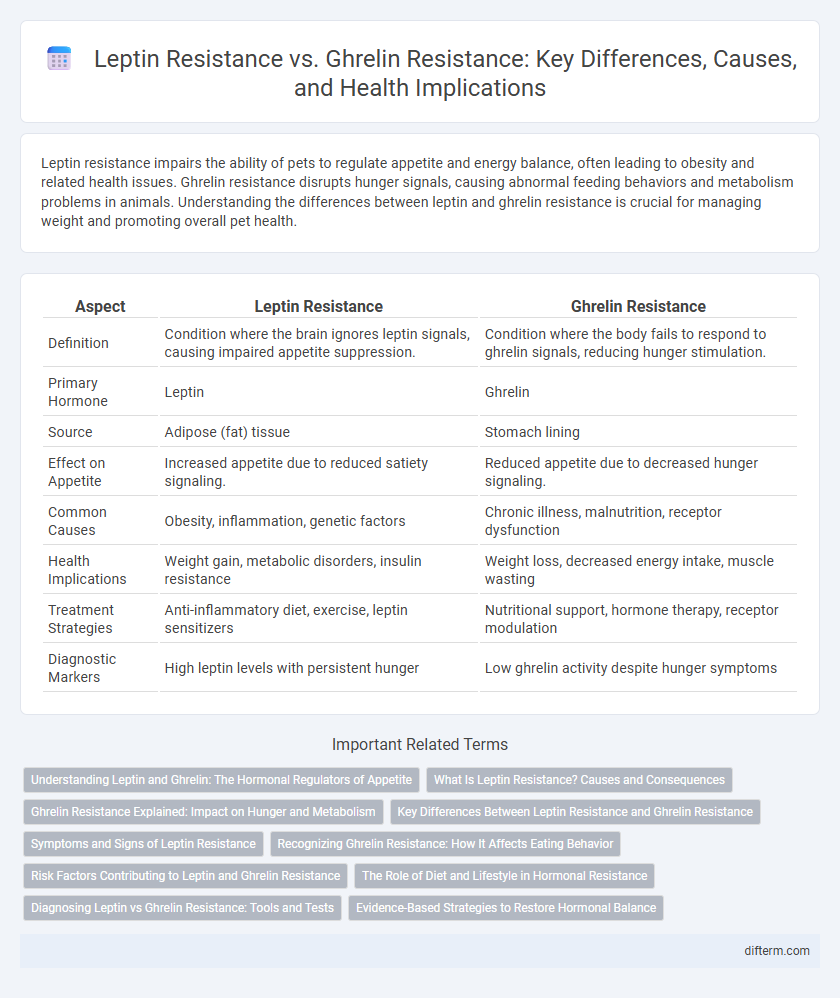
| Aspect | Leptin Resistance | Ghrelin Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Condition where the brain ignores leptin signals, causing impaired appetite suppression. | Condition where the body fails to respond to ghrelin signals, reducing hunger stimulation. |
| Primary Hormone | Leptin | Ghrelin |
| Source | Adipose (fat) tissue | Stomach lining |
| Effect on Appetite | Increased appetite due to reduced satiety signaling. | Reduced appetite due to decreased hunger signaling. |
| Common Causes | Obesity, inflammation, genetic factors | Chronic illness, malnutrition, receptor dysfunction |
| Health Implications | Weight gain, metabolic disorders, insulin resistance | Weight loss, decreased energy intake, muscle wasting |
| Treatment Strategies | Anti-inflammatory diet, exercise, leptin sensitizers | Nutritional support, hormone therapy, receptor modulation |
| Diagnostic Markers | High leptin levels with persistent hunger | Low ghrelin activity despite hunger symptoms |
Understanding Leptin and Ghrelin: The Hormonal Regulators of Appetite
Leptin and ghrelin are key hormonal regulators of appetite, where leptin signals satiety and energy sufficiency, while ghrelin stimulates hunger and food intake. Leptin resistance disrupts the brain's ability to recognize fullness, often leading to overeating and weight gain, whereas ghrelin resistance impairs hunger signaling, potentially causing reduced appetite and nutrient intake. Understanding the balance and dysfunction of these hormones is crucial for addressing obesity and metabolic disorders effectively.
What Is Leptin Resistance? Causes and Consequences
Leptin resistance occurs when the brain no longer responds effectively to the hormone leptin, which regulates hunger and energy balance. Causes include chronic inflammation, high-fat diets, and obesity, leading to impaired leptin signaling and disrupted appetite control. Consequences involve increased food intake, reduced energy expenditure, and higher risks of obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Ghrelin Resistance Explained: Impact on Hunger and Metabolism
Ghrelin resistance disrupts the body's natural ability to regulate hunger signals, leading to increased appetite and potential overeating. This impairment in ghrelin signaling affects metabolism by reducing energy expenditure and promoting fat storage. Understanding ghrelin resistance is crucial for developing targeted therapies to improve appetite control and metabolic function in obesity management.
Key Differences Between Leptin Resistance and Ghrelin Resistance
Leptin resistance and ghrelin resistance differ primarily in their roles in hunger regulation and energy balance; leptin resistance impairs the brain's ability to receive signals of satiety, leading to overeating, while ghrelin resistance involves diminished response to hunger signals, affecting appetite stimulation. Leptin resistance is commonly linked to obesity and chronic inflammation, whereas ghrelin resistance may be associated with malnutrition or metabolic disorders. Understanding these distinct hormonal dysfunctions is critical for developing targeted treatments for weight management and metabolic health.
Symptoms and Signs of Leptin Resistance
Leptin resistance often presents with symptoms such as persistent hunger despite adequate fat stores, difficulty losing weight, increased appetite, and fatigue, indicating disrupted energy balance and impaired satiety signaling. Common signs include elevated leptin levels in the blood and weight gain primarily around the abdomen. In contrast, ghrelin resistance typically involves reduced hunger signals leading to decreased appetite, but leptin resistance is more closely linked to obesity and metabolic syndrome due to its role in appetite regulation and energy homeostasis.
Recognizing Ghrelin Resistance: How It Affects Eating Behavior
Ghrelin resistance disrupts the brain's ability to respond to hunger signals, leading to impaired appetite regulation and increased food intake despite sufficient energy stores. This condition causes persistent feelings of hunger, contributing to overeating and weight gain. Recognizing ghrelin resistance involves observing abnormal eating patterns such as frequent snacking and an inability to feel satiated after meals.
Risk Factors Contributing to Leptin and Ghrelin Resistance
Obesity, chronic inflammation, and high sugar intake are primary risk factors contributing to leptin resistance, impairing the brain's ability to regulate appetite and energy balance. Ghrelin resistance, often linked to disrupted sleep patterns, stress, and metabolic disorders, diminishes hunger signaling, leading to dysfunctional eating behaviors. Both hormonal resistances exacerbate metabolic syndrome risk by altering insulin sensitivity and promoting weight gain.
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle in Hormonal Resistance
Leptin resistance and ghrelin resistance are significantly influenced by diet and lifestyle factors such as high intake of processed foods, excessive sugar consumption, and sedentary behavior, which disrupt hormonal signaling related to hunger and satiety. Chronic inflammation and insulin resistance, often caused by poor dietary choices and lack of exercise, exacerbate the dysfunction of leptin and ghrelin pathways, impairing appetite regulation and energy balance. Optimizing nutrition with whole, nutrient-dense foods and engaging in regular physical activity can improve hormonal sensitivity, reduce resistance, and support metabolic health.
Diagnosing Leptin vs Ghrelin Resistance: Tools and Tests
Diagnosing leptin resistance involves measuring serum leptin levels alongside evaluating symptoms of increased hunger and weight gain despite high leptin concentrations, often supported by leptin receptor sensitivity tests. Ghrelin resistance diagnosis includes assessing fasting and postprandial ghrelin levels through blood tests, with attention to altered appetite regulation and impaired satiety signaling. Advanced diagnostic tools such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and receptor gene expression analysis enhance accuracy in distinguishing between leptin and ghrelin resistance.
Evidence-Based Strategies to Restore Hormonal Balance
Leptin resistance disrupts the body's ability to regulate hunger and energy expenditure, often linked to obesity, while ghrelin resistance impairs appetite signaling, contributing to metabolic imbalance. Evidence-based strategies to restore hormonal balance include adopting a nutrient-dense diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, engaging in regular physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity, and prioritizing quality sleep to regulate hormone production. Interventions such as intermittent fasting and stress management techniques have shown promise in improving leptin and ghrelin sensitivity, promoting effective appetite control and weight management.
Leptin Resistance vs Ghrelin Resistance Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com