Holistic nutrition emphasizes the integration of whole foods, lifestyle factors, and mental well-being to promote overall health, addressing the root causes of ailments rather than just symptoms. Clinical nutrition focuses on medically tailored dietary plans designed to manage specific diseases or conditions through precise nutrient interventions. Both approaches contribute valuable perspectives to health management, with holistic nutrition fostering preventive care and clinical nutrition targeting therapeutic outcomes.
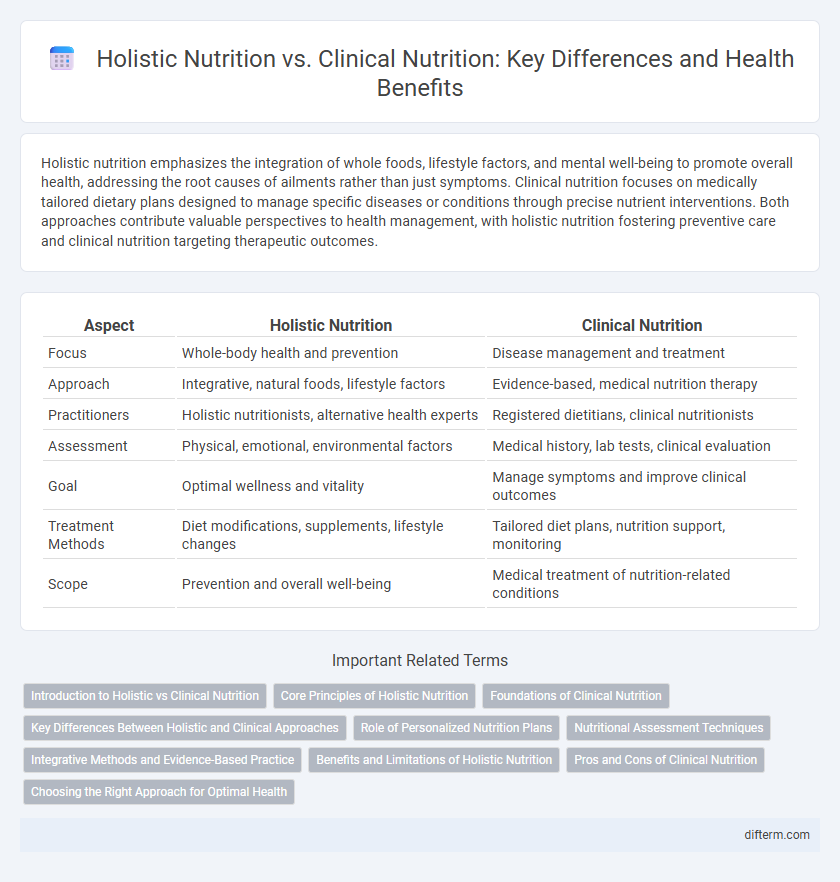
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Holistic Nutrition | Clinical Nutrition |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Whole-body health and prevention | Disease management and treatment |
| Approach | Integrative, natural foods, lifestyle factors | Evidence-based, medical nutrition therapy |
| Practitioners | Holistic nutritionists, alternative health experts | Registered dietitians, clinical nutritionists |
| Assessment | Physical, emotional, environmental factors | Medical history, lab tests, clinical evaluation |
| Goal | Optimal wellness and vitality | Manage symptoms and improve clinical outcomes |
| Treatment Methods | Diet modifications, supplements, lifestyle changes | Tailored diet plans, nutrition support, monitoring |
| Scope | Prevention and overall well-being | Medical treatment of nutrition-related conditions |
Introduction to Holistic vs Clinical Nutrition
Holistic nutrition emphasizes the integration of physical, emotional, and environmental factors to promote overall well-being through natural foods and lifestyle choices. Clinical nutrition focuses on diagnosing and managing specific medical conditions by tailoring nutrient intake based on scientific evidence and individualized patient needs. Both approaches aim to optimize health but differ in methodology, with holistic nutrition addressing prevention and comprehensive wellness, while clinical nutrition targets treatment and disease management.
Core Principles of Holistic Nutrition
Holistic nutrition emphasizes the integration of physical, emotional, and environmental factors to promote overall well-being, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and natural healing processes. It prioritizes personalized dietary approaches that consider lifestyle, mental health, and spiritual balance alongside nutrient intake. This contrasts with clinical nutrition, which centers on evidence-based interventions to manage specific medical conditions through precise dietary modifications.
Foundations of Clinical Nutrition
Clinical nutrition centers on diagnosing and treating nutritional deficiencies and chronic diseases through tailored dietary interventions based on biochemical, physiological, and clinical data. Foundations of clinical nutrition emphasize nutrient metabolism, assessment of nutritional status, and evidence-based therapeutic diets to support patient recovery and disease management. Unlike holistic nutrition, which considers overall lifestyle and wellness, clinical nutrition strictly integrates medical nutrition therapy within a healthcare setting.
Key Differences Between Holistic and Clinical Approaches
Holistic nutrition emphasizes whole-body wellness by integrating diet, lifestyle, and emotional health, focusing on natural, unprocessed foods and personalized plans. Clinical nutrition centers on medically guided dietary interventions to manage, treat, or prevent specific diseases using evidence-based protocols and nutrient therapy. The key differences lie in holistic nutrition's broader focus on overall well-being versus clinical nutrition's targeted approach to symptom management and disease treatment.
Role of Personalized Nutrition Plans
Holistic nutrition emphasizes individualized dietary approaches that consider physical, emotional, and environmental factors to promote overall well-being, integrating natural foods and lifestyle changes. Clinical nutrition focuses on evidence-based interventions targeting specific medical conditions, utilizing personalized nutrition plans tailored to patients' diagnoses, lab results, and treatment goals. Personalized nutrition plans in both fields optimize nutrient intake and metabolic health, enhancing prevention and management of chronic diseases through targeted, patient-centered strategies.
Nutritional Assessment Techniques
Holistic nutrition emphasizes comprehensive nutritional assessment techniques, including dietary history, lifestyle evaluation, and psychological factors to create personalized wellness plans. Clinical nutrition utilizes precise biochemical tests, such as blood panels and nutrient biomarkers, to diagnose deficiencies and medical conditions affecting nutritional status. Integrating both approaches enhances the accuracy of nutritional assessments and supports targeted interventions for optimal health outcomes.
Integrative Methods and Evidence-Based Practice
Holistic nutrition emphasizes integrative methods that combine dietary, lifestyle, and environmental factors to support overall well-being, utilizing personalized nutrition plans tailored to individual needs. Clinical nutrition relies heavily on evidence-based practice, incorporating rigorous scientific research and clinical trials to develop therapeutic diets targeting specific medical conditions. Both approaches aim to optimize health outcomes, with holistic nutrition focusing on prevention and balance, while clinical nutrition addresses disease management through precise nutrient interventions.
Benefits and Limitations of Holistic Nutrition
Holistic nutrition emphasizes whole foods and lifestyle changes, promoting overall well-being by addressing physical, emotional, and environmental factors, which can improve energy levels, digestion, and mental clarity. Its benefits include personalized dietary plans that support long-term health and prevention, yet limitations arise from a lack of standardized protocols and insufficient scientific validation for some alternative therapies. Holistic nutrition is best used as a complementary approach alongside evidence-based clinical nutrition that targets specific medical conditions with precise nutrient interventions.
Pros and Cons of Clinical Nutrition
Clinical nutrition focuses on the assessment and treatment of nutritional deficiencies and medical conditions using evidence-based dietary interventions, making it essential for managing chronic diseases like diabetes and kidney disorders. Pros include personalized treatment plans and improved patient outcomes through targeted nutrient therapy, while cons involve limited applicability in preventative care and potential dependence on medical supervision. This approach requires collaboration with healthcare professionals, emphasizing precision but sometimes overlooking broader lifestyle factors addressed by holistic nutrition.
Choosing the Right Approach for Optimal Health
Holistic nutrition emphasizes the integration of mind, body, and spirit by using whole foods, natural remedies, and lifestyle changes to promote overall wellness and prevent illness. Clinical nutrition focuses on evidence-based dietary interventions tailored to treat specific medical conditions and biochemical imbalances through precise nutrient management. Choosing the right approach depends on individual health goals, medical history, and the need for either comprehensive lifestyle support or targeted therapeutic treatment.
Holistic nutrition vs Clinical nutrition Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com