Casein protein digests slowly, providing a steady release of amino acids that supports muscle repair and growth over several hours, making it ideal for nighttime recovery in pets. Whey protein is rapidly absorbed, delivering quick muscle nourishment and energy, which benefits active or recovering pets requiring immediate protein intake. Choosing between casein and whey depends on your pet's activity level and specific nutritional needs for optimal health.
Table of Comparison
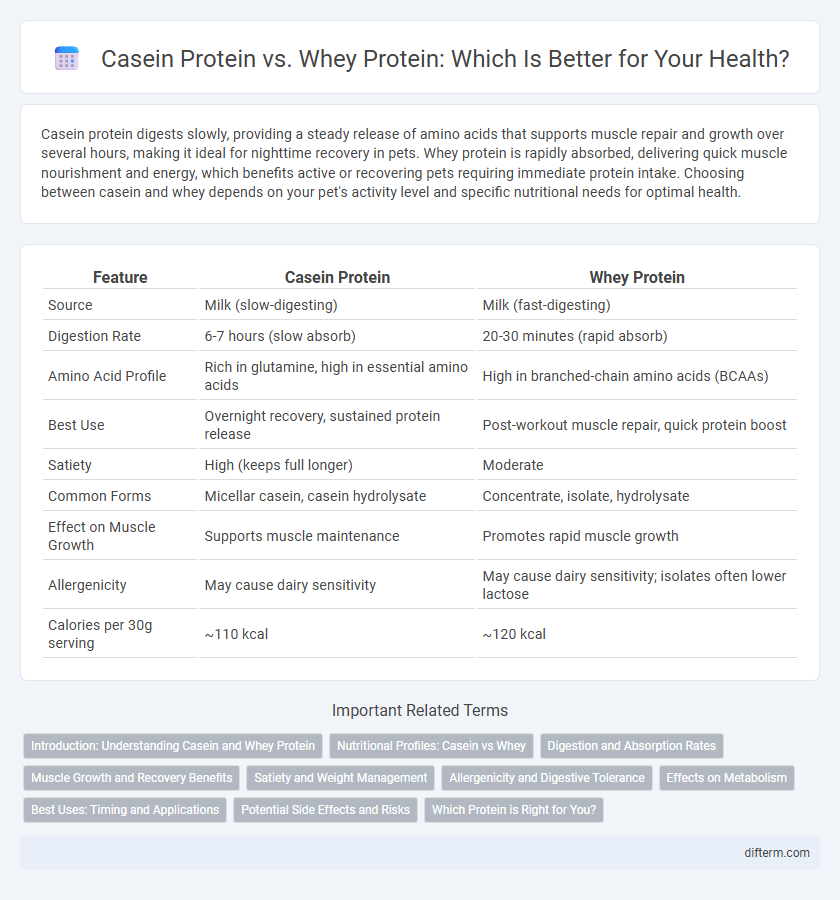
| Feature | Casein Protein | Whey Protein |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Milk (slow-digesting) | Milk (fast-digesting) |
| Digestion Rate | 6-7 hours (slow absorb) | 20-30 minutes (rapid absorb) |
| Amino Acid Profile | Rich in glutamine, high in essential amino acids | High in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) |
| Best Use | Overnight recovery, sustained protein release | Post-workout muscle repair, quick protein boost |
| Satiety | High (keeps full longer) | Moderate |
| Common Forms | Micellar casein, casein hydrolysate | Concentrate, isolate, hydrolysate |
| Effect on Muscle Growth | Supports muscle maintenance | Promotes rapid muscle growth |
| Allergenicity | May cause dairy sensitivity | May cause dairy sensitivity; isolates often lower lactose |
| Calories per 30g serving | ~110 kcal | ~120 kcal |
Introduction: Understanding Casein and Whey Protein
Casein protein, a slow-digesting dairy-derived protein, provides a sustained release of amino acids, making it ideal for muscle recovery during extended periods without food, such as overnight. Whey protein, known for its fast absorption and rich essential amino acid profile, is favored for rapid muscle repair and post-workout recovery. Understanding the distinct digestion rates and amino acid compositions of casein and whey proteins is crucial for optimizing muscle growth and overall health.
Nutritional Profiles: Casein vs Whey
Casein protein contains a slower digestion rate, providing a steady release of amino acids and is rich in glutamine, which supports muscle recovery and immune function. Whey protein features a fast absorption rate with a high concentration of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), especially leucine, promoting rapid muscle protein synthesis. Both proteins offer complete amino acid profiles, but whey typically contains more leucine per serving, making it ideal for post-workout recovery.
Digestion and Absorption Rates
Casein protein digests slowly, providing a steady release of amino acids over several hours, making it ideal for sustained muscle recovery and prolonged satiety. Whey protein absorbs rapidly, delivering a quick surge of amino acids that enhances muscle protein synthesis immediately after exercise. The distinct digestion and absorption rates of casein and whey proteins influence their optimal timing and functionality in nutrition and fitness regimes.
Muscle Growth and Recovery Benefits
Whey protein contains a high concentration of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) like leucine, which rapidly stimulates muscle protein synthesis, making it ideal for post-workout muscle growth and recovery. Casein protein digests slowly, providing a prolonged release of amino acids that helps reduce muscle breakdown and supports recovery during overnight fasting. Combining both proteins can optimize muscle repair by delivering immediate and sustained nutritional support.
Satiety and Weight Management
Casein protein promotes prolonged satiety due to its slow digestion rate, leading to reduced calorie intake and effective weight management. Whey protein digests rapidly, which can aid in muscle recovery but may offer shorter-lasting fullness compared to casein. Incorporating casein protein in meals or snacks supports appetite control and assists in maintaining a healthy weight over time.
Allergenicity and Digestive Tolerance
Casein protein often triggers allergic reactions due to its slower digestion and the presence of multiple allergenic components, making it less suitable for individuals with milk protein allergies. Whey protein is generally better tolerated in terms of digestibility and exhibits lower allergenicity, especially in its hydrolyzed form which reduces immune response. Digestive enzymes break down whey more rapidly, minimizing gastrointestinal discomfort compared to the prolonged digestion process of casein.
Effects on Metabolism
Casein protein digests slowly, providing a steady release of amino acids that supports prolonged muscle protein synthesis and stable blood sugar levels. Whey protein is rapidly absorbed, leading to a quick spike in amino acids that enhances immediate muscle repair and boosts metabolism through increased thermogenesis. Research indicates that combining both proteins can optimize metabolic rates and muscle recovery by balancing fast and slow digestion rates.
Best Uses: Timing and Applications
Casein protein is ideal for nighttime use due to its slow digestion rate, providing a steady release of amino acids for muscle repair during sleep. Whey protein, rapidly absorbed, suits post-workout recovery by quickly replenishing muscles and enhancing protein synthesis. For sustained muscle support throughout the day, casein helps maintain amino acid levels, while whey is preferred for immediate muscle recovery and energy boosts.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
Casein protein may cause digestive issues such as bloating or constipation due to slower digestion, while whey protein can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort including gas, cramps, or diarrhea, especially in individuals with lactose intolerance. Both proteins carry a risk of allergic reactions, particularly in those sensitive to dairy, and excessive intake may strain kidneys or contribute to nutrient imbalances. Monitoring dosage and consulting healthcare professionals are essential to minimize adverse effects and ensure safe supplementation.
Which Protein is Right for You?
Casein protein digests slowly, making it ideal for sustained muscle repair and overnight recovery, while whey protein is rapidly absorbed, perfect for post-workout muscle growth and immediate amino acid delivery. Individuals seeking prolonged protein release for muscle preservation during fasting periods should choose casein, whereas those needing quick recovery and muscle synthesis benefits after exercise benefit more from whey. Personal goals, digestion preferences, and timing of intake determine which protein suits your health and fitness regimen best.
Casein Protein vs Whey Protein Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com