Stimulants provide a rapid boost in energy and alertness by directly activating the central nervous system, often leading to temporary increased heart rate and heightened focus. Adaptogens help the body resist stressors by modulating hormonal responses and enhancing overall resilience without causing overstimulation or dependency. Choosing between stimulants and adaptogens depends on whether immediate energy or long-term balance and stress adaptation are the primary health goals.
Table of Comparison
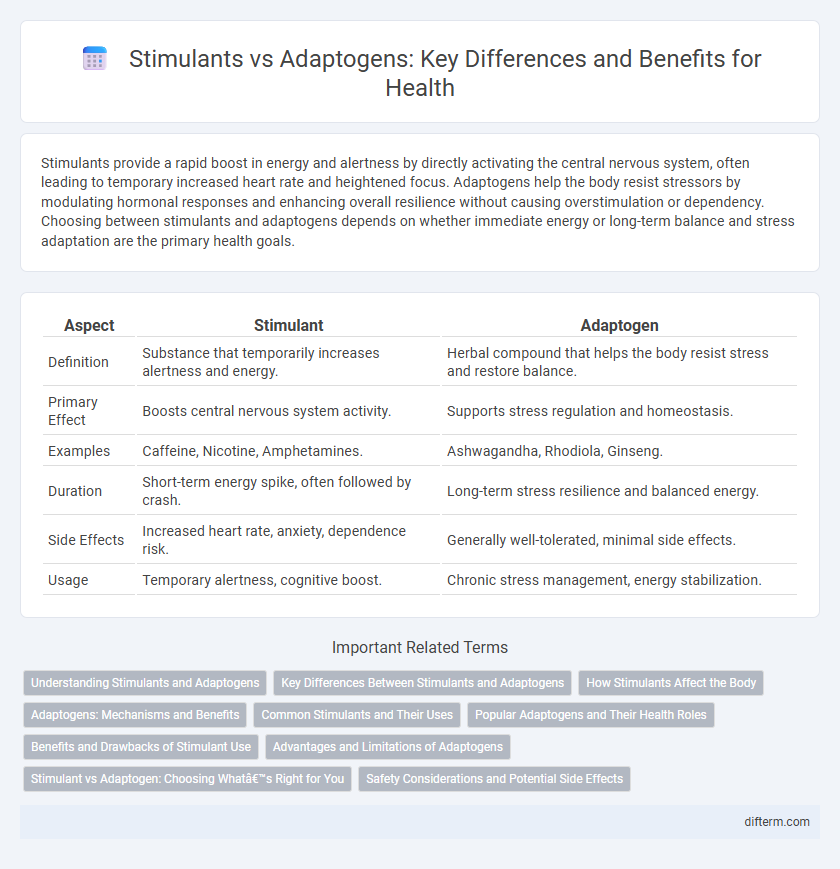
| Aspect | Stimulant | Adaptogen |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Substance that temporarily increases alertness and energy. | Herbal compound that helps the body resist stress and restore balance. |
| Primary Effect | Boosts central nervous system activity. | Supports stress regulation and homeostasis. |
| Examples | Caffeine, Nicotine, Amphetamines. | Ashwagandha, Rhodiola, Ginseng. |
| Duration | Short-term energy spike, often followed by crash. | Long-term stress resilience and balanced energy. |
| Side Effects | Increased heart rate, anxiety, dependence risk. | Generally well-tolerated, minimal side effects. |
| Usage | Temporary alertness, cognitive boost. | Chronic stress management, energy stabilization. |
Understanding Stimulants and Adaptogens
Stimulants are substances that increase central nervous system activity, leading to enhanced alertness, energy, and focus, often by boosting neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine. Adaptogens are natural compounds that help the body resist stressors by modulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and normalizing physiological functions. Understanding the distinct roles of stimulants and adaptogens is crucial for optimizing energy management and stress resilience in holistic health practices.
Key Differences Between Stimulants and Adaptogens
Stimulants increase energy and alertness by activating the central nervous system, often causing a rapid, short-term boost in focus and physical performance. Adaptogens support the body's ability to resist stress, promoting balance and sustained energy without the spikes or crashes associated with stimulants. Key differences include their mechanisms of action, with stimulants triggering immediate effects and adaptogens enhancing long-term resilience and homeostasis.
How Stimulants Affect the Body
Stimulants increase central nervous system activity, leading to heightened alertness, increased heart rate, and faster breathing. Common stimulants like caffeine and nicotine trigger adrenaline release, boosting energy and focus but may cause jitters, elevated blood pressure, and insomnia. Chronic use of stimulants can strain cardiovascular health and disrupt natural sleep patterns, making moderation crucial.
Adaptogens: Mechanisms and Benefits
Adaptogens modulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and balance cortisol levels, enhancing the body's resilience to physical, emotional, and environmental stressors. Key adaptogenic herbs like Rhodiola rosea, Ashwagandha, and Eleutherococcus senticosus improve energy metabolism, support immune function, and reduce fatigue without causing overstimulation. Unlike stimulants, adaptogens promote homeostasis and long-term vitality by normalizing stress responses and minimizing adrenal burnout.
Common Stimulants and Their Uses
Common stimulants such as caffeine, nicotine, and amphetamines are widely used to increase alertness, enhance focus, and boost energy levels by stimulating the central nervous system. These substances are often employed to improve cognitive performance, combat fatigue, and manage conditions like ADHD and narcolepsy. Unlike adaptogens that support resilience over time, stimulants provide immediate, short-term effects but can lead to dependency and tolerance with prolonged use.
Popular Adaptogens and Their Health Roles
Popular adaptogens such as Ashwagandha, Rhodiola Rosea, and Holy Basil support the body's resilience to stress by modulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and balancing cortisol levels. Unlike stimulants that provide temporary energy boosts through increased dopamine or norepinephrine release, adaptogens enhance long-term physiological stability and cognitive function without causing adrenal fatigue. Clinical studies highlight Ashwagandha's role in reducing anxiety, Rhodiola's ability to improve mental performance under stress, and Holy Basil's anti-inflammatory and immune-enhancing properties.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Stimulant Use
Stimulants like caffeine and amphetamines boost energy, alertness, and focus by increasing central nervous system activity, but their drawbacks include potential dependency, tolerance development, and heightened anxiety or cardiovascular strain. Adaptogens such as ashwagandha and rhodiola support the body's resilience to stress without causing the overstimulation or crash associated with stimulants. While stimulants offer immediate performance enhancement, their long-term use may impair sleep quality and induce withdrawal symptoms, unlike adaptogens which promote balance and gradual health improvement.
Advantages and Limitations of Adaptogens
Adaptogens offer a natural way to enhance the body's resilience to stress by balancing hormonal responses and improving energy levels without causing dependence or tolerance, unlike stimulants. They support long-term health by modulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and reducing fatigue, but effects may take weeks to manifest and vary among individuals. Limitations include potential interactions with medications and less immediate impact compared to stimulants, requiring consistent use for optimal benefits.
Stimulant vs Adaptogen: Choosing What’s Right for You
Stimulants, such as caffeine and amphetamines, increase energy and alertness by directly activating the central nervous system, often leading to rapid but short-lived effects and potential side effects like jitteriness or dependency. Adaptogens, including ashwagandha, rhodiola, and ginseng, support the body's ability to adapt to stress by regulating hormonal balance and enhancing resilience without causing overstimulation or crashes. Choosing between stimulants and adaptogens depends on whether immediate, heightened energy or long-term stress adaptation aligns better with your health goals and lifestyle.
Safety Considerations and Potential Side Effects
Stimulants like caffeine and amphetamines can cause increased heart rate, anxiety, and insomnia, posing risks for individuals with cardiovascular conditions or sensitivity to stimulants. Adaptogens such as ashwagandha, rhodiola, and ginseng are generally safer for long-term use, though they may lead to mild side effects like gastrointestinal upset or interactions with medications like blood thinners and immunosuppressants. Evaluating personal health conditions and consulting healthcare providers is crucial before incorporating either stimulants or adaptogens into a wellness regimen.
Stimulant vs Adaptogen Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com