Bacterial infections result from harmful bacteria multiplying in the body and can often be treated effectively with antibiotics. Viral infections are caused by viruses invading cells, requiring antiviral medications or supportive care as antibiotics are ineffective. Accurate diagnosis is essential to determine the appropriate treatment and prevent complications.
Table of Comparison
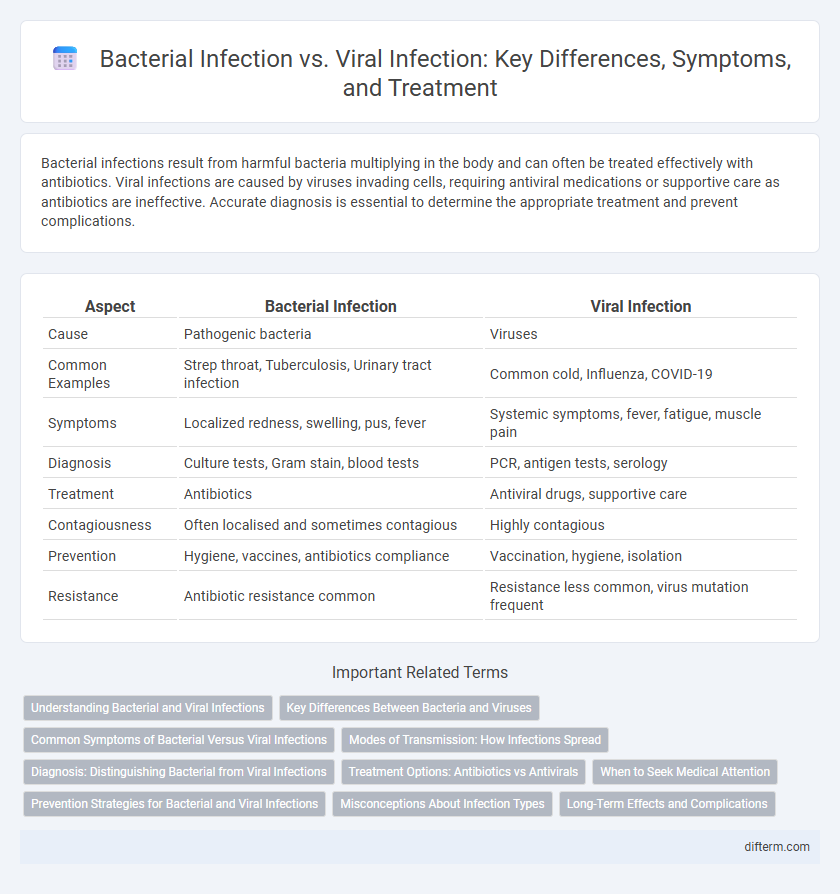
| Aspect | Bacterial Infection | Viral Infection |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Pathogenic bacteria | Viruses |
| Common Examples | Strep throat, Tuberculosis, Urinary tract infection | Common cold, Influenza, COVID-19 |
| Symptoms | Localized redness, swelling, pus, fever | Systemic symptoms, fever, fatigue, muscle pain |
| Diagnosis | Culture tests, Gram stain, blood tests | PCR, antigen tests, serology |
| Treatment | Antibiotics | Antiviral drugs, supportive care |
| Contagiousness | Often localised and sometimes contagious | Highly contagious |
| Prevention | Hygiene, vaccines, antibiotics compliance | Vaccination, hygiene, isolation |
| Resistance | Antibiotic resistance common | Resistance less common, virus mutation frequent |
Understanding Bacterial and Viral Infections
Bacterial infections are caused by single-celled microorganisms that can be treated with antibiotics, while viral infections result from viruses that require antiviral medications or supportive care for recovery. Both infections trigger immune responses but differ in replication methods, with bacteria capable of independent reproduction and viruses needing host cells. Accurate diagnosis through laboratory tests is essential for effective treatment and prevention of complications.
Key Differences Between Bacteria and Viruses
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that can thrive independently and often respond to antibiotics, whereas viruses require host cells to replicate and are unaffected by antibiotics. Bacterial infections typically cause localized symptoms and can be treated with targeted antibacterial medications, while viral infections often lead to systemic symptoms and are managed with antiviral drugs or supportive care. Understanding these key differences is critical for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment strategies in infectious diseases.
Common Symptoms of Bacterial Versus Viral Infections
Common symptoms of bacterial infections include localized redness, swelling, warmth, and pus formation, often accompanied by fever and fatigue. Viral infections typically manifest with systemic symptoms such as body aches, cough, congestion, and sore throat, along with fever and fatigue. Differentiating these symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment, as bacterial infections often require antibiotics while viral infections do not.
Modes of Transmission: How Infections Spread
Bacterial infections commonly spread through direct contact with infected wounds, contaminated surfaces, or respiratory droplets from coughing and sneezing. Viral infections transmit primarily via airborne particles, bodily fluids, and surface contact, with some viruses also spreading through vector-borne mechanisms like mosquito bites. Understanding these transmission modes is crucial for implementing effective hygiene and prevention strategies to reduce infection rates.
Diagnosis: Distinguishing Bacterial from Viral Infections
Accurate diagnosis distinguishing bacterial from viral infections relies on specific clinical tests such as complete blood counts, C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, and procalcitonin assays, which help identify infection type based on immune response markers. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and cultures remain essential for detecting viral genetic material or bacterial pathogens directly, enabling targeted treatment decisions. Early and precise differentiation prevents unnecessary antibiotic use and guides appropriate antiviral or antibiotic therapy, improving patient outcomes and combating antimicrobial resistance.
Treatment Options: Antibiotics vs Antivirals
Bacterial infections are primarily treated with antibiotics, which target and eliminate specific bacteria by disrupting their cell walls or protein synthesis, while antiviral medications inhibit the replication of viruses to reduce severity and duration. Antibiotics are ineffective against viral infections and their misuse can lead to antibiotic resistance, emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis. Effective viral treatment often includes antiviral drugs like oseltamivir for influenza or antiretrovirals for HIV, alongside supportive care to manage symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention promptly for bacterial infections presenting with high fever, persistent pain, swelling, or localized redness, as these symptoms often require antibiotics for effective treatment. Viral infections typically resolve on their own, but immediate care is essential if symptoms worsen, breathing difficulties occur, or dehydration develops. Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent complications and ensure appropriate management, distinguishing between bacterial and viral causes accurately.
Prevention Strategies for Bacterial and Viral Infections
Effective prevention strategies for bacterial infections include proper hand hygiene, timely vaccination, safe food handling, and thorough wound care to reduce pathogen exposure. For viral infections, measures such as regular hand washing, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, using masks in high-risk settings, and getting recommended vaccines are critical in limiting transmission. Maintaining overall immune health through balanced nutrition and sufficient rest further supports resistance against both bacterial and viral pathogens.
Misconceptions About Infection Types
Bacterial infections are often mistakenly treated with antibiotics, which are ineffective against viral infections like the flu or common cold. Many people confuse symptoms, believing that all infections cause fever and fatigue, but viral infections often present with systemic symptoms while bacterial infections may cause localized inflammation. Understanding these differences is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Long-Term Effects and Complications
Bacterial infections often lead to localized tissue damage and can cause chronic conditions such as osteomyelitis or endocarditis if untreated. Viral infections may trigger long-term complications like post-viral fatigue syndrome, chronic inflammation, or increased risk of autoimmune diseases. Understanding the distinct immune responses and treatment challenges helps mitigate lasting health impacts from both bacterial and viral pathogens.
Bacterial Infection vs Viral Infection Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com