Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation and support heart and brain health, while excessive omega-6 intake can promote inflammation and increase the risk of chronic diseases. Balancing omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the diet is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing inflammation-related conditions. Sources rich in omega-3 include fatty fish and flaxseeds, whereas omega-6 is commonly found in vegetable oils and processed foods.
Table of Comparison
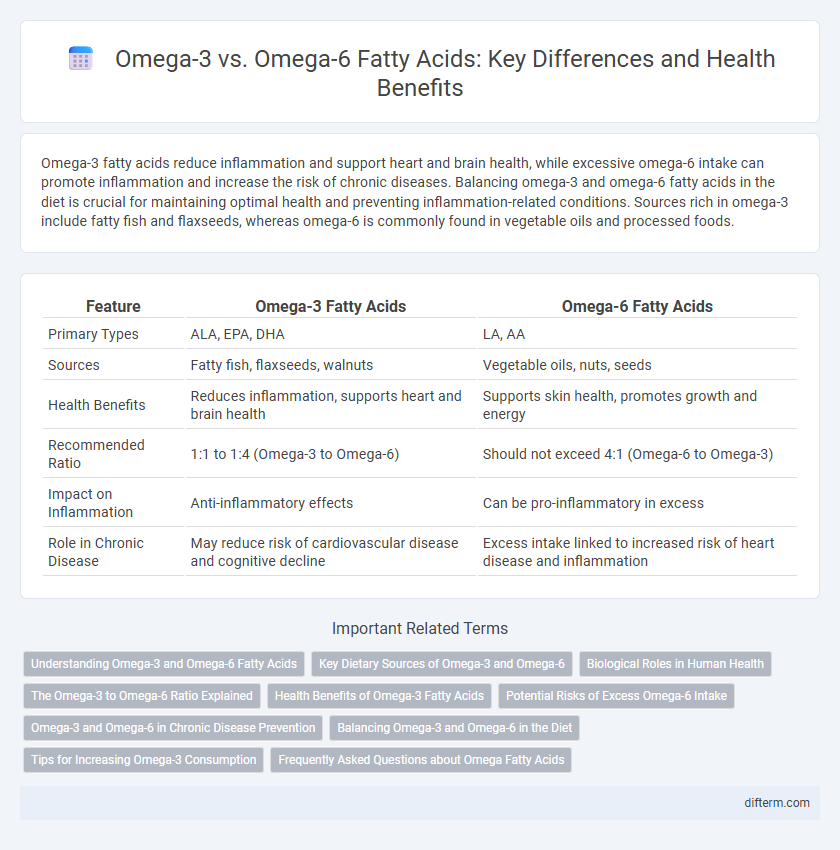
| Feature | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Omega-6 Fatty Acids |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Types | ALA, EPA, DHA | LA, AA |
| Sources | Fatty fish, flaxseeds, walnuts | Vegetable oils, nuts, seeds |
| Health Benefits | Reduces inflammation, supports heart and brain health | Supports skin health, promotes growth and energy |
| Recommended Ratio | 1:1 to 1:4 (Omega-3 to Omega-6) | Should not exceed 4:1 (Omega-6 to Omega-3) |
| Impact on Inflammation | Anti-inflammatory effects | Can be pro-inflammatory in excess |
| Role in Chronic Disease | May reduce risk of cardiovascular disease and cognitive decline | Excess intake linked to increased risk of heart disease and inflammation |
Understanding Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids are essential polyunsaturated fats crucial for maintaining cell membrane integrity and supporting brain function. Omega-3s, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, possess anti-inflammatory properties that promote cardiovascular health and cognitive development. Omega-6s, abundant in vegetable oils and processed foods, play a role in energy production but require balanced intake with Omega-3s to prevent chronic inflammation and related health issues.
Key Dietary Sources of Omega-3 and Omega-6
Omega-3 fatty acids are primarily found in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Omega-6 fatty acids are abundant in vegetable oils like corn oil, soybean oil, and sunflower oil, along with nuts and seeds. Balancing the intake of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids is crucial for reducing inflammation and promoting heart health.
Biological Roles in Human Health
Omega-3 fatty acids, such as EPA and DHA, are crucial for reducing inflammation, supporting brain function, and promoting cardiovascular health. In contrast, omega-6 fatty acids, primarily linoleic acid, play essential roles in cell membrane structure and immune response but can contribute to pro-inflammatory states when consumed in excess. Maintaining a balanced ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids is vital for optimizing biological processes and preventing chronic diseases.
The Omega-3 to Omega-6 Ratio Explained
The Omega-3 to Omega-6 ratio is crucial for maintaining balanced inflammatory responses and overall cardiovascular health. Modern diets often contain an excess of Omega-6 fatty acids, with ratios exceeding the recommended 1:1 to 1:4, which can promote inflammation and increase the risk of chronic diseases. Optimizing this ratio by increasing Omega-3 intake from sources like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts supports cellular function and reduces the prevalence of inflammatory conditions.
Health Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, primarily found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, play a crucial role in reducing inflammation and supporting cardiovascular health by lowering triglyceride levels and blood pressure. These essential fats contribute to brain function, improving cognitive performance and potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's. In contrast to omega-6 fatty acids, which are more prevalent in processed foods and can promote inflammation if consumed excessively, omega-3s offer a balanced anti-inflammatory effect that supports overall health and immune function.
Potential Risks of Excess Omega-6 Intake
Excessive intake of omega-6 fatty acids can disrupt the balance with omega-3s, promoting inflammation linked to cardiovascular diseases, arthritis, and other chronic conditions. High omega-6 consumption is associated with increased production of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids, potentially exacerbating inflammatory responses and contributing to immune system dysregulation. Maintaining an optimal omega-6 to omega-3 ratio is crucial for reducing risks related to chronic inflammation and supporting overall cardiovascular and metabolic health.
Omega-3 and Omega-6 in Chronic Disease Prevention
Omega-3 fatty acids, primarily found in fish oil and flaxseeds, play a crucial role in reducing inflammation and lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and arthritis. Excessive intake of Omega-6 fatty acids, abundant in vegetable oils, can promote inflammatory pathways that exacerbate conditions like obesity and type 2 diabetes. Balancing the ratio of Omega-3 to Omega-6 fatty acids is essential for optimizing immune function and preventing chronic disease progression.
Balancing Omega-3 and Omega-6 in the Diet
Balancing omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids is crucial for maintaining optimal health, as excessive omega-6 intake can promote inflammation while adequate omega-3 supports anti-inflammatory processes. The ideal dietary ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 is generally recommended to be around 4:1 or lower, but modern diets often have ratios as high as 15:1 or more, leading to increased risk of chronic diseases. Incorporating sources rich in EPA and DHA omega-3s, such as fatty fish, alongside reducing processed vegetable oils high in omega-6, can help restore a healthier fatty acid balance.
Tips for Increasing Omega-3 Consumption
Increasing omega-3 fatty acid intake can be achieved by regularly consuming fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, which are rich sources of EPA and DHA. Incorporating plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts into daily meals boosts ALA levels, the plant-derived omega-3. Choosing omega-3 fortified foods and considering high-quality supplements can also support achieving the ideal omega-3 to omega-6 ratio for cardiovascular and cognitive health.
Frequently Asked Questions about Omega Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, primarily found in fish oils and flaxseeds, are essential for reducing inflammation and supporting heart and brain health, while omega-6 fatty acids, abundant in vegetable oils and processed foods, play a crucial role in skin health and metabolism but can promote inflammation when consumed excessively. The ideal omega-6 to omega-3 ratio is typically recommended to be around 4:1 or lower to maintain optimal health and reduce chronic disease risk. Common questions often address the best dietary sources, the impact of imbalanced intake, recommended daily amounts, and how to effectively increase omega-3 consumption while moderating omega-6 intake.
Omega-3 vs Omega-6 Fatty Acids Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com