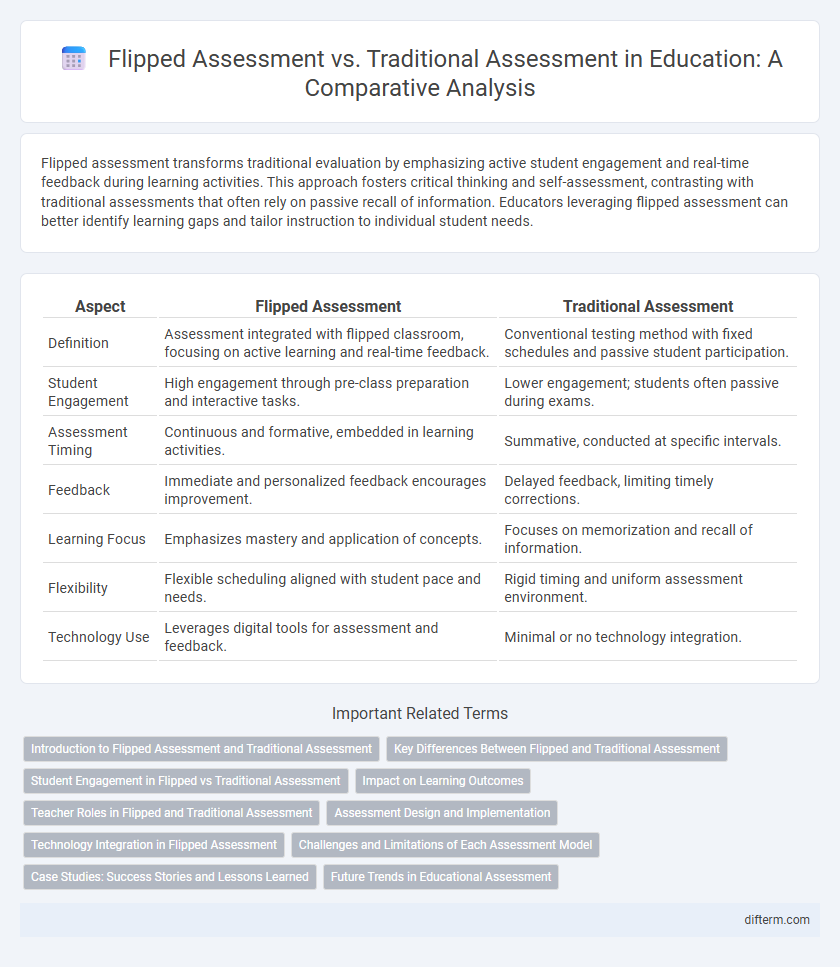
Flipped assessment transforms traditional evaluation by emphasizing active student engagement and real-time feedback during learning activities. This approach fosters critical thinking and self-assessment, contrasting with traditional assessments that often rely on passive recall of information. Educators leveraging flipped assessment can better identify learning gaps and tailor instruction to individual student needs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Flipped Assessment | Traditional Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessment integrated with flipped classroom, focusing on active learning and real-time feedback. | Conventional testing method with fixed schedules and passive student participation. |
| Student Engagement | High engagement through pre-class preparation and interactive tasks. | Lower engagement; students often passive during exams. |
| Assessment Timing | Continuous and formative, embedded in learning activities. | Summative, conducted at specific intervals. |
| Feedback | Immediate and personalized feedback encourages improvement. | Delayed feedback, limiting timely corrections. |
| Learning Focus | Emphasizes mastery and application of concepts. | Focuses on memorization and recall of information. |
| Flexibility | Flexible scheduling aligned with student pace and needs. | Rigid timing and uniform assessment environment. |
| Technology Use | Leverages digital tools for assessment and feedback. | Minimal or no technology integration. |
Introduction to Flipped Assessment and Traditional Assessment
Flipped assessment transforms traditional evaluation by shifting the focus from in-class testing to continuous, technology-driven feedback and self-paced learning outside the classroom. Traditional assessment relies heavily on timed, in-person examinations that primarily measure memorization and recall under supervised conditions. Incorporating flipped assessment methods enhances student engagement, promotes deeper understanding, and allows educators to tailor instruction based on real-time performance data.
Key Differences Between Flipped and Traditional Assessment
Flipped assessment emphasizes student-centered evaluation by integrating pre-class preparation with in-class active feedback, contrasting with traditional assessment's focus on summative exams conducted after instruction. Flipped models promote continuous formative assessment through quizzes and peer reviews, enhancing real-time learning adjustments, while traditional assessments rely heavily on final tests to measure comprehension. The key differences lie in timing, learner engagement, and the balance between formative and summative evaluation methods in educational settings.
Student Engagement in Flipped vs Traditional Assessment
Flipped assessment methods significantly enhance student engagement by promoting active learning through pre-class preparation and in-class interactive activities, contrasting with traditional assessments that often focus on passive knowledge recall. Research shows that students in flipped classrooms demonstrate higher motivation and participation rates, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills. The increased engagement in flipped assessments leads to improved academic performance and greater retention of material compared to traditional, exam-centered evaluation techniques.
Impact on Learning Outcomes
Flipped assessment enhances learning outcomes by promoting active engagement, critical thinking, and immediate feedback, leading to improved retention and higher-order cognitive skills. Traditional assessment often emphasizes rote memorization and summative evaluation, which may not fully capture students' understanding or promote deep learning. Research indicates that flipped assessments align better with personalized learning, resulting in increased student motivation and academic performance.
Teacher Roles in Flipped and Traditional Assessment
Teacher roles in flipped assessment emphasize facilitation and personalized feedback, enabling students to engage actively with content before class and demonstrate understanding during interactive sessions. In traditional assessment, teachers primarily serve as evaluators who deliver instruction first, then test knowledge through standardized exams or quizzes. This shift from passive knowledge transfer to active learning fosters deeper student involvement and continuous formative assessment.
Assessment Design and Implementation
Flipped assessment shifts the focus from passive evaluation to active learning by incorporating pre-class preparation and in-class application, enhancing student engagement and deeper understanding. Traditional assessment often emphasizes summative evaluation through standardized tests, which may limit opportunities for formative feedback and iterative improvement. Effective assessment design in flipped classrooms integrates diverse, authentic tasks aligned with learning outcomes, allowing real-time adjustments to instruction based on student performance.
Technology Integration in Flipped Assessment
Flipped assessment leverages technology integration to enhance student engagement and provide immediate feedback through digital platforms, unlike traditional assessments that rely heavily on in-person, paper-based testing. Tools such as learning management systems (LMS), online quizzes, and interactive simulations facilitate personalized learning pathways and allow educators to track student progress in real time. This technological shift promotes deeper understanding and adaptability in assessment practices by aligning evaluation methods with modern educational technologies.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Assessment Model
Flipped assessment poses challenges such as the need for reliable technology and student self-motivation, which can create inequities in learning outcomes. Traditional assessment often faces limitations in accurately measuring critical thinking and application skills due to its emphasis on rote memorization and standardized testing formats. Both models require careful alignment with learning objectives and ongoing instructor training to maximize effectiveness and fairness.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Lessons Learned
Case studies reveal that flipped assessments, where students engage with materials before class, significantly improve critical thinking and retention compared to traditional assessments that rely on in-class exams. Success stories highlight increased student engagement and personalized feedback as key benefits of flipped assessment methodologies. Lessons learned emphasize the necessity of clear instructional design and ongoing teacher training to maximize the effectiveness of flipped assessments in diverse educational settings.
Future Trends in Educational Assessment
Future trends in educational assessment emphasize the growing adoption of flipped assessment models, which prioritize student-centered evaluation through pre-class prep and in-class application activities. Data analytics and adaptive technologies enable personalized feedback and real-time performance tracking, surpassing limitations of traditional assessments that often rely on standardized testing and passive knowledge recall. Integration of AI-driven tools and formative assessment strategies promotes deeper learning and skill mastery, aligning evaluation methods with 21st-century educational goals.
flipped assessment vs traditional assessment Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com