Project-based learning immerses students in completing real-world tasks, fostering collaboration and creativity through extended projects. Problem-based learning centers on diagnosing and solving specific challenges, encouraging critical thinking and self-directed inquiry. Both approaches enhance practical skills, but project-based learning emphasizes creating a tangible outcome, while problem-based learning prioritizes analytical problem-solving processes.
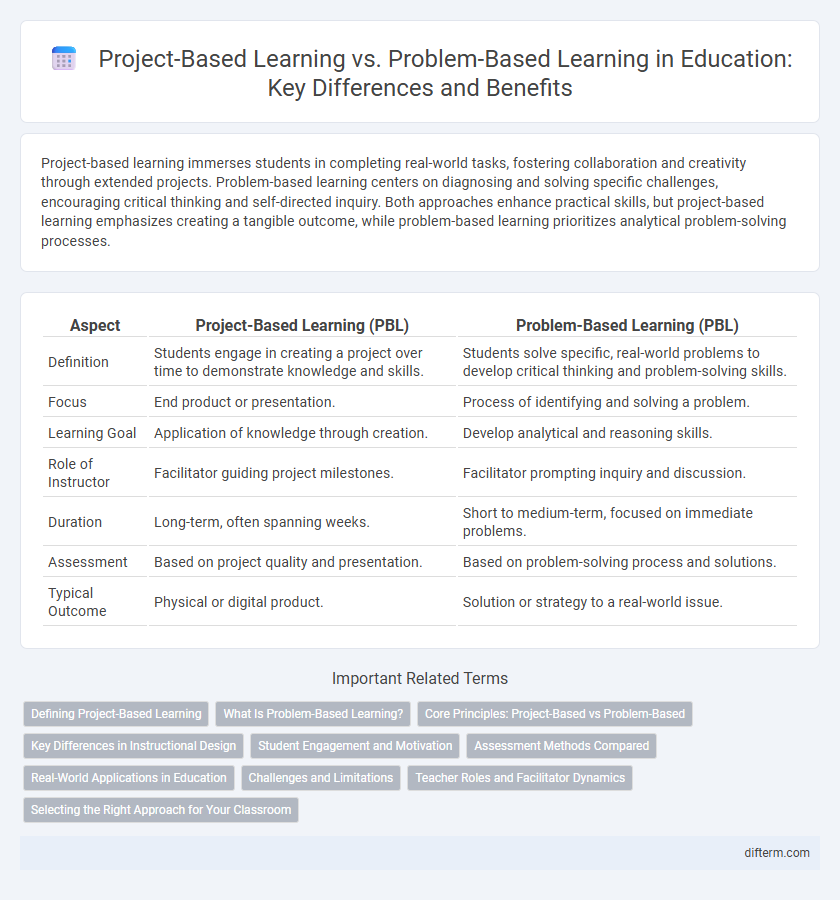
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Problem-Based Learning (PBL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students engage in creating a project over time to demonstrate knowledge and skills. | Students solve specific, real-world problems to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. |
| Focus | End product or presentation. | Process of identifying and solving a problem. |
| Learning Goal | Application of knowledge through creation. | Develop analytical and reasoning skills. |
| Role of Instructor | Facilitator guiding project milestones. | Facilitator prompting inquiry and discussion. |
| Duration | Long-term, often spanning weeks. | Short to medium-term, focused on immediate problems. |
| Assessment | Based on project quality and presentation. | Based on problem-solving process and solutions. |
| Typical Outcome | Physical or digital product. | Solution or strategy to a real-world issue. |
Defining Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional approach where students actively explore real-world challenges by creating tangible projects over an extended period, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills. This method emphasizes student-driven inquiry, collaboration, and practical application of knowledge across various subjects. Unlike Problem-Based Learning, which centers on solving specific problems, PBL integrates broader objectives through comprehensive project completion that culminates in a final product or presentation.
What Is Problem-Based Learning?
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional approach where students learn by actively solving real-world problems, fostering critical thinking and collaborative skills. It emphasizes student-centered inquiry, where learners identify what they need to know to address complex issues, integrating knowledge across disciplines. This method contrasts with Project-Based Learning by focusing specifically on problem resolution rather than project creation.
Core Principles: Project-Based vs Problem-Based
Project-based learning centers on completing complex, real-world projects that integrate multiple skills and disciplines to produce tangible outcomes. Problem-based learning emphasizes critical thinking and collaboration by tackling specific, open-ended problems without predetermined solutions, fostering self-directed inquiry. Both methodologies prioritize active engagement, but project-based learning focuses on the creation process while problem-based learning prioritizes problem-solving strategies.
Key Differences in Instructional Design
Project-based learning emphasizes extended tasks where students create a final product, integrating multiple skills and knowledge areas, while problem-based learning centers on solving specific, often real-world problems through inquiry and critical thinking. Instructional design for project-based learning involves scaffolding complex projects with milestones and assessments that promote collaboration and creativity. In contrast, problem-based learning requires designing scenarios and facilitating guided inquiry that encourages exploration and application of concepts to find viable solutions.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Project-based learning enhances student engagement by involving learners in hands-on, real-world tasks that foster creativity and collaboration, leading to intrinsic motivation. Problem-based learning motivates students through challenging scenarios that develop critical thinking and self-directed inquiry, promoting deeper understanding. Both approaches increase student motivation by making learning relevant and interactive, but project-based learning often results in higher sustained engagement due to its long-term, goal-oriented nature.
Assessment Methods Compared
Project-based learning assessment focuses on evaluating the overall project outcomes, including presentations, prototypes, and collaborative efforts, emphasizing real-world application and creativity. Problem-based learning assessment centers on critical thinking, problem-solving processes, and knowledge application through formative assessments like reflection journals and peer evaluations. Both methods utilize rubrics, but project-based learning often requires summative assessments tied to final deliverables, while problem-based learning prioritizes continuous assessment during the problem-solving journey.
Real-World Applications in Education
Project-based learning immerses students in extended tasks that simulate real-world challenges, promoting collaboration and practical skill development. Problem-based learning centers on tackling specific, complex problems, enhancing critical thinking and analytical skills through real-life contexts. Both approaches integrate real-world applications, but project-based learning offers broader, integrative experiences while problem-based learning targets focused problem-solving abilities.
Challenges and Limitations
Project-based learning often faces challenges related to time management and resource availability, which can hinder effective implementation and student engagement. Problem-based learning may encounter limitations due to its reliance on well-structured problems, potentially causing difficulties for learners lacking prior knowledge or critical thinking skills. Both approaches require significant instructor facilitation and assessment complexity, impacting scalability and consistent educational outcomes.
Teacher Roles and Facilitator Dynamics
Project-based learning positions teachers as designers and guides who scaffold student exploration through real-world projects, fostering autonomy and collaboration. In problem-based learning, educators act primarily as facilitators who prompt critical thinking and inquiry by presenting complex, open-ended problems without predetermined solutions. Both approaches emphasize dynamic teacher roles that support learner-centered environments, but project-based learning requires more structured guidance, while problem-based learning demands adaptive facilitation to encourage deep cognitive engagement.
Selecting the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Project-based learning emphasizes hands-on creation and extended inquiry, fostering collaboration and real-world application, making it ideal for classrooms aiming to develop critical thinking and teamwork skills. Problem-based learning centers on solving complex, open-ended problems, promoting self-directed learning and analytical reasoning, which suits environments focused on enhancing problem-solving abilities and knowledge retention. Educators should assess student needs, curriculum goals, and available resources to determine whether project-based or problem-based learning aligns best with their instructional objectives.
project-based learning vs problem-based learning Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com