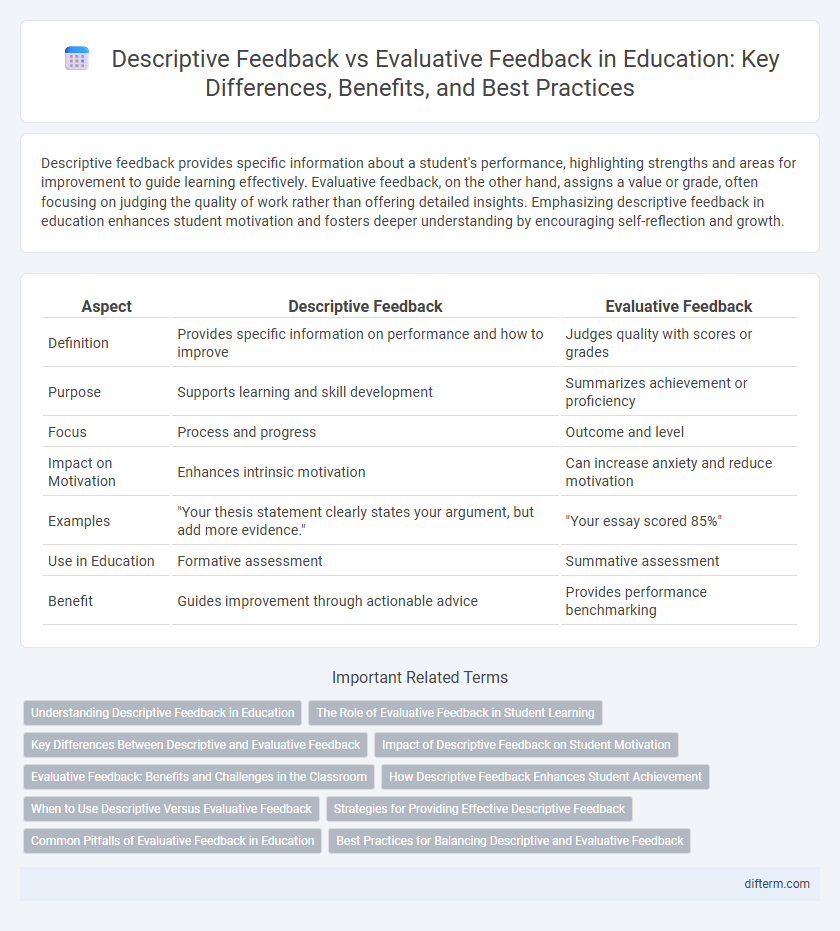
Descriptive feedback provides specific information about a student's performance, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement to guide learning effectively. Evaluative feedback, on the other hand, assigns a value or grade, often focusing on judging the quality of work rather than offering detailed insights. Emphasizing descriptive feedback in education enhances student motivation and fosters deeper understanding by encouraging self-reflection and growth.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Descriptive Feedback | Evaluative Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Provides specific information on performance and how to improve | Judges quality with scores or grades |
| Purpose | Supports learning and skill development | Summarizes achievement or proficiency |
| Focus | Process and progress | Outcome and level |
| Impact on Motivation | Enhances intrinsic motivation | Can increase anxiety and reduce motivation |
| Examples | "Your thesis statement clearly states your argument, but add more evidence." | "Your essay scored 85%" |
| Use in Education | Formative assessment | Summative assessment |
| Benefit | Guides improvement through actionable advice | Provides performance benchmarking |
Understanding Descriptive Feedback in Education
Descriptive feedback in education provides specific, detailed information about a student's performance, focusing on strengths and areas for improvement to guide learning processes effectively. It promotes deeper understanding and skill development by highlighting what was done well and what needs refinement, rather than simply assigning a grade or score. This type of feedback encourages active engagement and fosters a growth mindset, enhancing overall academic achievement.
The Role of Evaluative Feedback in Student Learning
Evaluative feedback plays a critical role in student learning by providing clear judgments about performance relative to established criteria, helping learners understand their current standing and what is required to improve. This type of feedback often includes grades, scores, or ratings that quantify achievement and motivate students to adjust their efforts. Research highlights that when combined with specific, actionable guidance, evaluative feedback enhances goal-setting and self-regulation in the learning process.
Key Differences Between Descriptive and Evaluative Feedback
Descriptive feedback provides specific, detailed information focused on students' performance and areas for improvement, enhancing learning by guiding next steps. Evaluative feedback assigns a judgment or grade, summarizing overall achievement without detailed guidance, which can limit opportunities for growth. The key difference lies in descriptive feedback's emphasis on constructive, actionable insights versus evaluative feedback's focus on assessment and ranking.
Impact of Descriptive Feedback on Student Motivation
Descriptive feedback enhances student motivation by providing specific, actionable insights that clarify learning goals and progress, fostering a growth mindset. This type of feedback encourages intrinsic motivation as students understand what they have done well and where improvement is needed, promoting self-regulation and persistence. Research highlights that students receiving descriptive feedback demonstrate higher engagement and improved academic outcomes compared to evaluative feedback, which often emphasizes judgment rather than development.
Evaluative Feedback: Benefits and Challenges in the Classroom
Evaluative feedback provides students with clear judgments on their performance, helping to identify strengths and areas for improvement efficiently. It supports goal-setting by measuring achievement against established standards, promoting accountability and motivation in the learning process. However, its challenges include potential negative impacts on student confidence and the risk of fostering dependency on grades rather than deeper understanding.
How Descriptive Feedback Enhances Student Achievement
Descriptive feedback provides specific information about a student's performance, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement, which fosters self-regulation and deepens understanding. Unlike evaluative feedback that assigns judgments or grades, descriptive feedback encourages active learning by guiding students on how to refine their skills and knowledge. Research shows that students receiving descriptive feedback demonstrate higher motivation, increased engagement, and significant gains in academic achievement.
When to Use Descriptive Versus Evaluative Feedback
Descriptive feedback is most effective during the learning process to guide students on specific improvements by providing detailed information about their performance. Evaluative feedback is better suited after task completion to summarize overall achievement, such as grades or ratings, helping students understand their standing. Using descriptive feedback promotes continuous growth, while evaluative feedback offers clear benchmarks for assessing success.
Strategies for Providing Effective Descriptive Feedback
Effective descriptive feedback in education focuses on specific observations of student performance, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement without assigning judgment. Strategies include using clear, objective language that addresses the task rather than the learner, providing actionable suggestions to guide progress, and encouraging self-reflection to enhance metacognitive skills. Incorporating timely and ongoing feedback fosters a growth mindset and supports deeper learning outcomes.
Common Pitfalls of Evaluative Feedback in Education
Evaluative feedback often leads to fixed mindset development, as students may focus solely on grades rather than learning progress or skill improvement. It tends to be vague or overly general, limiting students' understanding of specific areas needing growth. Such feedback can reduce motivation and increase anxiety, hindering meaningful engagement with the material and long-term educational development.
Best Practices for Balancing Descriptive and Evaluative Feedback
Effective feedback in education blends descriptive and evaluative approaches to enhance student learning and motivation. Best practices include providing specific, actionable comments that describe strengths and areas for improvement while integrating clear evaluative criteria to guide progress. Balancing these feedback types fosters a growth mindset and supports continuous skill development within educational settings.
descriptive feedback vs evaluative feedback Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com