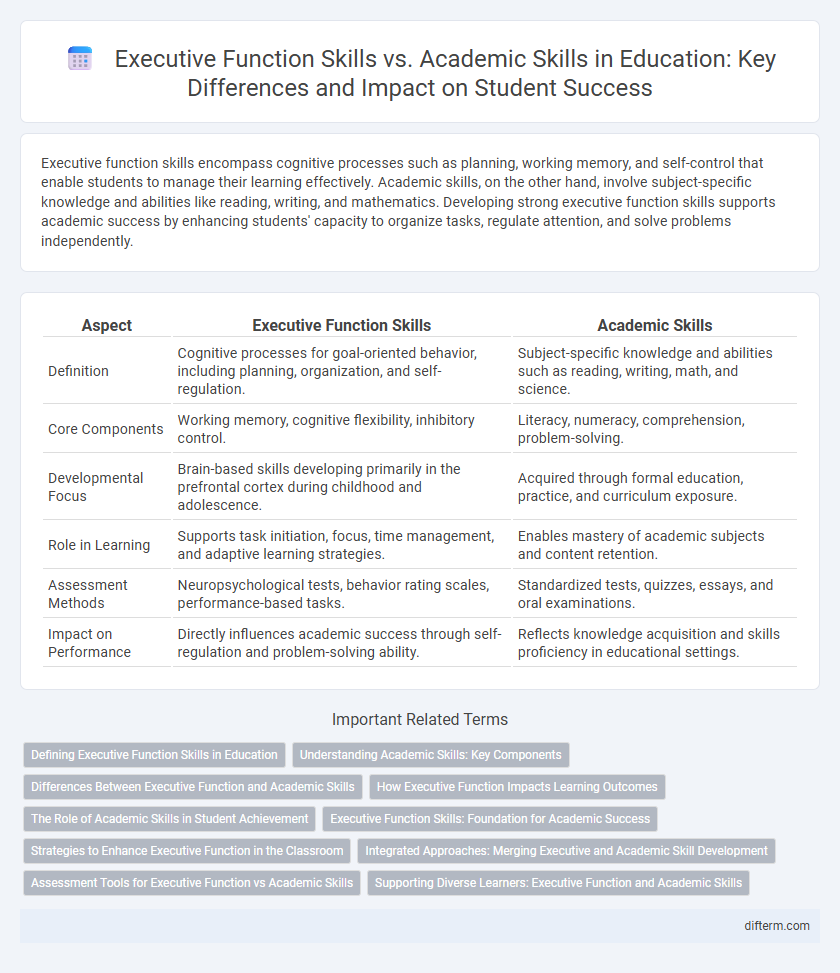
Executive function skills encompass cognitive processes such as planning, working memory, and self-control that enable students to manage their learning effectively. Academic skills, on the other hand, involve subject-specific knowledge and abilities like reading, writing, and mathematics. Developing strong executive function skills supports academic success by enhancing students' capacity to organize tasks, regulate attention, and solve problems independently.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Executive Function Skills | Academic Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cognitive processes for goal-oriented behavior, including planning, organization, and self-regulation. | Subject-specific knowledge and abilities such as reading, writing, math, and science. |
| Core Components | Working memory, cognitive flexibility, inhibitory control. | Literacy, numeracy, comprehension, problem-solving. |
| Developmental Focus | Brain-based skills developing primarily in the prefrontal cortex during childhood and adolescence. | Acquired through formal education, practice, and curriculum exposure. |
| Role in Learning | Supports task initiation, focus, time management, and adaptive learning strategies. | Enables mastery of academic subjects and content retention. |
| Assessment Methods | Neuropsychological tests, behavior rating scales, performance-based tasks. | Standardized tests, quizzes, essays, and oral examinations. |
| Impact on Performance | Directly influences academic success through self-regulation and problem-solving ability. | Reflects knowledge acquisition and skills proficiency in educational settings. |
Defining Executive Function Skills in Education
Executive function skills in education refer to cognitive processes such as planning, organization, working memory, flexible thinking, and self-control that enable students to manage tasks and regulate behavior effectively. These skills are crucial for goal-directed learning and problem-solving, differentiating them from academic skills like reading, writing, and math, which are subject-specific competencies. Developing strong executive function skills enhances a student's ability to succeed across various academic disciplines and adapt to complex learning environments.
Understanding Academic Skills: Key Components
Academic skills encompass fundamental capabilities such as reading comprehension, mathematical reasoning, and written communication, which directly influence student performance and achievement. Executive function skills, including working memory, cognitive flexibility, and inhibitory control, support the regulation and application of these academic abilities by enabling effective problem-solving and task management. Understanding the interplay between executive functions and core academic components is essential for designing targeted educational interventions and fostering holistic student development.
Differences Between Executive Function and Academic Skills
Executive function skills encompass cognitive processes such as working memory, flexible thinking, and self-control, which enable effective planning, problem-solving, and task management. Academic skills involve subject-specific knowledge and abilities in areas like reading, mathematics, and writing, essential for meeting curriculum standards. While executive function skills support the regulation and application of academic knowledge, academic skills measure mastery of content and factual information.
How Executive Function Impacts Learning Outcomes
Executive function skills, including working memory, cognitive flexibility, and inhibitory control, are critical for managing tasks, sustaining attention, and problem-solving in educational settings. These skills underpin academic performance by enabling effective organization, goal-setting, and self-regulation, directly influencing outcomes in reading comprehension, math problem-solving, and written expression. Deficits in executive function often correlate with challenges in classroom learning, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to enhance cognitive control and improve overall academic achievement.
The Role of Academic Skills in Student Achievement
Academic skills, including literacy, numeracy, and subject-specific knowledge, play a critical role in student achievement by providing the foundational tools necessary for learning and problem-solving. These skills directly impact students' ability to grasp curriculum content, complete assessments, and engage with complex tasks efficiently. Developing strong academic skills enhances cognitive processing and supports executive functions such as planning, organization, and task initiation, leading to improved overall educational outcomes.
Executive Function Skills: Foundation for Academic Success
Executive function skills, including working memory, cognitive flexibility, and inhibitory control, serve as the cognitive foundation crucial for academic success. These skills enable students to plan, organize, and regulate their behavior effectively, directly impacting their ability to acquire and apply academic knowledge. Strengthening executive function skills enhances problem-solving, attention, and self-monitoring, which are essential for mastering complex academic tasks.
Strategies to Enhance Executive Function in the Classroom
Strategies to enhance executive function in the classroom include using visual schedules, breaking tasks into manageable steps, and incorporating self-monitoring checklists to improve students' organization and time management. Teaching goal-setting techniques and providing regular feedback helps develop working memory and cognitive flexibility essential for academic success. Integrating mindfulness exercises and structured routines supports attention control, enabling better task completion and problem-solving skills.
Integrated Approaches: Merging Executive and Academic Skill Development
Integrated approaches that merge executive function skills with academic skill development enhance learners' cognitive flexibility, working memory, and goal-setting capabilities alongside subject-specific knowledge. Combining strategies such as metacognitive training, self-regulation exercises, and curriculum-based instruction promotes deeper understanding and improved problem-solving in mathematical reasoning, reading comprehension, and writing. Educational models emphasizing this synergy foster comprehensive skill acquisition, leading to better academic performance and lifelong learning adaptability.
Assessment Tools for Executive Function vs Academic Skills
Assessment tools for executive function skills often include performance-based tasks like the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test and the Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function (BRIEF), which measure cognitive processes such as working memory, cognitive flexibility, and inhibitory control. In contrast, academic skill assessments typically utilize standardized tests like the Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Achievement to evaluate reading, math, and writing proficiency. Accurate differentiation between executive function and academic skill assessments is critical for targeted interventions and personalized educational strategies.
Supporting Diverse Learners: Executive Function and Academic Skills
Supporting diverse learners requires understanding the distinct roles of executive function skills and academic skills in education. Executive function skills, including working memory, cognitive flexibility, and inhibitory control, enable students to manage tasks, regulate behavior, and adapt to new challenges, while academic skills focus on subject-specific knowledge like literacy, numeracy, and content mastery. Effective educational strategies integrate support for both skill sets to enhance learning outcomes and accommodate various learning styles and needs.
executive function skills vs academic skills Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com