Instructional design centers on creating engaging and effective learning experiences tailored to specific educational goals, while curriculum design involves structuring an entire course or program's content and objectives. Both disciplines contribute to education pet development by ensuring content is cohesive and suitable for diverse learner needs. Effective collaboration between instructional and curriculum designers enhances the overall quality of educational pet materials.
Table of Comparison
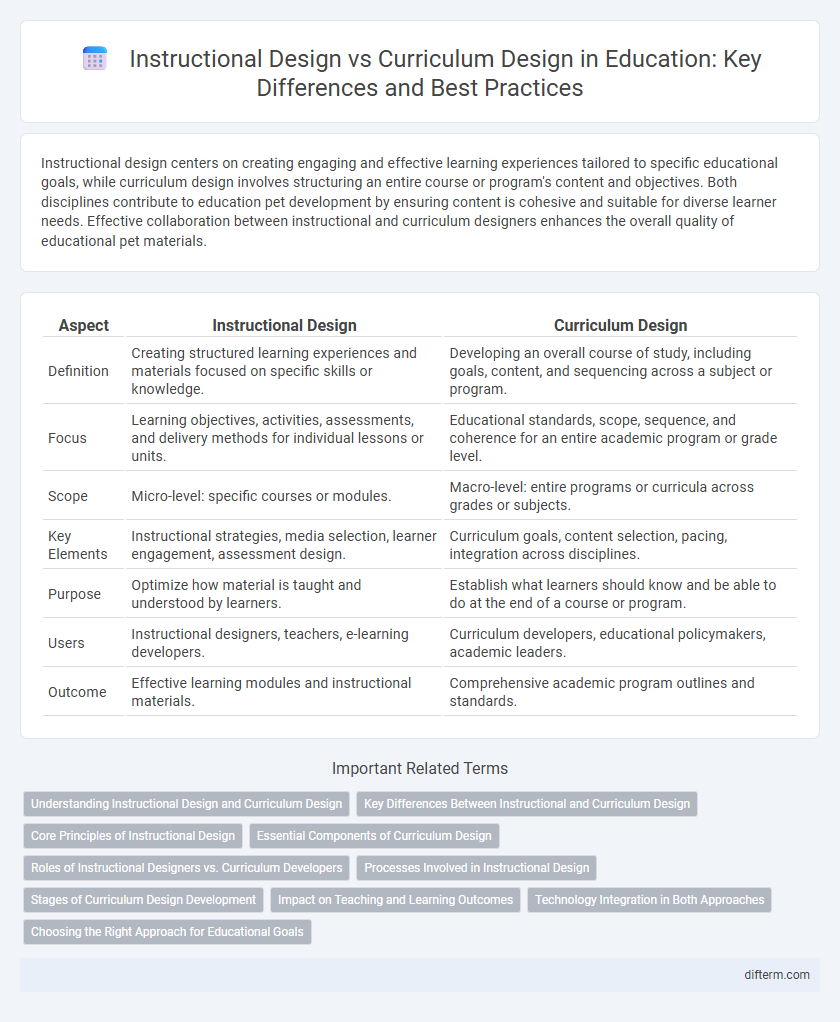
| Aspect | Instructional Design | Curriculum Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creating structured learning experiences and materials focused on specific skills or knowledge. | Developing an overall course of study, including goals, content, and sequencing across a subject or program. |
| Focus | Learning objectives, activities, assessments, and delivery methods for individual lessons or units. | Educational standards, scope, sequence, and coherence for an entire academic program or grade level. |
| Scope | Micro-level: specific courses or modules. | Macro-level: entire programs or curricula across grades or subjects. |
| Key Elements | Instructional strategies, media selection, learner engagement, assessment design. | Curriculum goals, content selection, pacing, integration across disciplines. |
| Purpose | Optimize how material is taught and understood by learners. | Establish what learners should know and be able to do at the end of a course or program. |
| Users | Instructional designers, teachers, e-learning developers. | Curriculum developers, educational policymakers, academic leaders. |
| Outcome | Effective learning modules and instructional materials. | Comprehensive academic program outlines and standards. |
Understanding Instructional Design and Curriculum Design
Instructional design focuses on creating effective learning experiences by systematically developing instructional materials and activities tailored to learners' needs. Curriculum design involves organizing and structuring the overall educational content, objectives, and assessments across a course or program to ensure coherent knowledge progression. Understanding the distinction between designing targeted instruction and shaping comprehensive curricula is crucial for educators to optimize teaching outcomes and student achievement.
Key Differences Between Instructional and Curriculum Design
Instructional design focuses on creating effective learning experiences and materials tailored to specific objectives, emphasizing the methods and strategies used to facilitate learning. Curriculum design involves structuring the overall educational program, including course content, sequence, and assessments aligned with broader educational goals and standards. Key differences lie in the scope, with instructional design addressing the "how" of teaching and curriculum design addressing the "what" and "when" within an educational framework.
Core Principles of Instructional Design
Instructional design centers on creating effective learning experiences through systematic analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation, emphasizing learner needs and objectives. Core principles include aligning content with clear objectives, incorporating active learning strategies, and continuous assessment to optimize knowledge retention. In contrast, curriculum design focuses on the broader educational program structure, integrating instructional units and resources across courses.
Essential Components of Curriculum Design
Curriculum design centers on developing essential components such as learning objectives, content sequencing, assessment methods, and instructional materials to create a coherent educational framework. It ensures alignment with educational standards and student needs, establishing clear goals and measurable outcomes. Unlike instructional design, which focuses on specific teaching strategies and learner engagement, curriculum design provides the overall structure and scope of the educational program.
Roles of Instructional Designers vs. Curriculum Developers
Instructional designers focus on creating engaging learning experiences by developing course materials, assessments, and multimedia content tailored to specific educational goals. Curriculum developers establish overarching educational frameworks, sequencing learning objectives, standards, and content scope to ensure cohesive program delivery. Both roles collaborate to align instructional strategies with curriculum goals, enhancing learner outcomes and educational effectiveness.
Processes Involved in Instructional Design
Instructional design involves systematic processes such as needs analysis, learning objective formulation, content sequencing, and assessment development to create effective and engaging learning experiences. This process emphasizes aligning instructional materials with specific learner outcomes and adapting instructional strategies based on learner feedback and evaluation. In contrast, curriculum design focuses on broader educational aims, content standards, and scope, while instructional design zeroes in on optimizing individual instructional units and delivery methods.
Stages of Curriculum Design Development
Curriculum design development involves key stages such as analysis of learner needs, formulation of learning objectives, content selection, organization of instructional materials, and evaluation planning. Instructional design focuses more specifically on the creation of effective learning experiences within the curriculum framework, emphasizing task analysis, media selection, and assessment alignment. Understanding these stages ensures curriculum designers create coherent educational programs that enhance student achievement and instructional effectiveness.
Impact on Teaching and Learning Outcomes
Instructional design focuses on creating effective learning experiences by integrating technology, multimedia, and assessment strategies that directly enhance student engagement and comprehension. Curriculum design encompasses the broader scope of structuring academic content, learning objectives, and skill progression over time to ensure alignment with educational standards and long-term learning goals. The synergy between instructional and curriculum design leads to improved teaching effectiveness and measurable gains in student achievement and retention rates.
Technology Integration in Both Approaches
Instructional design emphasizes the development of interactive learning experiences incorporating technology tools such as Learning Management Systems (LMS), multimedia content, and adaptive assessments to enhance learner engagement. Curriculum design integrates technology by aligning digital resources and educational software with course objectives, ensuring cohesive technology use across all units and grade levels. Both approaches prioritize the strategic use of technology to improve educational outcomes but differ in scope, with instructional design focusing on individual lesson delivery and curriculum design addressing the overall educational program structure.
Choosing the Right Approach for Educational Goals
Instructional design focuses on developing specific learning activities and materials tailored to achieve measurable learning outcomes, while curriculum design involves structuring the overall educational program and content sequence across a course or grade level. Selecting the right approach depends on the educational goals, where instructional design suits targeted skill acquisition and curriculum design supports comprehensive knowledge progression. Aligning the design method with objectives ensures effective learning experiences and maximized student achievement.
instructional design vs curriculum design Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com