Vertical integration enhances control over the supply chain by merging different production stages within a single company, improving efficiency and reducing costs. Horizontal integration expands market share by acquiring or merging with competitors in the same industry, leading to economies of scale and increased market power. Both strategies aim to strengthen competitive advantage, but vertical integration focuses on internal process control, while horizontal integration emphasizes market consolidation.
Table of Comparison
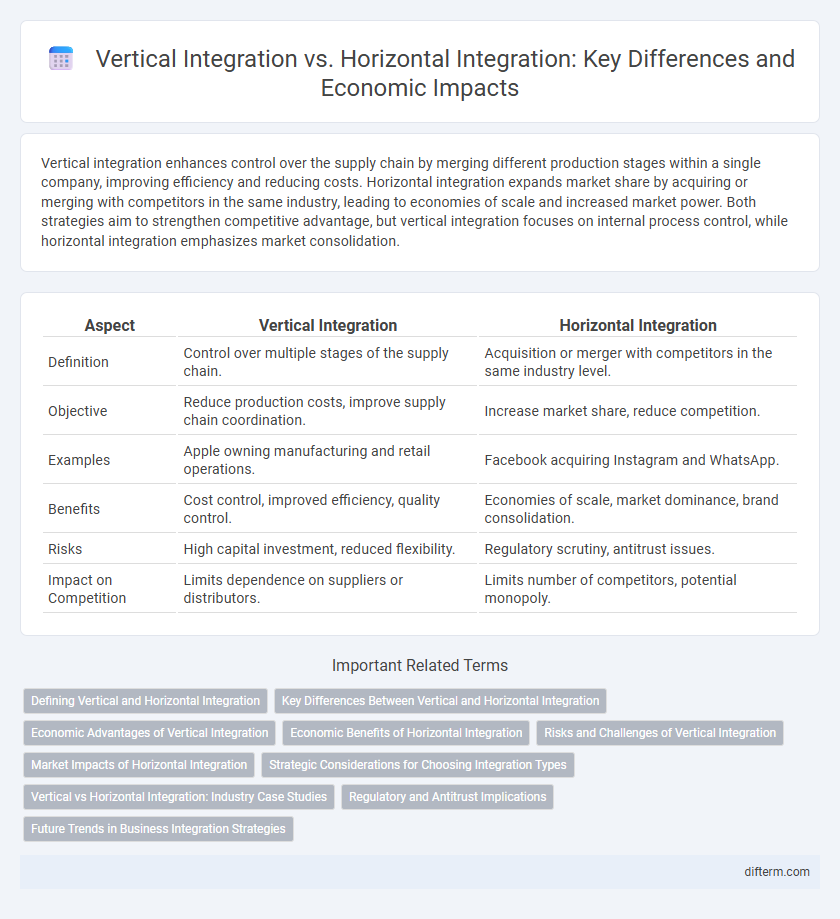
| Aspect | Vertical Integration | Horizontal Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control over multiple stages of the supply chain. | Acquisition or merger with competitors in the same industry level. |
| Objective | Reduce production costs, improve supply chain coordination. | Increase market share, reduce competition. |
| Examples | Apple owning manufacturing and retail operations. | Facebook acquiring Instagram and WhatsApp. |
| Benefits | Cost control, improved efficiency, quality control. | Economies of scale, market dominance, brand consolidation. |
| Risks | High capital investment, reduced flexibility. | Regulatory scrutiny, antitrust issues. |
| Impact on Competition | Limits dependence on suppliers or distributors. | Limits number of competitors, potential monopoly. |
Defining Vertical and Horizontal Integration
Vertical integration involves a company expanding its operations into different stages of the same production path, such as acquiring suppliers or distributors to control the supply chain. Horizontal integration occurs when a firm acquires or merges with competitors operating at the same level of the production process to increase market share and reduce competition. Both strategies aim to enhance operational efficiency but differ in terms of scope and market influence.
Key Differences Between Vertical and Horizontal Integration
Vertical integration involves a company expanding its operations by acquiring or merging with firms at different stages of the supply chain, aiming to control production, distribution, and supply processes. Horizontal integration occurs when a company acquires or merges with competitors operating at the same level of the supply chain to increase market share and reduce competition. Key differences include the scope of control, with vertical integration focusing on upstream or downstream activities, while horizontal integration targets consolidation within the same industry level.
Economic Advantages of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration enhances cost efficiency by streamlining supply chains and reducing reliance on external suppliers, leading to improved profit margins. It increases control over production processes and quality standards, minimizing risks associated with supply disruptions. Firms benefit from greater market power and the ability to capture value at multiple stages of the supply chain, boosting overall competitiveness.
Economic Benefits of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration enhances market share by allowing firms to consolidate resources and reduce competition within the same industry, leading to economies of scale and increased bargaining power. This strategy optimizes operational efficiency through the unification of production processes and distribution channels, often resulting in cost reductions and higher profit margins. Furthermore, horizontal integration fosters innovation by combining expertise and technologies from merged entities, accelerating product development and market responsiveness.
Risks and Challenges of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration presents significant risks such as high capital investment requirements, which can strain company resources and limit financial flexibility. It increases operational complexity by requiring expertise across multiple stages of the supply chain, potentially leading to inefficiencies and coordination challenges. Additionally, vertical integration can reduce market responsiveness and innovation due to decreased external partnerships and competitive pressures.
Market Impacts of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration expands a company's market share by acquiring or merging with competitors in the same industry, leading to reduced competition and increased pricing power. This strategy can result in greater economies of scale, enhanced product offerings, and access to a broader customer base, potentially triggering regulatory scrutiny due to antitrust concerns. Market consolidation through horizontal integration often shifts industry dynamics, influencing supply chains and consumer choice.
Strategic Considerations for Choosing Integration Types
Vertical integration involves a company expanding its operations into different stages of production within the same industry, enhancing control over the supply chain and reducing dependency on suppliers or distributors. Horizontal integration focuses on acquiring or merging with competitors to increase market share, reduce competition, and achieve economies of scale. Strategic considerations for choosing between vertical and horizontal integration include evaluating market power, cost efficiencies, potential regulatory challenges, and alignment with long-term business goals.
Vertical vs Horizontal Integration: Industry Case Studies
Vertical integration, exemplified by companies like Tesla controlling both manufacturing and supply chains, enhances operational efficiency and product quality by streamlining processes within a single industry. Horizontal integration, as seen in Facebook's acquisition of Instagram and WhatsApp, focuses on expanding market share and reducing competition by merging firms at the same production stage. Industry case studies reveal that vertical integration boosts control over the value chain, while horizontal integration drives market dominance and economies of scale.
Regulatory and Antitrust Implications
Vertical integration can raise regulatory concerns related to market foreclosure and reduced competition by controlling multiple supply chain stages, prompting antitrust authorities to scrutinize potential barriers for new entrants. Horizontal integration often attracts antitrust enforcement due to risks of market concentration, price-fixing, and monopolistic behavior, leading to mergers being challenged or blocked based on market share thresholds and competitive effects. Both integration types require compliance with competition laws such as the Sherman Act and the Clayton Act in the U.S., with regulators assessing the potential impact on consumer welfare and market dynamics.
Future Trends in Business Integration Strategies
Future business integration strategies emphasize a balanced approach between vertical integration, which enhances supply chain control, and horizontal integration, which expands market share and reduces competition. Advances in technology, such as AI and blockchain, are driving more sophisticated integration models that prioritize agility, data sharing, and sustainability. Companies increasingly adopt hybrid integration approaches to optimize operational efficiency and respond to rapidly changing market dynamics.
Vertical integration vs Horizontal integration Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com