The value chain encompasses the full range of activities a business undertakes to deliver a valuable product or service, emphasizing value creation at each stage. In contrast, the supply chain focuses primarily on the logistics and flow of goods from suppliers to the end customer, aiming to optimize efficiency and reduce costs. Understanding the distinction enables businesses to enhance competitive advantage by integrating both value creation and supply management strategies.
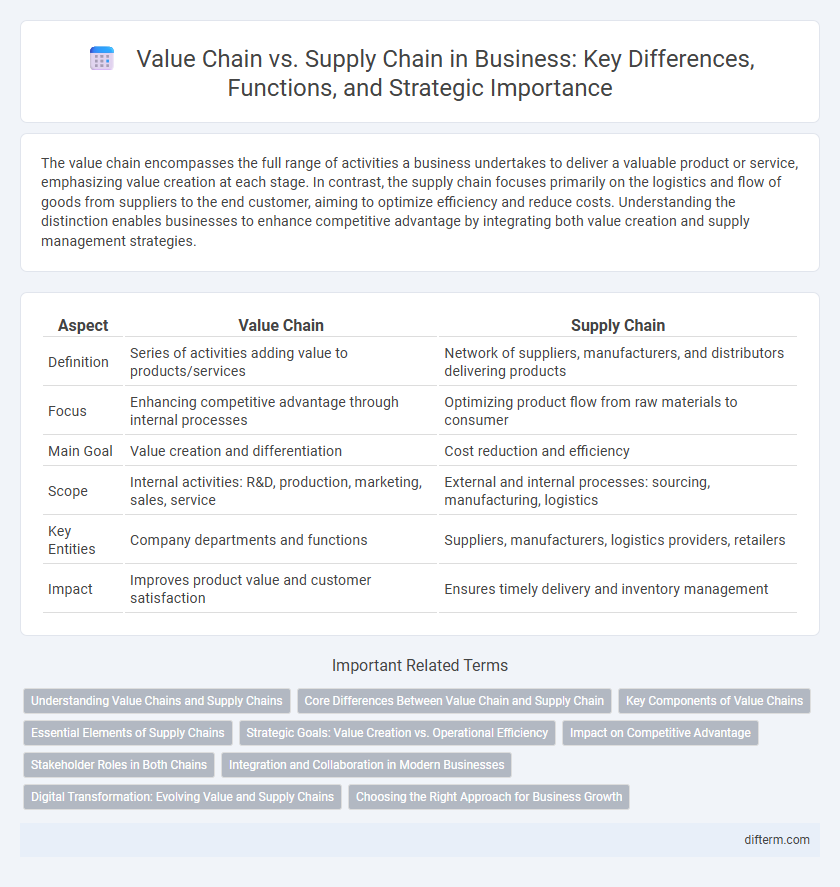
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Value Chain | Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Series of activities adding value to products/services | Network of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors delivering products |
| Focus | Enhancing competitive advantage through internal processes | Optimizing product flow from raw materials to consumer |
| Main Goal | Value creation and differentiation | Cost reduction and efficiency |
| Scope | Internal activities: R&D, production, marketing, sales, service | External and internal processes: sourcing, manufacturing, logistics |
| Key Entities | Company departments and functions | Suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, retailers |
| Impact | Improves product value and customer satisfaction | Ensures timely delivery and inventory management |
Understanding Value Chains and Supply Chains
Value chains encompass the full range of activities required to create a product or service, from raw materials to final delivery, emphasizing value creation at each step. Supply chains focus specifically on the logistics and processes involved in sourcing, production, and distribution to ensure efficient movement of goods. Understanding the distinction aids businesses in optimizing operations, reducing costs, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Core Differences Between Value Chain and Supply Chain
The core difference between value chain and supply chain lies in their primary focus: the value chain emphasizes activities that add value to the product or service, enhancing customer satisfaction and competitive advantage, while the supply chain concentrates on the efficient flow and management of materials, information, and finances from suppliers to end customers. Value chain analysis includes inbound logistics, operations, marketing, sales, and service, aiming to maximize value creation at each step. In contrast, the supply chain focuses on sourcing, production, distribution, and logistics, prioritizing cost reduction and process optimization.
Key Components of Value Chains
Key components of value chains include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service, all designed to add value at each stage of production. Effective management of these components enhances product quality and customer satisfaction, driving competitive advantage. Integrating support activities such as procurement, technology development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure further optimizes the value creation process.
Essential Elements of Supply Chains
Essential elements of supply chains include procurement, production, distribution, and logistics, which collectively ensure the smooth flow of goods from suppliers to customers. Inventory management, demand forecasting, and supplier relationship management are critical for optimizing cost efficiency and responsiveness. These components distinguish supply chains from value chains by emphasizing operational processes and physical product movement rather than strategic value creation.
Strategic Goals: Value Creation vs. Operational Efficiency
The value chain emphasizes strategic goals centered on value creation by enhancing product differentiation and customer satisfaction throughout the business process. The supply chain focuses on operational efficiency, optimizing logistics, inventory management, and cost reduction to ensure timely delivery and resource utilization. Aligning both frameworks enables businesses to achieve competitive advantage through integrated value generation and streamlined operations.
Impact on Competitive Advantage
Value chain analysis enhances competitive advantage by identifying core activities that create value and differentiating the business through innovation and efficiency. Supply chain management optimizes operational costs and ensures timely delivery, directly affecting customer satisfaction and market responsiveness. Together, a well-integrated value chain and supply chain drive sustainable competitive advantage by aligning internal capabilities with external supply dynamics.
Stakeholder Roles in Both Chains
Stakeholder roles in the value chain emphasize creating competitive advantage through activities like product development, marketing, and service, involving internal departments such as R&D, marketing, and operations. In contrast, supply chain stakeholders focus on efficient logistics, procurement, and distribution, including suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors who manage material flow and inventory. While the value chain centers on value creation for customers, the supply chain prioritizes coordination among external partners to ensure timely delivery and cost efficiency.
Integration and Collaboration in Modern Businesses
Integration in modern businesses involves synchronizing internal processes across the value chain to enhance efficiency, while supply chain collaboration extends this coordination to external partners such as suppliers and distributors. Emphasizing seamless communication and data sharing, businesses leverage technology platforms like ERP and SCM systems to optimize both value creation and delivery. Strong integration and collaboration reduce costs, improve product quality, and increase responsiveness to market changes, driving competitive advantage.
Digital Transformation: Evolving Value and Supply Chains
Digital transformation reshapes value chains by integrating advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain to enhance efficiency, customer engagement, and innovation across all business processes. Supply chains evolve through digital tools that enable real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and seamless logistics management, reducing costs and improving delivery speed. The convergence of digital capabilities drives interconnected value and supply chains, creating adaptable ecosystems that respond swiftly to market demands and disruptions.
Choosing the Right Approach for Business Growth
Selecting the appropriate value chain or supply chain strategy directly impacts business growth by enhancing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. A value chain approach emphasizes optimizing internal activities like product development, marketing, and after-sales support to create competitive advantage. Conversely, a supply chain focus improves logistics, procurement, and distribution networks, ensuring cost-effectiveness and timely delivery, which are crucial for scaling business operations.
value chain vs supply chain Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com