Early adopters in the business pet market embrace innovative products quickly, driving initial growth and setting trends, while the late majority waits for proven value and reliability before committing. Marketing strategies targeting early adopters emphasize novelty and cutting-edge features, whereas approaches for the late majority highlight practicality and widespread acceptance. Understanding these segments helps businesses tailor messaging and product development to maximize market penetration and customer satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
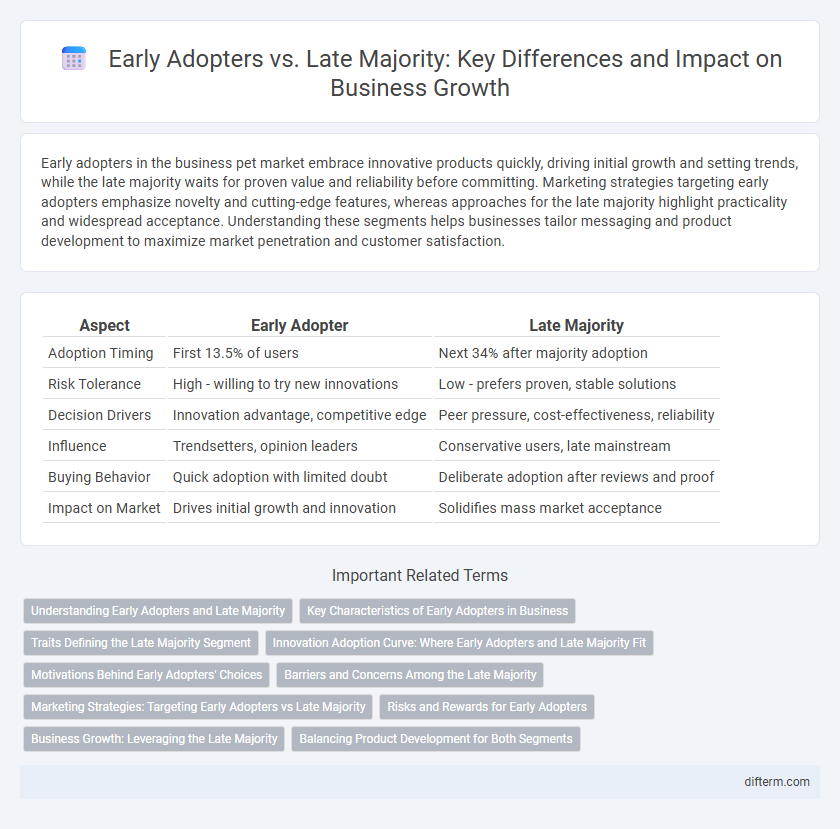
| Aspect | Early Adopter | Late Majority |
|---|---|---|
| Adoption Timing | First 13.5% of users | Next 34% after majority adoption |
| Risk Tolerance | High - willing to try new innovations | Low - prefers proven, stable solutions |
| Decision Drivers | Innovation advantage, competitive edge | Peer pressure, cost-effectiveness, reliability |
| Influence | Trendsetters, opinion leaders | Conservative users, late mainstream |
| Buying Behavior | Quick adoption with limited doubt | Deliberate adoption after reviews and proof |
| Impact on Market | Drives initial growth and innovation | Solidifies mass market acceptance |
Understanding Early Adopters and Late Majority
Early adopters are innovators who embrace new technologies and business practices quickly, driven by a desire for competitive advantage and innovation leadership. The late majority tends to adopt new products or services after they have become mainstream, often influenced by peer pressure and proven benefits. Understanding the distinct motivations and behaviors of early adopters versus the late majority enables businesses to tailor marketing strategies and product rollouts effectively.
Key Characteristics of Early Adopters in Business
Early adopters in business exhibit a strong willingness to embrace innovative products and technologies ahead of the mainstream market, often driven by a desire for competitive advantage and risk tolerance. They tend to have higher social status, greater financial liquidity, and access to expert information, facilitating informed decision-making. This group plays a critical role in influencing the late majority by validating new offerings and providing valuable feedback for refinement.
Traits Defining the Late Majority Segment
The late majority segment is characterized by skepticism toward new technologies, preferring proven and widely accepted solutions before adoption. This group values practicality, often influenced by peer pressure and extensive social proof, leading to cautious decision-making. Typically risk-averse, the late majority relies on established satisfaction from earlier adopters and looks for cost-effective, user-friendly products.
Innovation Adoption Curve: Where Early Adopters and Late Majority Fit
Early adopters play a critical role in the Innovation Adoption Curve by embracing new technologies or products soon after the innovators, driving early market validation and influencing broader acceptance. The late majority, representing a larger portion of the market, adopts innovations after observing the success and reliability established by early adopters and the early majority. Understanding the distinct characteristics and adoption timelines of these groups helps businesses tailor marketing strategies for effective product diffusion and market penetration.
Motivations Behind Early Adopters' Choices
Early adopters are driven by a strong desire for innovation and competitive advantage, seeking new technologies to gain early benefits and influence market trends. Their motivation often stems from a willingness to take calculated risks and a higher tolerance for uncertainty compared to the late majority. This contrasts with the late majority, who prioritize proven solutions and minimize risk by waiting for widespread adoption and established reliability.
Barriers and Concerns Among the Late Majority
The late majority often faces barriers such as risk aversion, skepticism about new technology benefits, and limited access to resources or support networks. Concerns include fear of high costs, complexity in implementation, and uncertainty about return on investment, which delay adoption. Overcoming these obstacles requires targeted education, simplified solutions, and proven case studies demonstrating value and reliability.
Marketing Strategies: Targeting Early Adopters vs Late Majority
Marketing strategies targeting early adopters emphasize innovation and exclusivity, leveraging social proof and influencer endorsements to build credibility and buzz. For the late majority, campaigns focus on demonstrating reliability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use, often using testimonials and detailed product information to reduce perceived risk. Tailoring messaging and channels to each group's distinct motivations and adoption behaviors maximizes product acceptance and market penetration.
Risks and Rewards for Early Adopters
Early adopters face higher risks due to unproven technology and potential market volatility but gain competitive advantages through early access to innovative solutions and customer loyalty. Their willingness to embrace change often leads to valuable feedback opportunities, shaping product development and securing market influence. Successful early adoption can result in substantial rewards, including brand differentiation and long-term profitability.
Business Growth: Leveraging the Late Majority
Businesses can significantly boost growth by targeting the Late Majority, who constitute approximately 34% of the market and tend to adopt products after seeing widespread acceptance. Leveraging detailed market analytics and social proof enhances trust and accelerates adoption among this more cautious segment. Tailored marketing strategies addressing specific pain points and offering clear value propositions can convert Late Majority customers, driving sustained revenue increase.
Balancing Product Development for Both Segments
Balancing product development for early adopters and the late majority requires a strategic approach to innovation and usability. Early adopters demand cutting-edge features and rapid iteration, while the late majority prioritizes reliability, ease of use, and comprehensive support. Successful businesses tailor their product roadmap to address both segments by integrating advanced functionalities with intuitive design and robust customer service.
early adopter vs late majority Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com