Hard skills refer to the specific, teachable abilities required to perform job functions, such as data analysis, coding, or financial modeling. Soft skills encompass interpersonal attributes like communication, teamwork, and problem-solving that enhance collaboration and leadership. Balancing hard skills with strong soft skills is essential for success, as technical expertise alone cannot drive effective business outcomes without emotional intelligence and adaptability.
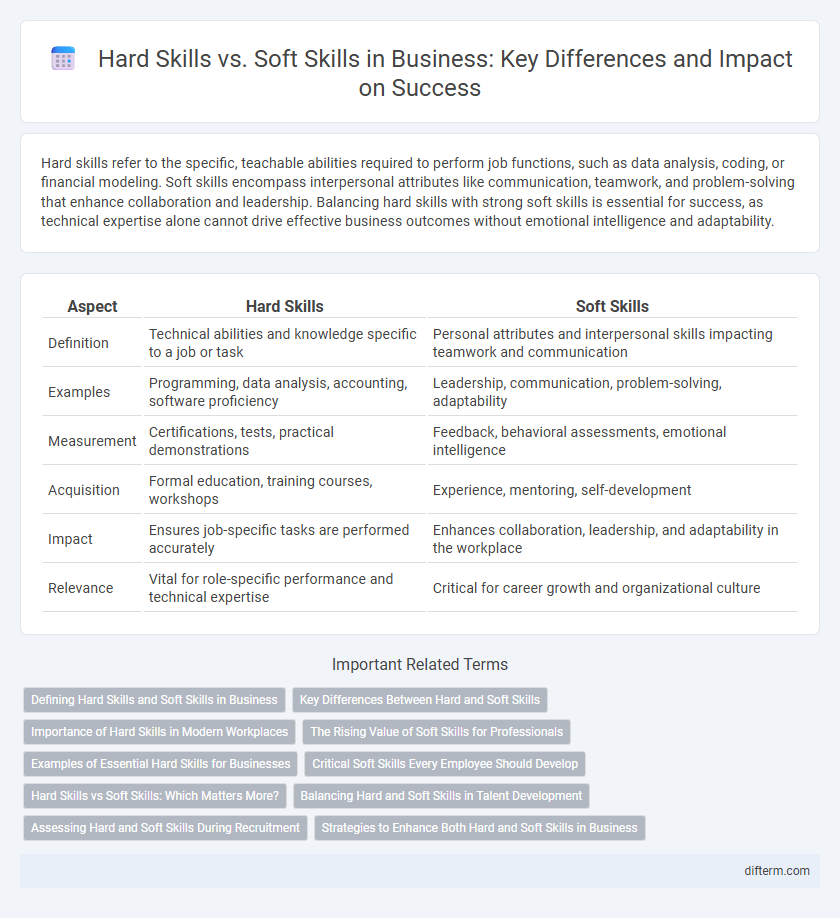
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hard Skills | Soft Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technical abilities and knowledge specific to a job or task | Personal attributes and interpersonal skills impacting teamwork and communication |
| Examples | Programming, data analysis, accounting, software proficiency | Leadership, communication, problem-solving, adaptability |
| Measurement | Certifications, tests, practical demonstrations | Feedback, behavioral assessments, emotional intelligence |
| Acquisition | Formal education, training courses, workshops | Experience, mentoring, self-development |
| Impact | Ensures job-specific tasks are performed accurately | Enhances collaboration, leadership, and adaptability in the workplace |
| Relevance | Vital for role-specific performance and technical expertise | Critical for career growth and organizational culture |
Defining Hard Skills and Soft Skills in Business
Hard skills in business refer to measurable, technical abilities such as data analysis, project management, and financial modeling that are essential for specific job functions. Soft skills encompass interpersonal attributes like communication, teamwork, and problem-solving that enhance workplace collaboration and leadership effectiveness. Mastery of both hard and soft skills drives organizational success and employee performance.
Key Differences Between Hard and Soft Skills
Hard skills encompass measurable technical abilities such as data analysis, coding, and financial modeling, essential for task execution and industry-specific roles. Soft skills involve interpersonal attributes like communication, teamwork, and problem-solving, critical for collaboration, leadership, and adapting to workplace dynamics. The key differences lie in hard skills being teachable and quantifiable, whereas soft skills are innate or developed through experience and influence overall job performance and organizational culture.
Importance of Hard Skills in Modern Workplaces
Hard skills, such as data analysis, programming, and project management, are essential in modern workplaces for measurable performance and task completion. Employers prioritize these technical abilities to ensure employees can operate specialized software, interpret complex information, and meet specific job requirements. Mastery of hard skills directly impacts productivity, innovation, and competitive advantage in fast-evolving industries.
The Rising Value of Soft Skills for Professionals
Soft skills such as communication, emotional intelligence, and adaptability have become critical differentiators in the competitive business landscape, driving team collaboration and leadership effectiveness. Employers increasingly prioritize these interpersonal abilities alongside technical expertise to enhance innovation and customer satisfaction. Mastery of soft skills leads to improved problem-solving and resilience, essential for navigating dynamic professional environments.
Examples of Essential Hard Skills for Businesses
Proficiency in data analysis, financial modeling, and advanced Excel techniques are essential hard skills for effective business decision-making. Expertise in project management software such as Microsoft Project or Trello enhances operational efficiency and team coordination. Knowledge of coding languages like Python or SQL supports data-driven strategies and automation in business processes.
Critical Soft Skills Every Employee Should Develop
Critical soft skills every employee should develop include communication, adaptability, and problem-solving, which drive effective teamwork and leadership. Emotional intelligence enhances workplace relationships and conflict resolution, promoting a positive organizational culture. Time management and critical thinking further empower employees to optimize productivity and make informed decisions in dynamic business environments.
Hard Skills vs Soft Skills: Which Matters More?
Hard skills, such as data analysis, programming, and financial modeling, provide measurable competencies essential for specific job functions. Soft skills like communication, teamwork, and problem-solving enhance collaboration and adaptability, driving long-term career success. Employers increasingly value a balance, with hard skills securing initial job placement and soft skills influencing leadership and organizational impact.
Balancing Hard and Soft Skills in Talent Development
Balancing hard and soft skills in talent development enhances overall employee effectiveness and drives business success. Technical expertise like data analysis or coding must be complemented by communication, leadership, and problem-solving abilities to adapt in dynamic markets. Organizations that integrate ongoing training in both skills foster innovation, collaboration, and resilient workforce performance.
Assessing Hard and Soft Skills During Recruitment
Assessing hard skills during recruitment involves evaluating candidates' technical abilities, certifications, and proficiency with specific tools or software essential for the job. Soft skills assessment focuses on communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and adaptability through behavioral interviews, situational judgment tests, or personality assessments. Combining both evaluation methods ensures a holistic understanding of a candidate's potential to perform and thrive within the company culture.
Strategies to Enhance Both Hard and Soft Skills in Business
Employ targeted training programs and certification courses to elevate hard skills such as data analysis, coding, and financial modeling crucial for business operations. Foster communication workshops, emotional intelligence training, and leadership development initiatives to strengthen soft skills like teamwork, adaptability, and conflict resolution. Integrate continuous feedback mechanisms and real-world project assignments to simultaneously refine both skill sets, enhancing overall organizational performance.
Hard Skills vs Soft Skills Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com