Unit economics analyzes the direct revenues and costs associated with a single product unit, providing clarity on profitability at the most granular level. Contribution margin measures the difference between sales revenue and variable costs, highlighting how much revenue contributes to fixed costs and overall profit. Understanding both metrics is essential for optimizing pricing strategies and scaling business operations effectively.
Table of Comparison
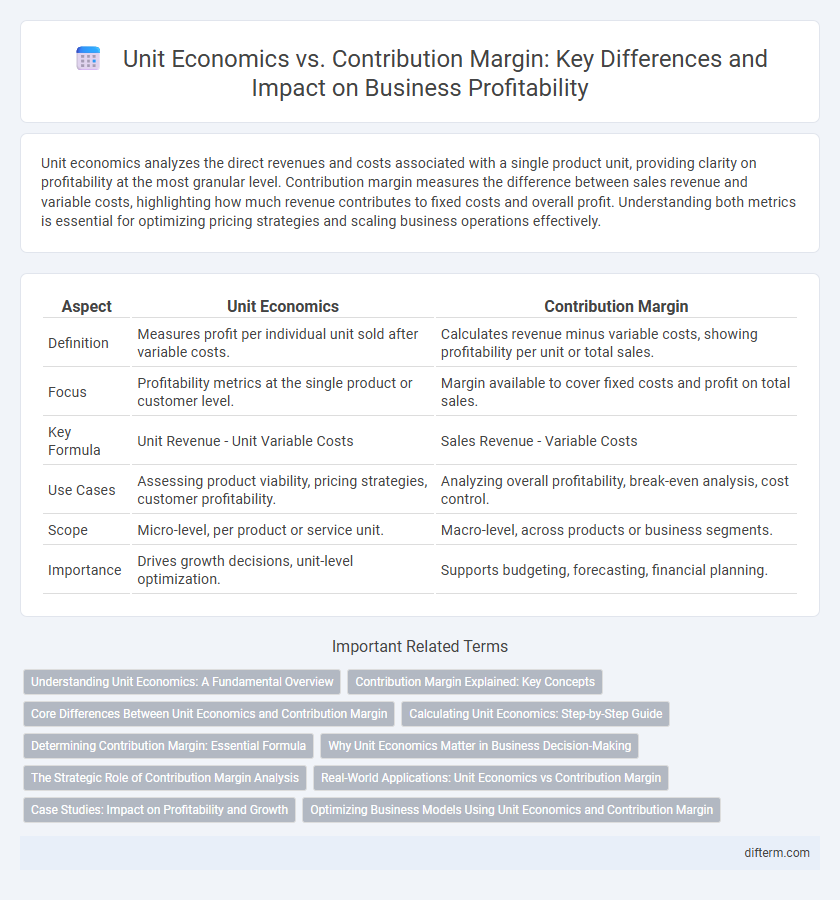
| Aspect | Unit Economics | Contribution Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures profit per individual unit sold after variable costs. | Calculates revenue minus variable costs, showing profitability per unit or total sales. |
| Focus | Profitability metrics at the single product or customer level. | Margin available to cover fixed costs and profit on total sales. |
| Key Formula | Unit Revenue - Unit Variable Costs | Sales Revenue - Variable Costs |
| Use Cases | Assessing product viability, pricing strategies, customer profitability. | Analyzing overall profitability, break-even analysis, cost control. |
| Scope | Micro-level, per product or service unit. | Macro-level, across products or business segments. |
| Importance | Drives growth decisions, unit-level optimization. | Supports budgeting, forecasting, financial planning. |
Understanding Unit Economics: A Fundamental Overview
Unit economics analyze the direct revenues and costs associated with a single unit of product or service, providing essential insights into profitability at the micro level. Contribution margin measures the incremental profit earned from each unit sold after variable costs, directly influencing pricing and scaling decisions. Understanding both concepts enables businesses to optimize cost structures and enhance strategic growth by focusing on the financial impact of individual products.
Contribution Margin Explained: Key Concepts
Contribution margin represents the revenue remaining after deducting variable costs directly associated with producing a product or service, serving as a critical metric to assess profitability at the unit level. It highlights how much money contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profit, differing from unit economics which encompasses a broader analysis of cost and revenue on a per-unit basis. Understanding contribution margin enables businesses to make informed pricing, production, and investment decisions, optimizing overall financial performance.
Core Differences Between Unit Economics and Contribution Margin
Unit economics analyzes profitability at the individual unit level, considering variable costs and revenues to determine the break-even point and scaling potential. Contribution margin focuses on the difference between sales revenue and variable costs, highlighting how much income contributes to fixed costs and profit generation. The core difference lies in unit economics providing a holistic view of per-unit profitability, while contribution margin specifically measures the incremental profit per unit sold.
Calculating Unit Economics: Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating unit economics involves identifying the revenue generated per unit and subtracting the variable costs associated with producing that unit, which provides insight into profitability at the individual product level. Key components include customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value (LTV), cost of goods sold (COGS), and operating expenses directly tied to the unit. Precise calculation of these metrics enables businesses to optimize pricing strategies and resource allocation for sustainable growth.
Determining Contribution Margin: Essential Formula
Determining contribution margin involves subtracting variable costs from total sales revenue, highlighting the amount available to cover fixed costs and generate profit. This key unit economics metric guides businesses in pricing strategies and cost management by revealing the profitability per unit sold. Accurate calculation of contribution margin is essential for making informed decisions on scaling operations and optimizing product portfolios.
Why Unit Economics Matter in Business Decision-Making
Unit economics provides a granular view of revenue and cost per unit, enabling businesses to assess product profitability at the smallest scale. Understanding unit economics helps identify which products drive overall profit and supports pricing strategies that improve long-term sustainability. Contribution margin complements this by highlighting the portion of sales revenue that contributes to covering fixed costs, but unit economics offers deeper insight into operational efficiency and scalable growth.
The Strategic Role of Contribution Margin Analysis
Contribution margin analysis plays a strategic role in business by revealing the profitability of individual products or services, enabling more informed pricing and product mix decisions. It helps identify which offerings generate sufficient revenue to cover fixed costs and contribute to overall profit, guiding resource allocation and operational focus. Understanding contribution margin allows companies to optimize cost structures and improve financial forecasting for sustainable growth.
Real-World Applications: Unit Economics vs Contribution Margin
Unit economics provides a granular view of profit metrics per individual unit sold, enabling businesses to assess customer acquisition cost and lifetime value with precision. Contribution margin focuses on the revenue remaining after variable costs, which helps determine scalability and pricing strategies for products or services. In real-world applications, combining unit economics and contribution margin allows startups and enterprises to optimize operational efficiency and make data-driven decisions on growth investments.
Case Studies: Impact on Profitability and Growth
Case studies demonstrate that understanding Unit Economics, which analyzes revenue and costs per unit, enables businesses to identify profitable customer segments and optimize pricing strategies for sustainable growth. In contrast, Contribution Margin focuses on the proportion of sales contributing to fixed costs and profit, providing insights for short-term decision-making and cost control. Companies leveraging both metrics effectively balance customer acquisition costs and operational efficiency, driving enhanced profitability and scalable expansion.
Optimizing Business Models Using Unit Economics and Contribution Margin
Optimizing business models requires a deep understanding of unit economics and contribution margin as critical financial metrics. Unit economics evaluates the profitability of individual products or services by analyzing revenues and costs per unit, while contribution margin assesses the portion of sales revenue that exceeds variable costs, contributing to fixed expenses and profit. Leveraging these metrics allows businesses to identify cost drivers, improve pricing strategies, and enhance operational efficiency, ultimately driving sustainable growth and maximizing profitability.
Unit Economics vs Contribution Margin Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com