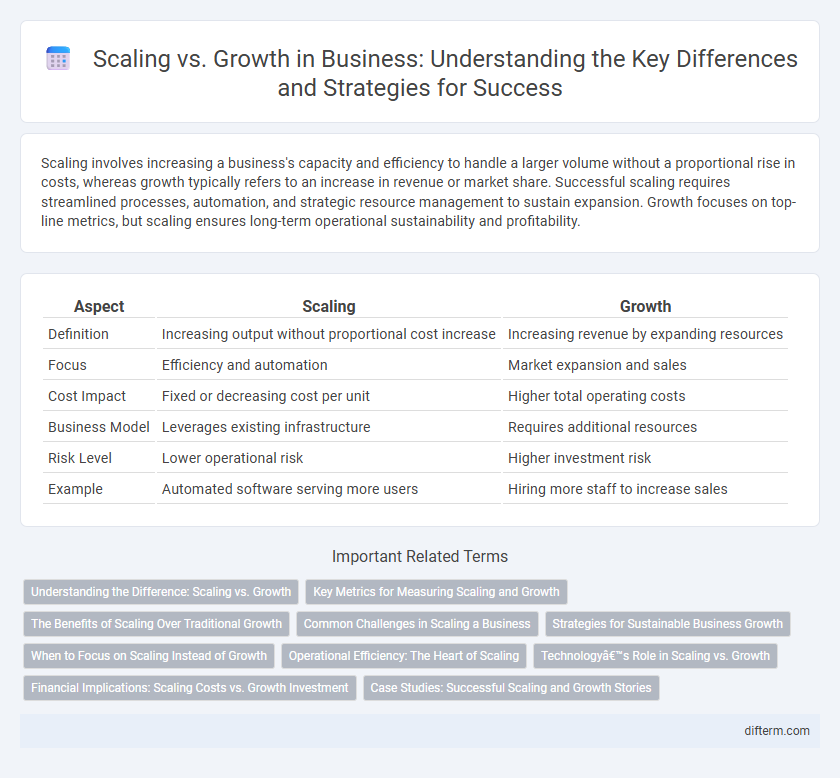
Scaling involves increasing a business's capacity and efficiency to handle a larger volume without a proportional rise in costs, whereas growth typically refers to an increase in revenue or market share. Successful scaling requires streamlined processes, automation, and strategic resource management to sustain expansion. Growth focuses on top-line metrics, but scaling ensures long-term operational sustainability and profitability.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Scaling | Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increasing output without proportional cost increase | Increasing revenue by expanding resources |
| Focus | Efficiency and automation | Market expansion and sales |
| Cost Impact | Fixed or decreasing cost per unit | Higher total operating costs |
| Business Model | Leverages existing infrastructure | Requires additional resources |
| Risk Level | Lower operational risk | Higher investment risk |
| Example | Automated software serving more users | Hiring more staff to increase sales |
Understanding the Difference: Scaling vs. Growth
Scaling in business refers to increasing revenue exponentially while maintaining or minimally increasing costs, enabling higher profit margins with efficiency improvements. Growth, on the other hand, often involves proportional increases in resources and expenses alongside revenue, such as hiring more staff or expanding physical locations. Understanding the difference between scaling and growth is crucial for strategic planning and sustainable expansion.
Key Metrics for Measuring Scaling and Growth
Key metrics for measuring scaling include customer acquisition cost (CAC), churn rate, and operational efficiency, which indicate how well a business manages increased demand without sacrificing quality. Growth metrics focus on revenue growth rate, market share expansion, and profit margins, highlighting the company's ability to increase its size and financial performance. Tracking both sets of metrics provides a comprehensive view of sustainability and long-term business success.
The Benefits of Scaling Over Traditional Growth
Scaling enables businesses to increase revenue exponentially without a corresponding rise in costs, maximizing profit margins and operational efficiency. By leveraging technology and streamlined processes, companies can handle larger market demands swiftly while maintaining quality. This approach offers sustainable expansion, minimizing resource strain compared to traditional linear growth models.
Common Challenges in Scaling a Business
Scaling a business often encounters challenges such as maintaining consistent cash flow, optimizing operational processes, and managing workforce expansion while preserving company culture. Rapid scaling can strain resources, leading to inefficiencies and decreased customer satisfaction if systems are not adapted properly. Entrepreneurs must prioritize robust infrastructure and scalable technology solutions to support sustainable growth trajectories.
Strategies for Sustainable Business Growth
Sustainable business growth requires balancing scaling strategies that optimize operational efficiency with growth approaches that expand market reach and customer base. Implementing scalable systems, investing in technology, and maintaining strong financial management are essential to support long-term expansion without compromising quality. Prioritizing customer retention, innovation, and adaptive leadership drives consistent value creation and competitive advantage.
When to Focus on Scaling Instead of Growth
Focus on scaling instead of growth when the business model is proven and processes are standardized, enabling efficient replication without proportional increases in costs. Emphasize automation, technology integration, and optimizing operational capacity to handle increased demand seamlessly. Prioritizing scaling maximizes profitability by leveraging fixed resources and expanding output without significant additional investment.
Operational Efficiency: The Heart of Scaling
Operational efficiency is the cornerstone of scaling a business, enabling sustainable expansion without proportional increases in resources. Streamlining processes, optimizing workflow automation, and leveraging data analytics reduce costs while maintaining quality and output. This strategic focus differentiates scaling from mere growth by enhancing capacity and profitability through smarter operations.
Technology’s Role in Scaling vs. Growth
Technology accelerates scaling by automating processes, enhancing operational efficiency, and enabling rapid expansion without proportional increases in resources. Growth often relies on increased sales and market demand, while scaling leverages technology platforms, cloud computing, and AI to support larger volumes seamlessly. Companies employing scalable technologies maintain agility, reduce costs per unit, and sustain long-term competitive advantages beyond mere revenue growth.
Financial Implications: Scaling Costs vs. Growth Investment
Scaling a business often requires significant upfront costs related to infrastructure, technology, and workforce expansion, which can temporarily reduce profitability but enable higher operational efficiency and revenue capacity. Growth investment focuses more on market development, product diversification, and customer acquisition, typically involving ongoing expenses that aim to increase top-line revenue over time. Understanding the financial implications of scaling versus growth helps businesses allocate capital effectively to balance short-term cash flow pressures with long-term value creation.
Case Studies: Successful Scaling and Growth Stories
Case studies reveal that successful scaling requires replicable processes and robust infrastructure to handle increased demand without compromising quality. Growth stories often highlight strategic market expansion and customer acquisition as key drivers, with companies leveraging technology to optimize operations. Both scaling and growth are exemplified by firms like Amazon and Airbnb, which balance rapid market penetration with sustainable operational frameworks.
scaling vs growth Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com