Outsourcing leverages external expertise to reduce costs and increase flexibility, while insourcing maintains greater control over quality and internal processes. Businesses must weigh the advantages of specialized third-party services against the benefits of direct oversight and integration with company culture. Strategic decisions hinge on balancing efficiency, risk management, and long-term operational goals.
Table of Comparison
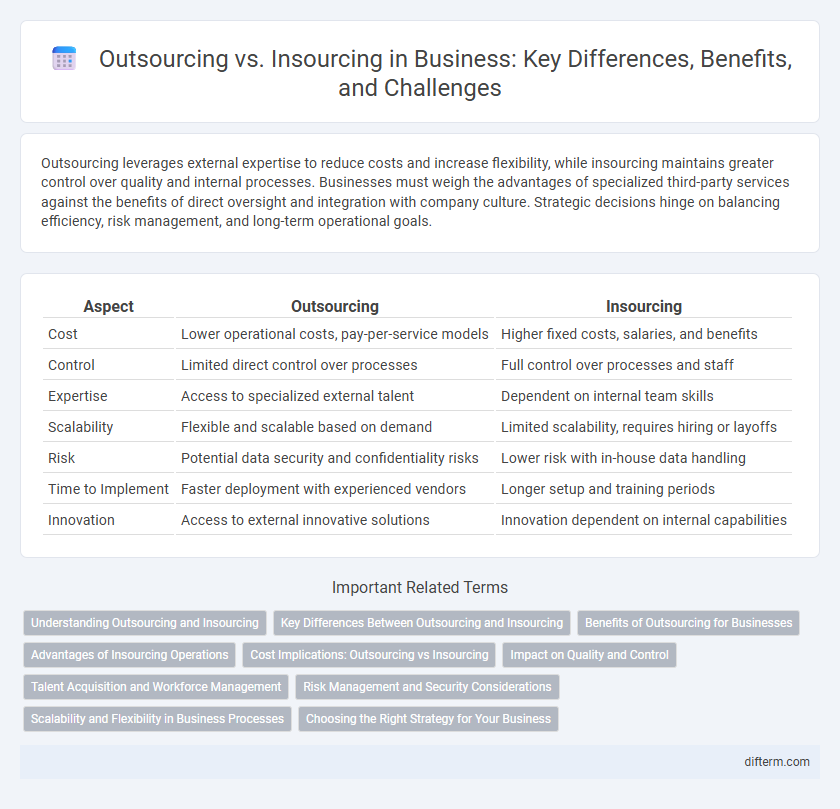
| Aspect | Outsourcing | Insourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower operational costs, pay-per-service models | Higher fixed costs, salaries, and benefits |
| Control | Limited direct control over processes | Full control over processes and staff |
| Expertise | Access to specialized external talent | Dependent on internal team skills |
| Scalability | Flexible and scalable based on demand | Limited scalability, requires hiring or layoffs |
| Risk | Potential data security and confidentiality risks | Lower risk with in-house data handling |
| Time to Implement | Faster deployment with experienced vendors | Longer setup and training periods |
| Innovation | Access to external innovative solutions | Innovation dependent on internal capabilities |
Understanding Outsourcing and Insourcing
Outsourcing involves delegating specific business functions or processes to external service providers, enabling companies to access specialized expertise and reduce operational costs. In contrast, insourcing relies on internal resources and employees to perform tasks, ensuring greater control over quality, security, and communication. Understanding the strategic implications of outsourcing and insourcing helps businesses optimize efficiency, scalability, and competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Key Differences Between Outsourcing and Insourcing
Outsourcing involves delegating business processes or functions to external third-party providers, optimizing cost-efficiency and access to specialized expertise. Insourcing retains these operations within the company, promoting greater control, quality assurance, and alignment with corporate culture. Key differences include cost structure, risk management, and flexibility, where outsourcing offers scalability and cost savings, while insourcing emphasizes direct oversight and internal resource investment.
Benefits of Outsourcing for Businesses
Outsourcing enables businesses to reduce operational costs by leveraging specialized external expertise and economies of scale, enhancing overall efficiency. It allows companies to focus on core competencies while accessing advanced technology and skilled labor without significant capital investment. Furthermore, outsourcing provides flexibility in scaling operations and managing risks associated with market fluctuations and employee turnover.
Advantages of Insourcing Operations
Insourcing operations enhances control over quality and proprietary processes, leading to improved product consistency and customer satisfaction. It fosters stronger team collaboration and knowledge retention within the company, boosting innovation and employee expertise. Maintaining operations internally reduces risks associated with data security and regulatory compliance, ensuring better protection of sensitive information.
Cost Implications: Outsourcing vs Insourcing
Outsourcing often reduces labor and operational costs by leveraging external providers in lower-cost regions, enabling businesses to convert fixed costs into variable costs. Insourcing, while typically involving higher upfront investment in infrastructure and salaries, offers greater control over quality and process efficiency. Careful cost-benefit analysis of hidden expenses such as management overhead, communication barriers, and potential delays is crucial when comparing outsourcing vs insourcing financial implications.
Impact on Quality and Control
Outsourcing often challenges quality control due to reliance on external vendors with varying standards, which can lead to inconsistent product or service outcomes. Insourcing enhances quality assurance by granting businesses direct oversight, enabling stricter adherence to organizational standards and faster issue resolution. Prioritizing control through insourcing supports consistent quality but may increase operational costs compared to outsourcing models.
Talent Acquisition and Workforce Management
Outsourcing talent acquisition enables businesses to access specialized recruitment expertise and reduce operational costs, while insourcing facilitates deeper alignment with company culture and strategic workforce planning. Workforce management in outsourcing often leverages external technology platforms and scalable resources, whereas insourcing allows for direct control over employee development and retention strategies. Companies must evaluate factors such as cost-efficiency, quality of hires, and long-term talent engagement when choosing between outsourcing and insourcing.
Risk Management and Security Considerations
Outsourcing business functions introduces third-party risks, including data breaches and compliance challenges, requiring rigorous vendor risk assessments and security protocols. Insourcing allows for greater control over sensitive information and internal risk management processes, enhancing the ability to enforce company-specific security policies. Balancing these approaches depends on the organization's capacity to manage cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, and operational risks effectively.
Scalability and Flexibility in Business Processes
Outsourcing enhances scalability by allowing businesses to quickly adjust resources according to demand fluctuations without the burden of long-term commitments. Insourcing provides greater flexibility in aligning business processes with internal goals and maintaining direct control over quality and workflow adaptations. Combining both strategies can optimize operational efficiency by leveraging the scalability of external providers and the customization benefits of in-house teams.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business
Selecting the optimal strategy between outsourcing and insourcing depends on factors such as cost efficiency, control over processes, and access to specialized expertise. Outsourcing can reduce operational expenses and provide scalability, while insourcing ensures greater control over quality and alignment with corporate culture. Businesses must evaluate project complexity, resource availability, and long-term goals to determine the most effective approach for sustainable growth.
outsourcing vs insourcing Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com