A co-founder is an individual who actively participates in establishing a business from inception, sharing significant responsibilities and equity. A founding member may join the company shortly after its creation and contribute to its development, often with less influence or ownership compared to a co-founder. Understanding the distinction is crucial for defining roles, authority, and equity distribution within a startup.
Table of Comparison
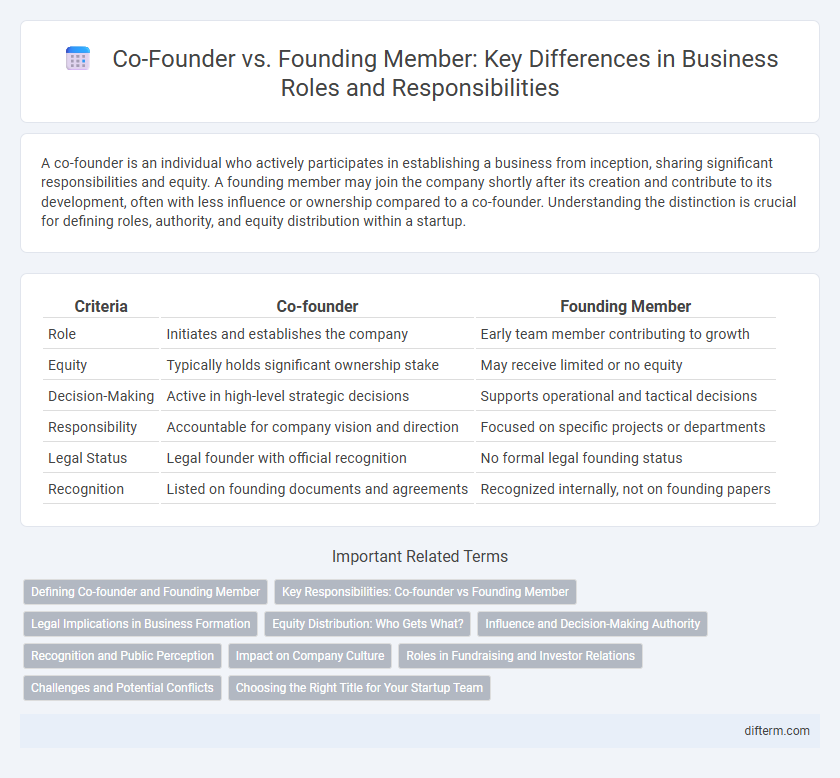
| Criteria | Co-founder | Founding Member |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Initiates and establishes the company | Early team member contributing to growth |
| Equity | Typically holds significant ownership stake | May receive limited or no equity |
| Decision-Making | Active in high-level strategic decisions | Supports operational and tactical decisions |
| Responsibility | Accountable for company vision and direction | Focused on specific projects or departments |
| Legal Status | Legal founder with official recognition | No formal legal founding status |
| Recognition | Listed on founding documents and agreements | Recognized internally, not on founding papers |
Defining Co-founder and Founding Member
A co-founder is an individual who actively participates in the initial creation and strategic direction of a startup, often contributing significant capital, ideas, or leadership. A founding member, while integral to the early phase of the company, may join slightly later or have a less prominent role in decision-making and equity distribution. Clear distinctions in legal agreements and ownership stakes often differentiate co-founders from founding members in business structures.
Key Responsibilities: Co-founder vs Founding Member
Co-founders typically hold equity stakes and are responsible for establishing the company's vision, securing initial funding, and making high-level strategic decisions. Founding members contribute by executing operational tasks, building core products, and supporting the growth framework without necessarily having equity or decision-making power. Clear delineation of responsibilities between co-founders and founding members ensures efficient startup development and role accountability.
Legal Implications in Business Formation
A co-founder holds a formal legal status as a principal owner with specific rights and responsibilities outlined in founding documents, whereas a founding member may lack official recognition in legal agreements, affecting equity distribution and decision-making authority. Legal implications in business formation require clear differentiation to prevent disputes over ownership stakes, intellectual property, and fiduciary duties. Properly defining roles and documenting agreements ensures compliance with corporate laws and protects all parties' interests during the startup phase.
Equity Distribution: Who Gets What?
Equity distribution between co-founders and founding members varies significantly, with co-founders typically receiving larger shares due to their critical role in establishing the company and contributing initial capital. Founding members, who join after the company is established or contribute less capital, often receive smaller equity portions as compensation for their involvement. Clear agreements and documented equity splits are essential to prevent disputes and ensure fair ownership distribution among all parties.
Influence and Decision-Making Authority
Co-founders typically hold significant influence and primary decision-making authority in a startup, shaping the company's vision, strategy, and key operational choices. Founding members contribute to the early development and growth but usually have more limited authority compared to co-founders, often focusing on specific roles or departments. The distinction lies in the level of control and responsibility, with co-founders driving core governance and founding members supporting execution within the agreed framework.
Recognition and Public Perception
Co-founders receive higher recognition and public visibility as key architects of a business, often being credited with the company's inception and strategic vision. Founding members contribute significantly to early development but typically occupy supportive roles with less media and stakeholder attention. This distinction affects personal branding and can influence opportunities for future ventures and leadership positions.
Impact on Company Culture
Co-founders typically play a pivotal role in shaping company culture through their vision, values, and leadership style, setting the tone from inception. Founding members contribute significantly by embedding those cultural elements into daily operations, fostering cohesion and a sense of shared purpose. The dynamic between co-founders and founding members often determines the company's cultural resilience and adaptability during growth phases.
Roles in Fundraising and Investor Relations
Co-founders typically hold primary responsibility for leading fundraising efforts and managing key investor relationships, leveraging their strategic vision and equity stakes to secure capital. Founding members often support these initiatives by contributing expertise, expanding networks, and assisting in due diligence processes, though they may have less influence in high-level negotiations. Clear role delineation between co-founders and founding members ensures efficient capital acquisition and robust investor engagement throughout the business lifecycle.
Challenges and Potential Conflicts
Co-founders often face challenges related to equity distribution, decision-making authority, and public recognition, which can lead to potential conflicts if roles and responsibilities are not clearly defined from the outset. Founding members may struggle with ambiguity in their influence and contributions, creating tensions around their status and rewards compared to co-founders. Clear communication and formal agreements are critical to mitigating disputes and ensuring alignment among all key stakeholders in early-stage startups.
Choosing the Right Title for Your Startup Team
Choosing between Co-founder and Founding Member titles impacts startup equity distribution, decision-making authority, and investor perception. Co-founders typically hold significant ownership stakes and are deeply involved in strategic decisions, whereas founding members may have smaller equity shares and more specialized roles. Clarifying these distinctions ensures clear team roles and aligns expectations as the startup scales.
Co-founder vs Founding Member Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com