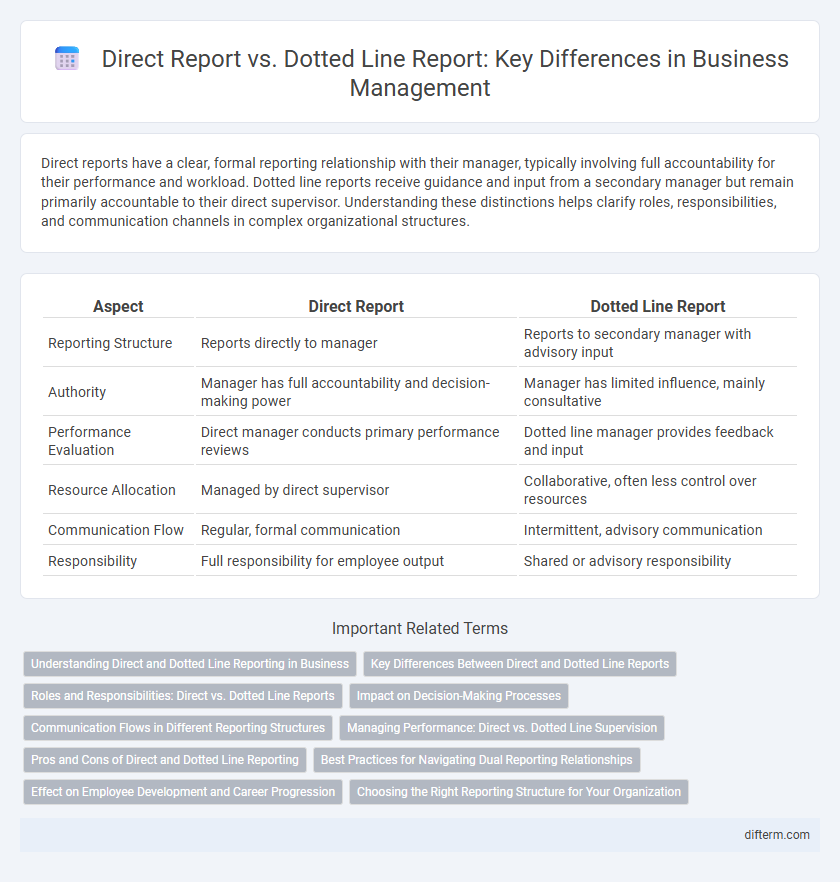
Direct reports have a clear, formal reporting relationship with their manager, typically involving full accountability for their performance and workload. Dotted line reports receive guidance and input from a secondary manager but remain primarily accountable to their direct supervisor. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify roles, responsibilities, and communication channels in complex organizational structures.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Direct Report | Dotted Line Report |
|---|---|---|
| Reporting Structure | Reports directly to manager | Reports to secondary manager with advisory input |
| Authority | Manager has full accountability and decision-making power | Manager has limited influence, mainly consultative |
| Performance Evaluation | Direct manager conducts primary performance reviews | Dotted line manager provides feedback and input |
| Resource Allocation | Managed by direct supervisor | Collaborative, often less control over resources |
| Communication Flow | Regular, formal communication | Intermittent, advisory communication |
| Responsibility | Full responsibility for employee output | Shared or advisory responsibility |
Understanding Direct and Dotted Line Reporting in Business
Direct reports have formal, clear lines of authority where employees report directly to a manager responsible for performance evaluations and daily oversight. Dotted line reports signify indirect relationships, often reflecting advisory or collaborative responsibilities without primary accountability for employee outcomes. Understanding these distinctions clarifies roles, enhances communication, and ensures effective organizational structure in business management.
Key Differences Between Direct and Dotted Line Reports
Direct reports have a formal reporting relationship with a manager, involving clear accountability for performance, objectives, and daily supervision. Dotted line reports maintain a secondary or advisory relationship, often collaborating across functions without full managerial authority or responsibility for performance reviews. The key differences lie in the clarity of authority, responsibility for outcomes, and level of supervision each report type entails.
Roles and Responsibilities: Direct vs. Dotted Line Reports
Direct reports have clear, primary accountability for performance, receiving formal instruction, evaluations, and career development guidance from their manager. Dotted line reports involve a secondary, less formal reporting relationship where roles focus on collaboration, advice, or matrix leadership without direct accountability for performance outcomes. Managers of direct reports hold authority over assignments and appraisals, while those overseeing dotted line reports influence decision-making through coordination and support functions.
Impact on Decision-Making Processes
Direct reports have clear accountability, enabling faster and more decisive decision-making within their primary team or department. Dotted line reports influence decisions through advisory or collaborative roles but often require coordination across multiple units, which can slow down processes. Understanding the distinction in reporting structures helps organizations optimize decision efficiency and clarify responsibility boundaries.
Communication Flows in Different Reporting Structures
Direct reports typically have clear, formal communication channels with their managers, facilitating direct and immediate feedback on performance and tasks. Dotted line reports often require more flexible communication flows, involving coordination between multiple supervisors to align goals and expectations effectively. Effective communication in these structures enhances collaboration, ensures clarity in responsibilities, and reduces potential conflicts arising from dual reporting lines.
Managing Performance: Direct vs. Dotted Line Supervision
Direct reports receive formal performance evaluations and clear accountability, enabling managers to set specific goals, deliver regular feedback, and enforce consequences. Dotted line reports involve collaborative oversight where influence is shared, requiring nuanced communication to align expectations and support development without formal authority. Effective management in both structures depends on clarity in roles, consistent feedback loops, and mutual understanding of performance objectives.
Pros and Cons of Direct and Dotted Line Reporting
Direct reporting ensures clear accountability and streamlined communication, fostering strong leadership oversight and quicker decision-making. Dotted line reporting offers flexibility and cross-functional collaboration but may create ambiguity in authority and conflicting priorities. Balancing direct and dotted line reports enhances organizational agility but requires careful management to avoid confusion and maintain consistent performance standards.
Best Practices for Navigating Dual Reporting Relationships
Establish clear communication channels and define roles explicitly to manage direct report versus dotted line report relationships effectively. Implement regular alignment meetings to ensure accountability and avoid conflicting priorities between managers. Leverage centralized performance metrics and feedback systems to create transparency and support collaborative decision-making across dual reporting lines.
Effect on Employee Development and Career Progression
Direct reports typically receive clear guidance, consistent feedback, and targeted performance evaluations from their primary manager, which enhances focused skill development and career growth. In contrast, dotted line reports experience varied input and less consolidated support, potentially leading to fragmented development opportunities and slower career advancement. Structured mentorship and aligned objectives in direct reporting relationships significantly contribute to more effective employee development and clearer career progression paths.
Choosing the Right Reporting Structure for Your Organization
Choosing the right reporting structure hinges on clarity in roles and accountability, where direct reports ensure clear authority and performance evaluation, while dotted line reports provide cross-functional collaboration and advisory input without full managerial control. Organizations benefit by aligning reporting types with their strategic goals, promoting efficiency through direct oversight and flexibility through matrix relationships. Prioritizing communication channels and decision-making protocols optimizes the impact of both direct and dotted line reporting on organizational success.
direct report vs dotted line report Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com