Wet sump lubrication stores engine oil in a pan beneath the crankshaft, providing simplicity and cost-effectiveness for most automotive applications. Dry sump lubrication uses external reservoirs and multiple scavenging pumps to ensure consistent oil delivery under high-performance conditions, preventing oil starvation in aggressive driving or racing scenarios. This system also improves engine reliability and allows for lower engine placement, enhancing vehicle handling.
Table of Comparison
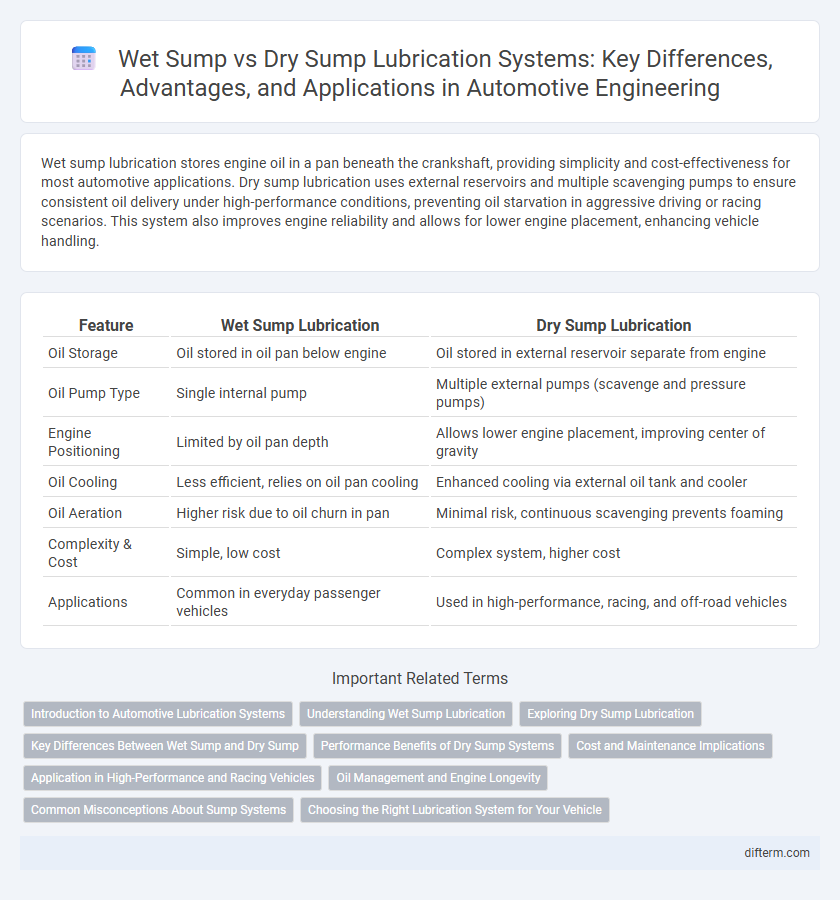
| Feature | Wet Sump Lubrication | Dry Sump Lubrication |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Storage | Oil stored in oil pan below engine | Oil stored in external reservoir separate from engine |
| Oil Pump Type | Single internal pump | Multiple external pumps (scavenge and pressure pumps) |
| Engine Positioning | Limited by oil pan depth | Allows lower engine placement, improving center of gravity |
| Oil Cooling | Less efficient, relies on oil pan cooling | Enhanced cooling via external oil tank and cooler |
| Oil Aeration | Higher risk due to oil churn in pan | Minimal risk, continuous scavenging prevents foaming |
| Complexity & Cost | Simple, low cost | Complex system, higher cost |
| Applications | Common in everyday passenger vehicles | Used in high-performance, racing, and off-road vehicles |
Introduction to Automotive Lubrication Systems
Wet sump lubrication systems store engine oil in a pan beneath the crankshaft, ensuring continuous oil circulation through a simple pump design ideal for standard passenger vehicles. Dry sump systems utilize an external reservoir and multiple scavenging pumps to manage oil flow, offering superior cooling and lubrication under high-performance or extreme driving conditions. Choosing between wet and dry sump lubrication directly impacts engine efficiency, reliability, and maintenance in automotive applications.
Understanding Wet Sump Lubrication
Wet sump lubrication stores engine oil in a pan beneath the crankshaft, allowing the oil pump to circulate it through the engine components for cooling and lubrication. This system is simpler, more cost-effective, and commonly used in passenger cars and motorcycles due to its compact design and ease of maintenance. Wet sump systems can face oil starvation during high-performance driving, but advances in baffle design and oil pan shape help mitigate this risk.
Exploring Dry Sump Lubrication
Dry sump lubrication systems utilize an external reservoir to store oil, ensuring consistent oil pressure and superior cooling, especially under high-performance driving conditions. This method reduces oil starvation risks by actively scavenging oil from the engine crankcase, enhancing engine reliability and longevity in racing and off-road vehicles. The improved oil control and reduced windage losses contribute to increased horsepower and efficiency compared to traditional wet sump systems.
Key Differences Between Wet Sump and Dry Sump
Wet sump lubrication stores engine oil in a pan beneath the engine, relying on a single oil pump to circulate oil, making it simpler and more cost-effective but less effective in high-performance or off-road conditions. Dry sump lubrication uses external reservoirs and multiple scavenging pumps to circulate oil, providing superior oil control, reduced engine wear, and improved performance under extreme conditions. The key differences include oil storage location, pump complexity, system cost, and performance suitability in demanding automotive applications.
Performance Benefits of Dry Sump Systems
Dry sump lubrication systems significantly enhance engine performance by maintaining consistent oil pressure during high-speed cornering and acceleration, preventing oil starvation common in wet sump systems. This system reduces parasitic drag on the engine through improved oil scavenging and allows for a lower engine placement, lowering the vehicle's center of gravity and improving handling dynamics. The increased oil capacity and superior cooling efficiency of dry sump setups also contribute to prolonged engine durability under extreme driving conditions.
Cost and Maintenance Implications
Wet sump lubrication systems generally have lower upfront costs and simpler maintenance due to their integrated oil pan design, making them suitable for standard passenger vehicles. Dry sump systems, while more expensive initially, offer extended engine life and reduced oil starvation risk through external oil reservoirs and multiple scavenge pumps, necessitating specialized maintenance and higher operational complexity. Choosing between these systems involves balancing cost-efficiency and long-term durability, particularly in high-performance or racing automotive applications.
Application in High-Performance and Racing Vehicles
Wet sump lubrication systems are commonly used in standard high-performance vehicles due to their simpler design and lower cost, efficiently delivering oil to critical engine components under moderate g-forces. Dry sump lubrication is preferred in racing vehicles and extreme-performance applications because it prevents oil starvation during high lateral acceleration, maintaining consistent oil pressure and improving engine reliability. The dry sump setup also reduces engine drag and allows for a lower center of gravity by eliminating the oil pan, directly benefiting vehicle handling and performance on the track.
Oil Management and Engine Longevity
Wet sump lubrication stores engine oil in a pan beneath the crankshaft, offering simpler design and lower cost but potential oil starvation during high-performance or off-road driving. Dry sump systems use external reservoirs and multiple scavenging pumps to maintain consistent oil pressure and effective heat dissipation, significantly reducing engine wear and enhancing longevity. Optimal oil management in dry sump lubrication prevents oil aeration and ensures constant lubrication under extreme conditions, improving overall engine reliability and performance.
Common Misconceptions About Sump Systems
Many assume wet sump systems always cause oil starvation during high-performance driving, but modern designs often include baffling to mitigate this risk. Dry sump systems are frequently believed to be necessary only for racing applications, although they enhance lubrication and engine longevity in various high-stress automotive contexts. The notion that dry sump setups are prohibitively expensive is misleading, as advancements have made them more accessible for performance street vehicles.
Choosing the Right Lubrication System for Your Vehicle
Wet sump lubrication features oil stored in a pan beneath the engine, offering simplicity and lower cost ideal for everyday passenger cars and lower-performance vehicles. Dry sump lubrication uses external reservoirs and multiple pumps, providing superior oil control and cooling, essential for high-performance, racing, or off-road vehicles operating under extreme conditions. Selecting the appropriate system depends on engine design, driving conditions, and performance requirements to ensure optimal lubrication and engine longevity.
Wet Sump vs Dry Sump Lubrication Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com