Turbocharged engines use exhaust gases to spin a turbine, providing increased power and better fuel efficiency by recovering energy that would otherwise be wasted. Supercharged engines rely on a belt-driven compressor connected directly to the engine, delivering immediate boost and improved throttle response at the expense of some additional fuel consumption. Choosing between turbocharged and supercharged systems depends on whether priority is placed on fuel economy or instant power delivery in performance vehicles.
Table of Comparison
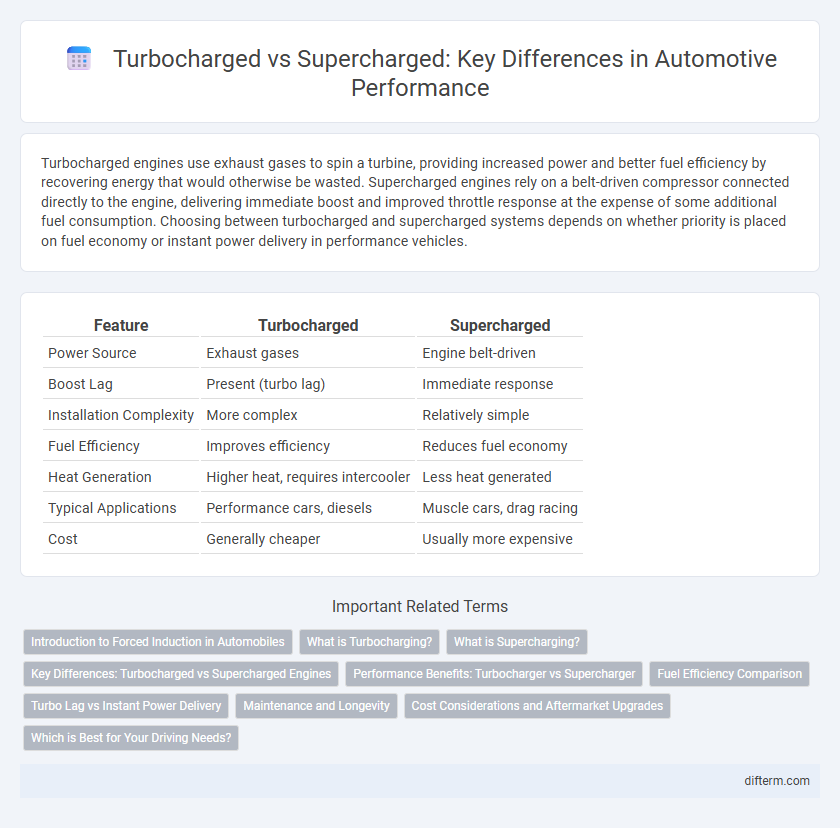
| Feature | Turbocharged | Supercharged |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Exhaust gases | Engine belt-driven |
| Boost Lag | Present (turbo lag) | Immediate response |
| Installation Complexity | More complex | Relatively simple |
| Fuel Efficiency | Improves efficiency | Reduces fuel economy |
| Heat Generation | Higher heat, requires intercooler | Less heat generated |
| Typical Applications | Performance cars, diesels | Muscle cars, drag racing |
| Cost | Generally cheaper | Usually more expensive |
Introduction to Forced Induction in Automobiles
Forced induction in automobiles enhances engine performance by increasing air intake pressure, allowing more fuel combustion and greater power output. Turbochargers utilize exhaust gas energy to spin a turbine and compress intake air, improving efficiency and reducing lag, while superchargers are mechanically driven by the engine, delivering immediate boost at low RPMs. Both systems optimize power and torque, but turbochargers typically provide better fuel economy and higher peak performance in modern vehicles.
What is Turbocharging?
Turbocharging is a forced induction system that uses exhaust gases to spin a turbine, which drives a compressor to increase air intake pressure into the engine. This process boosts engine power and efficiency by delivering more oxygen for combustion without significantly increasing engine weight. Turbochargers are widely used in modern vehicles to enhance performance while improving fuel economy and reducing emissions.
What is Supercharging?
Supercharging is a forced induction method that increases an engine's power output by compressing air and delivering it to the combustion chamber, improving combustion efficiency. Unlike turbochargers that rely on exhaust gas energy, superchargers are mechanically driven by the engine, providing instant boost without lag. This results in enhanced acceleration and responsiveness, making superchargers ideal for high-performance automotive applications.
Key Differences: Turbocharged vs Supercharged Engines
Turbocharged engines utilize exhaust gases to spin a turbine, increasing air intake and improving fuel efficiency, while supercharged engines rely on a belt-driven compressor directly connected to the crankshaft for immediate power delivery. Turbochargers generally provide better fuel economy and higher peak power, but superchargers offer more consistent boost and quicker throttle response. The choice between turbocharged and supercharged systems depends on driving preferences, with turbos favored for efficiency and high-end power, and superchargers preferred for low-end torque and instant acceleration.
Performance Benefits: Turbocharger vs Supercharger
Turbochargers enhance engine performance by utilizing exhaust gases to increase air intake, delivering higher horsepower and improved fuel efficiency compared to superchargers. Superchargers provide instant boost and better throttle response due to their mechanical connection to the engine, benefiting low-end torque and acceleration. While turbochargers excel at high RPM power and efficiency, superchargers dominate in immediate power delivery and consistent boost across all engine speeds.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison
Turbocharged engines generally offer better fuel efficiency compared to supercharged engines because they utilize exhaust gases to spin the turbine, reducing the need for additional engine power. Superchargers are mechanically driven by the engine, which can increase fuel consumption due to the extra load on the crankshaft. Studies show that turbocharged vehicles achieve higher miles per gallon (MPG) ratings, making them more favorable for fuel-conscious drivers.
Turbo Lag vs Instant Power Delivery
Turbocharged engines experience turbo lag due to the time required for exhaust gases to spool the turbine, causing a delay in power delivery. Supercharged engines provide instant power delivery as the compressor is mechanically driven by the engine, eliminating lag. This difference significantly impacts acceleration responsiveness and throttle control in performance vehicles.
Maintenance and Longevity
Turbocharged engines typically require more frequent oil changes and careful heat management to maintain longevity, as the turbocharger operates under high temperatures and pressures. Supercharged engines tend to have simpler maintenance due to their belt-driven design, but the supercharger belt and associated components need regular inspection and replacement to ensure durability. Both systems benefit from high-quality lubricants and scheduled maintenance to prevent premature wear and extend engine life.
Cost Considerations and Aftermarket Upgrades
Turbocharged systems generally offer better cost-efficiency due to their smaller size and use of exhaust gases, resulting in lower initial installation expenses compared to supercharged setups. Aftermarket upgrades for turbochargers are widely available, providing options for increased boost, intercoolers, and electronic tuning, which can enhance performance without extensive mechanical modifications. Superchargers require more robust engine components and a direct drive belt, often leading to higher upgrade and maintenance costs in the aftermarket scene.
Which is Best for Your Driving Needs?
Turbocharged engines offer improved fuel efficiency and greater power at high RPMs by utilizing exhaust gases to spin the turbine, making them ideal for drivers seeking fuel economy and highway performance. Supercharged engines provide instant boost and consistent power delivery regardless of RPM, better suited for drivers needing immediate throttle response and strong low-end torque, such as in off-road or towing scenarios. Evaluating your driving style, terrain, and performance priorities helps determine whether a turbocharged or supercharged setup best aligns with your automotive needs.
turbocharged vs supercharged Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com