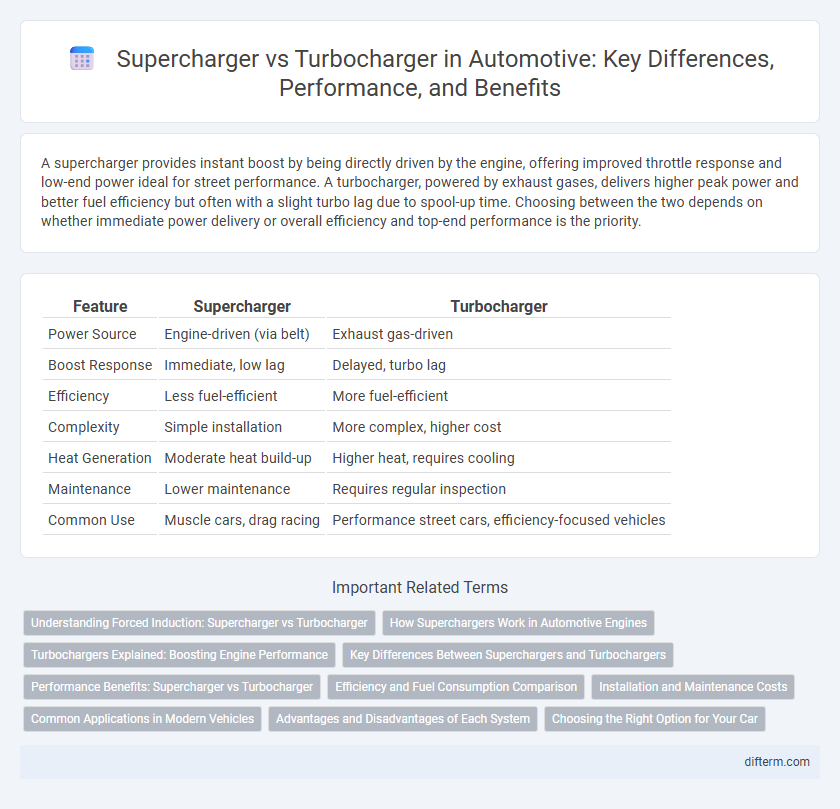
A supercharger provides instant boost by being directly driven by the engine, offering improved throttle response and low-end power ideal for street performance. A turbocharger, powered by exhaust gases, delivers higher peak power and better fuel efficiency but often with a slight turbo lag due to spool-up time. Choosing between the two depends on whether immediate power delivery or overall efficiency and top-end performance is the priority.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Supercharger | Turbocharger |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Engine-driven (via belt) | Exhaust gas-driven |
| Boost Response | Immediate, low lag | Delayed, turbo lag |
| Efficiency | Less fuel-efficient | More fuel-efficient |
| Complexity | Simple installation | More complex, higher cost |
| Heat Generation | Moderate heat build-up | Higher heat, requires cooling |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance | Requires regular inspection |
| Common Use | Muscle cars, drag racing | Performance street cars, efficiency-focused vehicles |
Understanding Forced Induction: Supercharger vs Turbocharger
Forced induction enhances engine power by increasing air intake pressure, with superchargers and turbochargers as the primary technologies. Superchargers are belt-driven by the engine, providing immediate boost and improved throttle response, but they consume engine power. Turbochargers utilize exhaust gases to spin a turbine, offering greater efficiency and higher boost potential, though they may experience lag before delivering full power.
How Superchargers Work in Automotive Engines
Superchargers in automotive engines operate by using a belt-driven compressor connected directly to the engine crankshaft to force more air into the combustion chamber, increasing air density and oxygen supply. This process results in higher engine power and improved throttle response due to immediate boost delivery without lag. Unlike turbochargers, superchargers provide consistent boost at low RPMs, enhancing acceleration and overall engine performance.
Turbochargers Explained: Boosting Engine Performance
Turbochargers increase engine performance by using exhaust gases to spin a turbine, compressing the intake air and delivering more oxygen to the combustion chamber. This process enhances power output and fuel efficiency compared to naturally aspirated engines, making turbochargers a popular choice in modern automotive applications. Turbochargers typically provide better low-end torque and reduced lag when engineered with advanced materials and variable geometry technology.
Key Differences Between Superchargers and Turbochargers
Superchargers deliver instant power by being mechanically driven off the engine's crankshaft, providing immediate boost without lag, while turbochargers rely on exhaust gas to spin a turbine, which can cause a slight delay known as turbo lag. Superchargers typically consume more engine power due to their direct mechanical connection, whereas turbochargers improve fuel efficiency by utilizing otherwise wasted exhaust energy. The choice between a supercharger and a turbocharger significantly impacts engine responsiveness, fuel economy, and overall vehicle performance.
Performance Benefits: Supercharger vs Turbocharger
Superchargers deliver instant boost by being directly driven by the engine, providing immediate throttle response and enhanced low-end torque for rapid acceleration. Turbochargers utilize exhaust gases to spin a turbine, offering higher peak power and better fuel efficiency through improved air intake under high RPM conditions. While superchargers excel in low-speed performance, turbochargers dominate in maximizing overall engine output and efficiency at elevated speeds.
Efficiency and Fuel Consumption Comparison
Superchargers provide immediate boost by directly driven belt systems, enhancing low-end torque but often resulting in higher fuel consumption due to continuous engine load. Turbochargers utilize exhaust gases to spool up, improving efficiency and fuel economy by recovering otherwise wasted energy and reducing engine pumping losses. Vehicles equipped with turbochargers typically achieve better fuel efficiency under varied driving conditions compared to supercharged counterparts.
Installation and Maintenance Costs
Superchargers typically have higher installation costs due to their direct connection to the engine, requiring more complex modifications and custom fittings. Maintenance expenses for superchargers can be lower since they operate via belt drive and have fewer heat-related components compared to turbochargers. Turbochargers often incur higher maintenance costs due to their reliance on exhaust gases, which increase wear on turbine components and necessitate more frequent oil changes and inspections.
Common Applications in Modern Vehicles
Superchargers are commonly found in muscle cars and high-performance vehicles due to their ability to provide immediate power boost with minimal lag. Turbochargers are widely used in modern passenger cars and trucks, enhancing fuel efficiency and power by utilizing exhaust gas energy. Many manufacturers integrate turbochargers in smaller displacement engines to meet stringent emissions regulations while maintaining performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each System
Superchargers provide immediate power boost with no lag due to mechanical drive from the engine, enhancing low-end torque and throttle response; however, they consume engine power, reducing overall efficiency. Turbochargers increase engine power by utilizing exhaust gases, improving fuel efficiency and high-end performance but often suffer from turbo lag, delaying boost response. Choosing between superchargers and turbochargers depends on the desired balance of power delivery, efficiency, and engine responsiveness in automotive applications.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Car
Selecting between a supercharger and a turbocharger depends on your car's performance goals and engine compatibility; superchargers provide immediate, consistent boost through belt-driven compression, ideal for low-end torque and linear acceleration. Turbochargers utilize exhaust gases to spin a turbine, offering greater top-end power and efficiency but with potential turbo lag, making them preferred for fuel economy and high-speed performance. Consider your driving style, engine layout, and desired power delivery to determine the optimal forced induction system for enhanced automotive performance.
supercharger vs turbocharger Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com