Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) offer rapid gear shifts and improved driving dynamics by using two separate clutches for odd and even gears, resulting in enhanced acceleration and fuel efficiency. Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) provide seamless and stepless gear ratios, optimizing engine performance for smoother rides and better fuel economy in stop-and-go traffic. Choosing between DCT and CVT depends on prioritizing sporty performance with quick gear changes or prioritizing smoothness and efficiency in daily commutes.
Table of Comparison
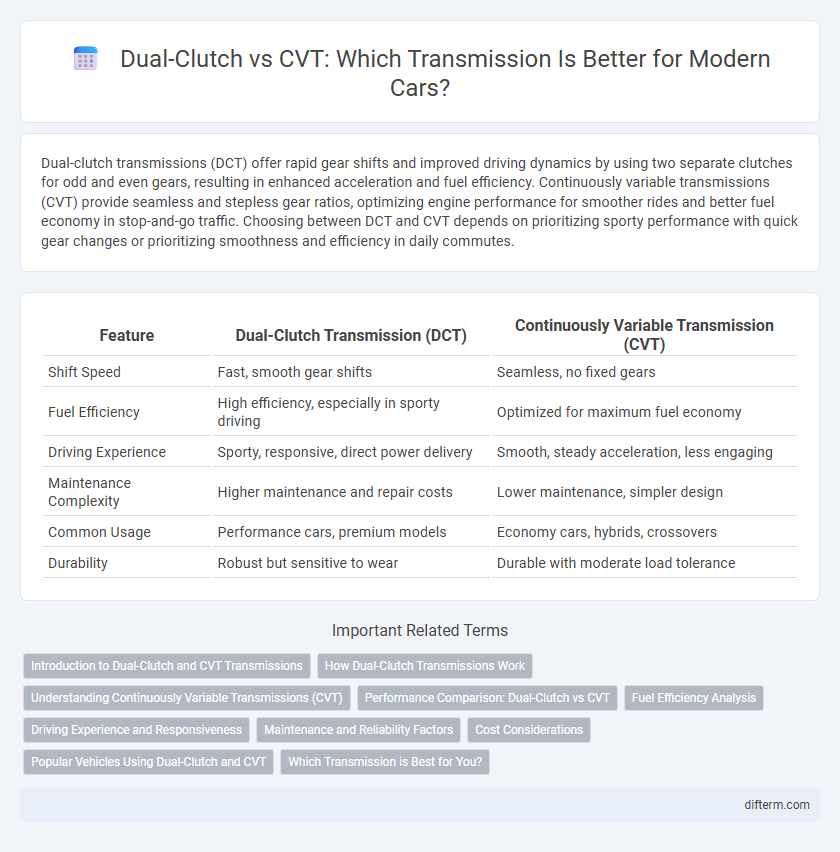
| Feature | Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT) | Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) |
|---|---|---|
| Shift Speed | Fast, smooth gear shifts | Seamless, no fixed gears |
| Fuel Efficiency | High efficiency, especially in sporty driving | Optimized for maximum fuel economy |
| Driving Experience | Sporty, responsive, direct power delivery | Smooth, steady acceleration, less engaging |
| Maintenance Complexity | Higher maintenance and repair costs | Lower maintenance, simpler design |
| Common Usage | Performance cars, premium models | Economy cars, hybrids, crossovers |
| Durability | Robust but sensitive to wear | Durable with moderate load tolerance |
Introduction to Dual-Clutch and CVT Transmissions
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) use two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets, enabling faster and smoother gear changes compared to traditional automatics. Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) provide seamless acceleration by using a belt and pulley system to offer an infinite range of gear ratios, optimizing fuel efficiency and engine performance. Both technologies enhance driving experience but cater to different priorities: DCTs emphasize sportier performance, while CVTs focus on fuel economy and comfort.
How Dual-Clutch Transmissions Work
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) use two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets, enabling rapid and seamless gear shifts without interrupting power delivery. This system pre-selects the next gear while the current gear is engaged, allowing smoother acceleration and improved fuel efficiency compared to traditional automatic transmissions. DCT technology enhances driving performance by reducing shift times and minimizing torque loss during gear changes.
Understanding Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT)
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT) offer seamless acceleration by using a system of belts and pulleys that provide an infinite range of gear ratios, enhancing fuel efficiency and smooth driving experience in modern vehicles. Unlike dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) that rely on multiple gears and clutches for rapid gear shifts, CVTs eliminate traditional gear changes, reducing mechanical complexity and maintenance costs. CVTs are favored in compact and hybrid cars for optimizing engine performance and contributing to lower emissions through consistently optimal engine speed.
Performance Comparison: Dual-Clutch vs CVT
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) deliver faster and more precise gear shifts compared to continuously variable transmissions (CVT), enhancing acceleration and driving dynamics. CVTs provide smoother, stepless acceleration but often sacrifice responsiveness and sporty performance due to their belt-driven design. High-performance vehicles typically favor dual-clutch systems for superior torque handling and quicker shift times, while CVTs excel in fuel efficiency and comfort-oriented driving.
Fuel Efficiency Analysis
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) deliver higher fuel efficiency than conventional automatics by enabling quicker gear shifts with minimal power loss. Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) optimize engine operation by maintaining ideal RPM levels, resulting in smoother acceleration and improved fuel economy in city driving. For highway cruising, DCTs often outperform CVTs due to their fixed gear ratios providing better power transfer and reduced energy wastage.
Driving Experience and Responsiveness
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) provide rapid, seamless gear shifts that enhance driving responsiveness and deliver a sporty, engaging experience favored in performance vehicles. Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) offer smooth, stepless acceleration optimizing fuel efficiency but may create a less direct and sometimes sluggish driving feel. Drivers seeking precise control and immediate throttle response typically prefer DCTs, while those prioritizing comfort and efficiency lean toward CVTs.
Maintenance and Reliability Factors
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) often require more frequent maintenance due to complex hydraulic systems and clutch wear, making them less reliable over long-term use compared to CVTs. Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT) have fewer moving parts, leading to lower maintenance costs and improved reliability, though belt or chain wear can still necessitate replacement. Evaluating factors such as fluid change intervals, component durability, and repair complexity is crucial for assessing the maintenance and reliability of these transmission types in automotive applications.
Cost Considerations
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) generally incur higher initial purchase and repair costs due to their complex mechanical design and electronic control systems compared to continuously variable transmissions (CVT). CVTs offer better fuel efficiency and lower maintenance expenses, making them a cost-effective option for budget-conscious consumers. For long-term ownership, CVTs tend to reduce total cost of ownership through fewer part replacements and smoother operation, especially in compact and mid-sized vehicles.
Popular Vehicles Using Dual-Clutch and CVT
Popular vehicles using dual-clutch transmissions include the Volkswagen Golf GTI, Ford Focus RS, and Audi S3, renowned for their rapid gear shifts and sporty driving dynamics. In contrast, many Toyota Prius models, Honda Accord hybrids, and Nissan Altima employ CVT systems, which prioritize fuel efficiency and smooth acceleration. Both transmission types cater to different driving preferences, with dual-clutch systems often found in performance-oriented vehicles and CVTs favored in eco-friendly and comfort-focused cars.
Which Transmission is Best for You?
Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) offer faster gear shifts and better fuel efficiency, making them ideal for drivers seeking sporty performance and precise control. Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT) provide smoother acceleration and improved fuel economy in stop-and-go city driving, perfect for urban commuters prioritizing comfort and efficiency. Choosing the best transmission depends on your driving style and the balance between performance and fuel savings you value most.
Dual-clutch vs CVT Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com