Sequential gearboxes offer faster and more direct shifts ideal for high-performance driving, while dual-clutch transmissions provide smooth, nearly seamless gear changes that enhance comfort and fuel efficiency. Sequential gearboxes are typically favored in racing environments for their robust design and quick manual control, whereas dual-clutch transmissions combine the convenience of an automatic with the responsiveness of a manual. Understanding these differences is crucial for automotive enthusiasts seeking either sport-oriented precision or everyday driving ease.
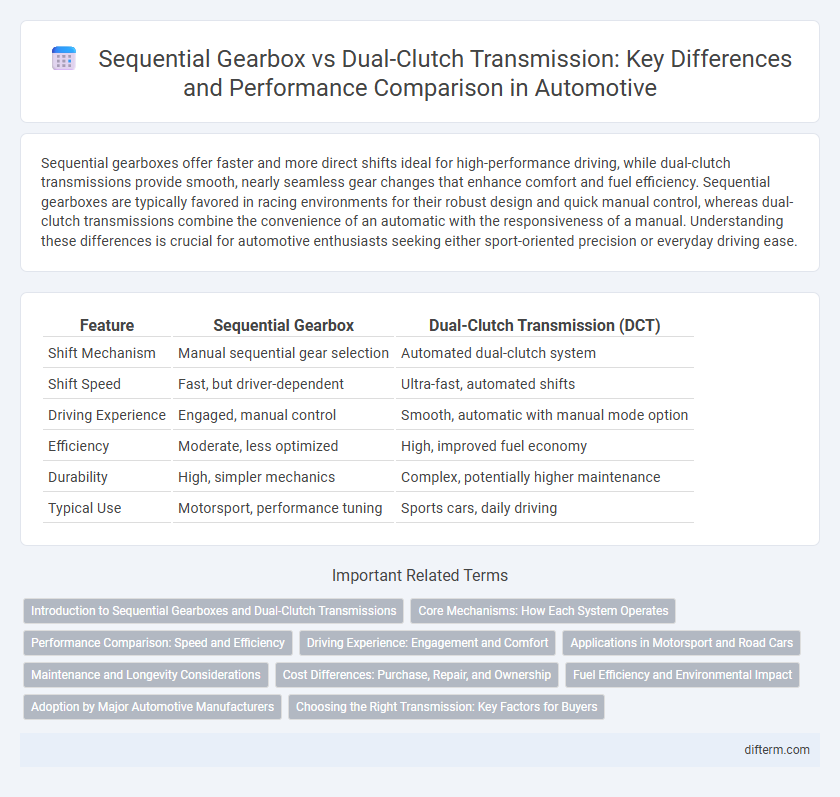
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sequential Gearbox | Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT) |
|---|---|---|
| Shift Mechanism | Manual sequential gear selection | Automated dual-clutch system |
| Shift Speed | Fast, but driver-dependent | Ultra-fast, automated shifts |
| Driving Experience | Engaged, manual control | Smooth, automatic with manual mode option |
| Efficiency | Moderate, less optimized | High, improved fuel economy |
| Durability | High, simpler mechanics | Complex, potentially higher maintenance |
| Typical Use | Motorsport, performance tuning | Sports cars, daily driving |
Introduction to Sequential Gearboxes and Dual-Clutch Transmissions
Sequential gearboxes utilize a straightforward mechanism where gears are engaged in a fixed order, allowing rapid gear shifts without the need to manually select each gear, commonly found in motorcycles and motorsport vehicles. Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) employ two separate clutches for odd and even gears, enabling seamless and fast gear changes with improved fuel efficiency and smoother driving performance in high-end sports cars and modern passenger vehicles. Both systems enhance driving dynamics, but sequential gearboxes prioritize shift speed and mechanical simplicity, while DCTs focus on combining efficiency and comfort.
Core Mechanisms: How Each System Operates
Sequential gearboxes use a linear shift pattern where gears are engaged one after another through a drum or ratchet mechanism, allowing rapid and precise gear changes ideal for racing applications. Dual-clutch transmissions (DCTs) employ two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets, enabling seamless and near-instantaneous gear shifts without interrupting torque delivery to the wheels. The sequential gearbox prioritizes mechanical simplicity and direct driver control, while the DCT combines electronic controls and hydraulics for optimized performance and fuel efficiency in modern vehicles.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Efficiency
Sequential gearboxes deliver rapid gear shifts with minimal interruption in power delivery, optimizing speed and driver control in high-performance automotive applications. Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) enhance efficiency by pre-selecting gears and allowing seamless shifts, reducing torque loss and improving fuel economy. While sequential gearboxes excel in track-focused speed and simplicity, DCTs provide superior balance between acceleration performance and everyday drivability.
Driving Experience: Engagement and Comfort
Sequential gearboxes provide a highly engaging driving experience with rapid, precise shifts that appeal to enthusiasts seeking control and feedback. Dual-clutch transmissions enhance comfort by delivering smooth, almost seamless gear changes that minimize interruption in power delivery. While sequential gearboxes excel in driver involvement, dual-clutch systems prioritize refinement and ease, making them suitable for both sporty and everyday driving.
Applications in Motorsport and Road Cars
Sequential gearboxes are favored in motorsport for their rapid, precise gear changes and simple mechanical design, enabling drivers to maintain focus and achieve faster lap times. Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) combine the efficiency of automated shifting with smoothness, making them popular in high-performance road cars such as the Audi R8 and Porsche 911 for enhanced driving dynamics and everyday usability. While sequential gearboxes dominate racecars like MotoGP and touring cars, DCTs bridge the gap between racing technology and consumer convenience in street-legal supercars.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Sequential gearboxes typically require less frequent clutch replacements due to their simpler design and durable components, making maintenance more straightforward and cost-effective over time. Dual-clutch transmissions demand regular software updates and fluid changes to ensure optimal performance, with potential for higher repair costs due to their complex mechatronic systems. Longevity of sequential gearboxes often exceeds that of dual-clutch transmissions in high-stress racing environments, while dual-clutch systems provide smoother shifts suited for everyday driving but may face earlier wear in harsh conditions.
Cost Differences: Purchase, Repair, and Ownership
Sequential gearboxes generally have a lower initial purchase cost compared to dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) due to simpler mechanical design and fewer components. Repair expenses for sequential gearboxes tend to be more affordable, as parts are less complex and easier to service, whereas DCT repairs often require specialized diagnostics and higher labor costs. Over the vehicle's lifespan, ownership costs for sequential gearboxes remain lower, driven by reduced maintenance requirements and improved durability, while DCT ownership can incur higher expenses linked to intricate technology and potential clutch replacements.
Fuel Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Sequential gearboxes typically offer better fuel efficiency due to their lighter weight and simpler mechanical design, which reduces energy losses during gear shifts. Dual-clutch transmissions (DCTs) provide faster, smoother shifts that optimize engine performance and fuel consumption, especially in urban driving conditions. Environmental impact is minimized in both systems by improved fuel economy, but DCTs often yield lower CO2 emissions thanks to their advanced control systems and reduced drivetrain drag.
Adoption by Major Automotive Manufacturers
Major automotive manufacturers widely adopt dual-clutch transmissions (DCTs) for their ability to deliver faster gear changes and improved fuel efficiency, as seen in brands like Volkswagen, Ford, and BMW. Sequential gearboxes remain prominent in motorsport and high-performance vehicles manufactured by companies such as Yamaha and Ducati due to their straightforward design and rapid shift capabilities. The trend in passenger vehicles favors DCTs because of consumer demand for smoother driving experiences and lower emissions, driving global production towards advanced transmission technologies.
Choosing the Right Transmission: Key Factors for Buyers
When choosing the right transmission for automotive performance, buyers must consider factors such as shift speed, driving style, and maintenance requirements. Sequential gearboxes offer rapid, precise gear changes favored in racing, while dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) provide smooth, seamless shifts ideal for daily driving and efficiency. Evaluating vehicle use, fuel economy goals, and long-term reliability ensures the optimal balance between performance and practicality.
sequential gearbox vs dual-clutch transmission Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com