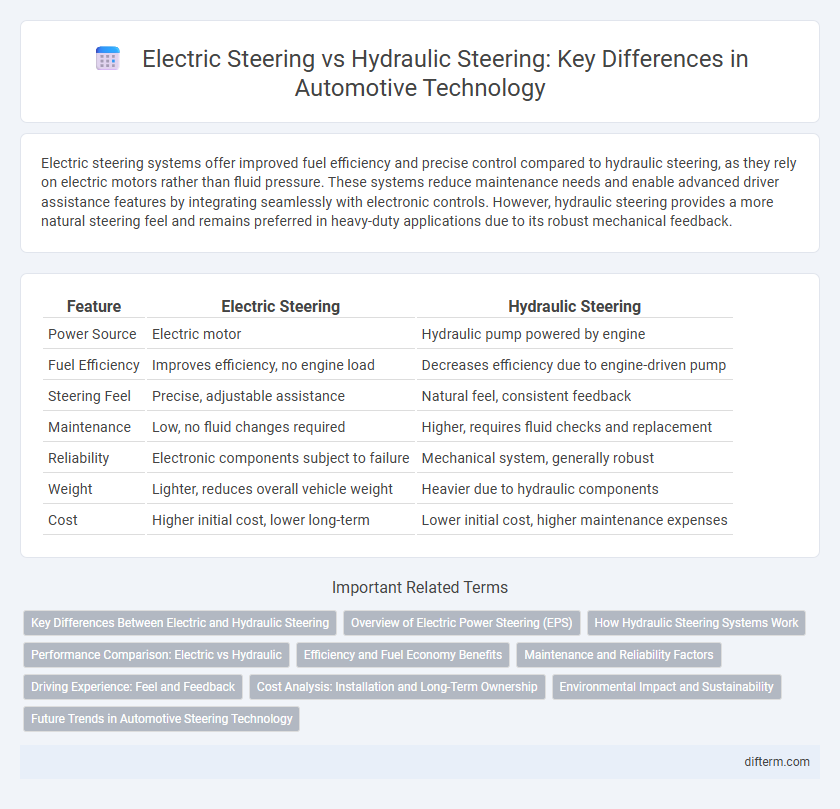
Electric steering systems offer improved fuel efficiency and precise control compared to hydraulic steering, as they rely on electric motors rather than fluid pressure. These systems reduce maintenance needs and enable advanced driver assistance features by integrating seamlessly with electronic controls. However, hydraulic steering provides a more natural steering feel and remains preferred in heavy-duty applications due to its robust mechanical feedback.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electric Steering | Hydraulic Steering |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Electric motor | Hydraulic pump powered by engine |
| Fuel Efficiency | Improves efficiency, no engine load | Decreases efficiency due to engine-driven pump |
| Steering Feel | Precise, adjustable assistance | Natural feel, consistent feedback |
| Maintenance | Low, no fluid changes required | Higher, requires fluid checks and replacement |
| Reliability | Electronic components subject to failure | Mechanical system, generally robust |
| Weight | Lighter, reduces overall vehicle weight | Heavier due to hydraulic components |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower long-term | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance expenses |
Key Differences Between Electric and Hydraulic Steering
Electric steering systems use an electric motor for assistance, offering precise control and energy efficiency, while hydraulic steering relies on fluid pressure generated by a pump, resulting in higher power consumption. Electric power steering (EPS) provides faster response times and easier integration with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), contrasting with the mechanical complexity and maintenance requirements of hydraulic steering. The transition from hydraulic to electric steering enhances fuel efficiency and reduces emissions by eliminating the engine-driven hydraulic pump.
Overview of Electric Power Steering (EPS)
Electric Power Steering (EPS) utilizes an electric motor to assist driver input, enhancing steering precision and reducing fuel consumption compared to hydraulic systems. By replacing traditional hydraulic pumps, EPS offers variable assistance adjusted to driving conditions, improving overall vehicle efficiency and responsiveness. Integration with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) enables features like lane keeping assist and automated parking, underscoring EPS as a key technology in modern automotive design.
How Hydraulic Steering Systems Work
Hydraulic steering systems operate by using pressurized fluid transmitted through hoses to a steering gear, which amplifies the driver's input force for easier maneuvering. A pump driven by the engine supplies the hydraulic pressure, while valves control the flow of fluid to assist with turning the wheels. These systems provide smooth, responsive steering but generally require more maintenance and energy compared to electric power steering.
Performance Comparison: Electric vs Hydraulic
Electric steering systems offer faster response times and improved precision compared to hydraulic steering, enhancing overall vehicle handling and driver control. They reduce energy consumption by only drawing power when steering input is applied, unlike hydraulic systems that continuously run a pump, which impacts fuel efficiency. While hydraulic steering provides robust feedback and reliability in heavy-duty applications, electric steering delivers superior efficiency and adaptability in modern automotive designs.
Efficiency and Fuel Economy Benefits
Electric steering systems enhance vehicle efficiency by reducing the energy consumption associated with hydraulic pumps, which run continuously in hydraulic steering setups. This leads to noticeable fuel economy improvements, with electric systems delivering up to a 5% increase in miles per gallon compared to traditional hydraulic steering. The elimination of hydraulic fluid and associated mechanical components also reduces overall vehicle weight, further contributing to energy savings and improved fuel efficiency.
Maintenance and Reliability Factors
Electric steering systems require less maintenance compared to hydraulic steering due to fewer moving parts and the absence of fluid that can leak or degrade over time. Hydraulic steering systems demand regular fluid checks and potential hose replacements, increasing the risk of leaks and mechanical wear. Reliability in electric steering is enhanced by electronic controls and self-diagnostic capabilities, whereas hydraulic systems are more prone to mechanical failures and maintenance-related downtime.
Driving Experience: Feel and Feedback
Electric steering systems provide precise feedback and adjustable resistance, enhancing driver control and comfort during various driving conditions. Hydraulic steering delivers a more natural, heavier feel that some drivers prefer for its tactile connection to the road. Modern electric power steering (EPS) systems increasingly mimic hydraulic steering feedback while improving energy efficiency and responsiveness.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Long-Term Ownership
Electric steering systems typically present lower installation costs due to fewer mechanical components and simpler integration with modern vehicle electronics compared to hydraulic steering. Long-term ownership expenses favor electric steering as it requires less maintenance, avoids fluid replacement, and reduces the risk of leaks or pump failures common in hydraulic systems. Cost analysis also shows electric power steering enhances fuel efficiency, contributing to reduced operational costs over the vehicle's lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Electric steering systems significantly reduce environmental impact by eliminating the need for hydraulic fluid, thus preventing potential leaks and minimizing hazardous waste. Their higher energy efficiency lowers overall fuel consumption and reduces carbon emissions compared to hydraulic steering, which relies on engine-driven pumps that increase fuel usage. The sustainable design of electric steering aligns with automotive industry goals to enhance vehicle efficiency and support global emissions reduction targets.
Future Trends in Automotive Steering Technology
Electric steering systems are anticipated to dominate future automotive designs due to their enhanced energy efficiency and seamless integration with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Innovations in steer-by-wire technology eliminate mechanical linkages, enabling precise, customizable steering responses and facilitating autonomous driving capabilities. As regulations tighten on emissions and fuel consumption, electric power steering (EPS) development prioritizes lightweight components and adaptive steering algorithms to optimize vehicle performance and safety.
electric steering vs hydraulic steering Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com