Disc brakes offer superior stopping power and heat dissipation compared to drum brakes, making them more effective for high-performance and safety-critical situations in automotive applications. Drum brakes, while generally less expensive and simpler in design, tend to suffer from heat buildup and reduced braking efficiency under heavy use. Choosing between disc and drum brakes depends on vehicle type, driving conditions, and maintenance considerations, with disc brakes favored for modern passenger cars and performance vehicles.
Table of Comparison
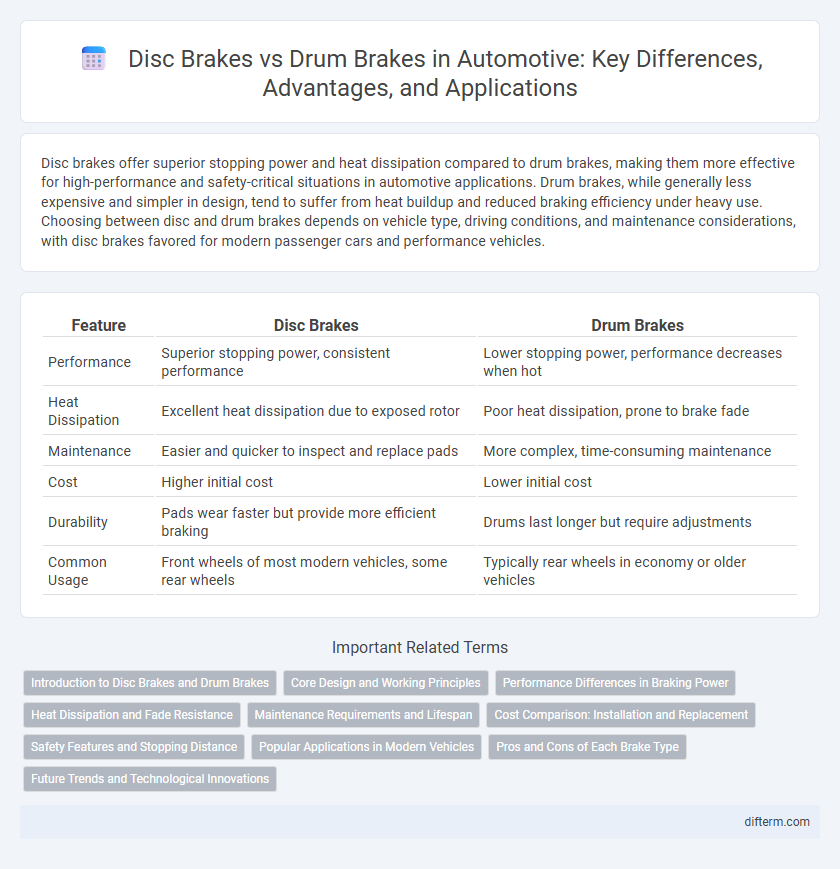
| Feature | Disc Brakes | Drum Brakes |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Superior stopping power, consistent performance | Lower stopping power, performance decreases when hot |
| Heat Dissipation | Excellent heat dissipation due to exposed rotor | Poor heat dissipation, prone to brake fade |
| Maintenance | Easier and quicker to inspect and replace pads | More complex, time-consuming maintenance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Durability | Pads wear faster but provide more efficient braking | Drums last longer but require adjustments |
| Common Usage | Front wheels of most modern vehicles, some rear wheels | Typically rear wheels in economy or older vehicles |
Introduction to Disc Brakes and Drum Brakes
Disc brakes utilize a rotor and caliper system to provide efficient stopping power through friction pads, offering superior heat dissipation and consistent braking performance compared to drum brakes. Drum brakes consist of brake shoes pressing against a rotating drum, often used in older or budget vehicles due to lower production costs but prone to heat buildup and reduced effectiveness under heavy use. Understanding the fundamental design and operational differences between disc and drum brakes is crucial for optimizing vehicle safety and braking efficiency in various automotive applications.
Core Design and Working Principles
Disc brakes feature a rotor clamped by hydraulic calipers with friction pads, converting kinetic energy into heat through direct contact, offering superior heat dissipation and consistent stopping power. Drum brakes consist of a rotating drum attached to the wheel, with brake shoes expanding outward to press against the inner surface, relying on friction to slow the vehicle but are prone to heat buildup and fade. The core design of disc brakes promotes efficient cooling and quick response, while drum brakes provide a simpler, enclosed mechanism often favored in rear axle applications.
Performance Differences in Braking Power
Disc brakes deliver superior braking power compared to drum brakes due to their enhanced heat dissipation and consistent contact with the brake pads, reducing brake fade during prolonged use. Their open design allows for better airflow, which helps maintain optimal performance even under high stress conditions. Drum brakes, on the other hand, tend to suffer from heat buildup and reduced stopping power, especially in heavy-duty or high-speed scenarios.
Heat Dissipation and Fade Resistance
Disc brakes outperform drum brakes in heat dissipation due to their exposed design, allowing faster cooling and reducing the risk of brake fade during prolonged use. Drum brakes tend to retain heat within the enclosed drum, leading to higher temperatures and decreased fade resistance under heavy or repeated braking conditions. Improved heat management in disc brakes ensures more consistent braking performance and enhanced safety, especially in high-demand driving scenarios.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Disc brakes offer easier maintenance due to their exposed rotor design, allowing for quick inspection and replacement of brake pads. Drum brakes typically require more labor-intensive servicing as the drum must be removed to access internal components, increasing maintenance time. In terms of lifespan, disc brakes generally have a longer service life because they dissipate heat more effectively, reducing wear and the risk of brake fade under heavy use.
Cost Comparison: Installation and Replacement
Disc brakes generally have a higher initial installation cost compared to drum brakes due to their complex design and precision components. Replacement parts for disc brakes, such as rotors and pads, tend to be more expensive but offer longer durability and better performance. Drum brakes have lower upfront costs but may incur more frequent replacement expenses, impacting overall long-term maintenance budgets.
Safety Features and Stopping Distance
Disc brakes offer superior safety features compared to drum brakes due to better heat dissipation and resistance to brake fade, enhancing consistent stopping power under heavy use. The open design of disc brakes allows for quicker cooling, resulting in shorter stopping distances, especially in wet or emergency conditions. Drum brakes, however, often exhibit longer stopping distances due to heat buildup and reduced performance during prolonged braking.
Popular Applications in Modern Vehicles
Disc brakes dominate modern passenger cars, high-performance vehicles, and motorcycles due to their superior heat dissipation and consistent stopping power. Drum brakes remain common in budget-friendly compact cars and rear axles of light trucks, offering cost-effective durability and effective parking brake integration. Commercial vehicles and heavy-duty trucks often utilize a combination, employing drum brakes for rear wheels to enhance load-bearing capacity and disc brakes upfront for efficient braking.
Pros and Cons of Each Brake Type
Disc brakes offer superior stopping power and heat dissipation, making them highly effective in high-performance and wet conditions. Drum brakes provide better braking force at low speeds and are cost-effective, but they are prone to overheating and fade under heavy use. Choosing between disc and drum brakes depends on the vehicle's intended use, with disc brakes favored for performance and safety, while drum brakes suit budget-friendly or rear axle applications.
Future Trends and Technological Innovations
Disc brakes continue to evolve with advancements such as integrated electronic brake systems and lightweight composite materials, enhancing performance and fuel efficiency in modern vehicles. Drum brakes are increasingly being phased out in favor of disc brakes due to superior heat dissipation and braking reliability, but innovations in regenerative braking technology are extending their relevance in electric and hybrid vehicles. Future trends emphasize smart braking systems with AI-driven adaptive control, improving safety and maintenance through real-time diagnostics and automated adjustments.
disc brakes vs drum brakes Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com