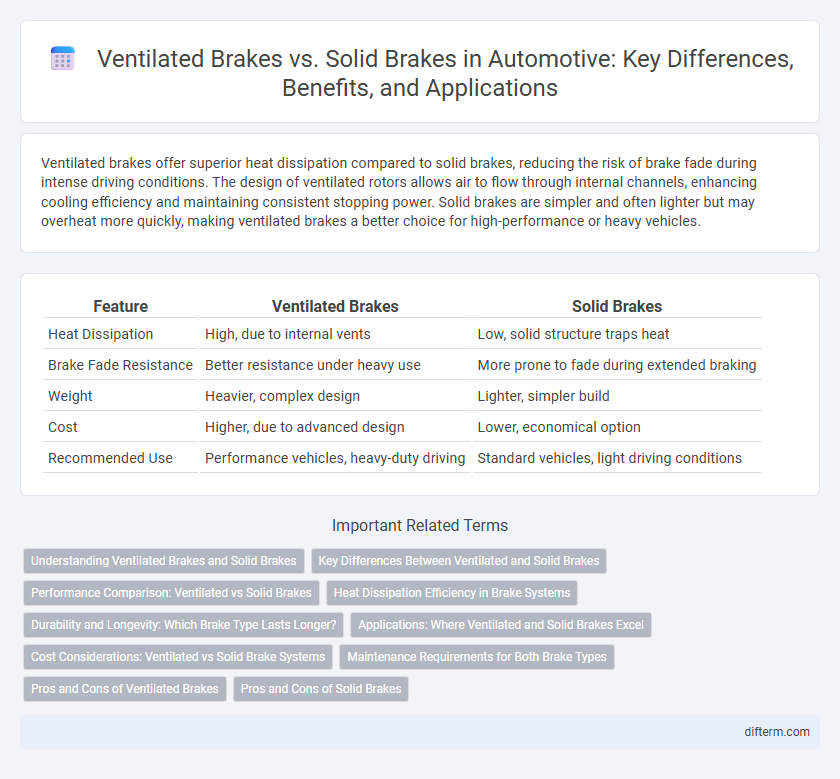
Ventilated brakes offer superior heat dissipation compared to solid brakes, reducing the risk of brake fade during intense driving conditions. The design of ventilated rotors allows air to flow through internal channels, enhancing cooling efficiency and maintaining consistent stopping power. Solid brakes are simpler and often lighter but may overheat more quickly, making ventilated brakes a better choice for high-performance or heavy vehicles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ventilated Brakes | Solid Brakes |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Dissipation | High, due to internal vents | Low, solid structure traps heat |
| Brake Fade Resistance | Better resistance under heavy use | More prone to fade during extended braking |
| Weight | Heavier, complex design | Lighter, simpler build |
| Cost | Higher, due to advanced design | Lower, economical option |
| Recommended Use | Performance vehicles, heavy-duty driving | Standard vehicles, light driving conditions |
Understanding Ventilated Brakes and Solid Brakes
Ventilated brakes feature a dual-layer disc design with internal channels that enhance heat dissipation during intense braking, reducing the risk of brake fade. Solid brakes consist of a single solid disc, which provides consistent braking performance but heats up more quickly under heavy use. Choosing ventilated brakes is ideal for high-performance or heavy vehicles requiring superior cooling and prolonged stopping power.
Key Differences Between Ventilated and Solid Brakes
Ventilated brakes feature dual-layered rotors with internal channels that enhance heat dissipation and reduce brake fade compared to solid brakes, which have a single solid rotor. The design of ventilated brakes improves cooling performance, making them more suitable for heavy-duty and high-performance vehicles. Solid brakes, being simpler and more cost-effective, are typically used in lighter vehicles with less aggressive braking demands.
Performance Comparison: Ventilated vs Solid Brakes
Ventilated brakes provide superior heat dissipation through their internal air channels, reducing brake fade and maintaining consistent stopping power during high-performance or extended use. Solid brakes, while simpler and lighter, tend to retain heat more quickly, leading to decreased braking efficiency under strenuous conditions. The enhanced cooling capabilities of ventilated brakes make them the preferred choice for vehicles requiring reliable performance in demanding driving environments.
Heat Dissipation Efficiency in Brake Systems
Ventilated brakes outperform solid brakes in heat dissipation efficiency due to their internal vaned design, which allows air to flow between the disc surfaces and cool the brake system more effectively. This enhanced cooling reduces the risk of brake fade during prolonged or high-intensity braking, ensuring consistent stopping power and improved safety. Automotive engineers prioritize ventilated discs in performance and heavy-duty vehicles to maintain optimal braking performance under strenuous conditions.
Durability and Longevity: Which Brake Type Lasts Longer?
Ventilated brakes feature internal cooling channels that dissipate heat more effectively, reducing wear and extending the lifespan of brake components compared to solid brakes. Solid brakes, while simpler and less expensive, tend to retain more heat, which accelerates brake pad and rotor degradation under heavy use. For enhanced durability and longer service intervals, ventilated brakes are generally the preferred choice in automotive applications requiring consistent high performance.
Applications: Where Ventilated and Solid Brakes Excel
Ventilated brakes excel in high-performance and heavy-duty applications such as sports cars and trucks due to their superior heat dissipation and reduced brake fade during aggressive driving or heavy loads. Solid brakes are ideal for lighter vehicles and urban driving conditions where braking demands are moderate, offering cost-effective and reliable performance. Industrial machinery and compact cars benefit from solid brakes' simplicity and durability, while ventilated brakes are preferred in racing and hill-climbing vehicles requiring consistent, high braking efficiency.
Cost Considerations: Ventilated vs Solid Brake Systems
Ventilated brake systems typically incur higher initial costs due to their complex design, incorporating dual-layer rotors with internal vanes for improved heat dissipation. Solid brake rotors offer a budget-friendly alternative with simpler construction and lower manufacturing expenses, but may require more frequent replacements under heavy use. When evaluating cost considerations, factors such as maintenance frequency, vehicle usage patterns, and thermal performance efficiency drive the long-term economic impact of ventilated versus solid brake systems.
Maintenance Requirements for Both Brake Types
Ventilated brakes require less frequent maintenance due to improved heat dissipation, which reduces the risk of brake fade and extends pad life. Solid brakes, while simpler in design, often need more regular inspection and replacement because heat buildup can accelerate wear and lead to warping. Regular monitoring of brake pad thickness and rotor condition is essential for both types to ensure consistent performance and safety.
Pros and Cons of Ventilated Brakes
Ventilated brakes offer superior heat dissipation due to their dual-disc design with internal vanes, reducing the risk of brake fade during intense or prolonged braking. Their enhanced cooling efficiency improves overall braking performance and longevity compared to solid brakes, which are more prone to overheating. However, ventilated brakes tend to be heavier and more expensive, potentially affecting vehicle weight and cost efficiency.
Pros and Cons of Solid Brakes
Solid brakes offer simplicity and lower cost, making them ideal for everyday driving and light vehicles due to easier maintenance and longer-lasting pads. However, they lack the heat dissipation capabilities of ventilated brakes, leading to quicker brake fade and reduced performance during heavy braking or high-speed conditions. Their compact design benefits lightweight applications but limits efficiency in high-performance or commercial automotive use.
ventilated brakes vs solid brakes Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com