Rims refer specifically to the outer circular design of the wheel that holds the tire in place, while wheels include the entire assembly, consisting of the rim, hub, and spokes or disc. Choosing the right rim impacts both the aesthetic appeal and performance, as it affects tire compatibility and weight distribution. Proper understanding of rim versus wheel ensures informed decisions for upgrades or replacements in automotive maintenance.
Table of Comparison
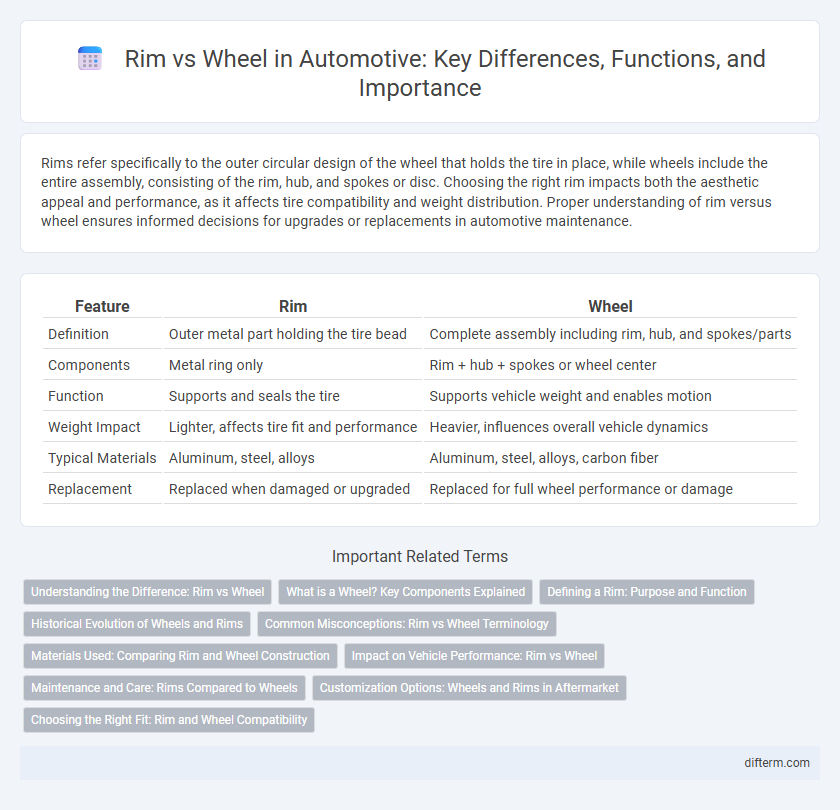
| Feature | Rim | Wheel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outer metal part holding the tire bead | Complete assembly including rim, hub, and spokes/parts |
| Components | Metal ring only | Rim + hub + spokes or wheel center |
| Function | Supports and seals the tire | Supports vehicle weight and enables motion |
| Weight Impact | Lighter, affects tire fit and performance | Heavier, influences overall vehicle dynamics |
| Typical Materials | Aluminum, steel, alloys | Aluminum, steel, alloys, carbon fiber |
| Replacement | Replaced when damaged or upgraded | Replaced for full wheel performance or damage |
Understanding the Difference: Rim vs Wheel
The wheel is the entire circular component that includes the rim, spokes, hub, and tire, while the rim specifically refers to the outer edge that holds the tire in place. Understanding the difference is crucial for maintenance and upgrades, as rims affect tire fitment and aesthetics, whereas wheels impact overall vehicle performance and handling. Selecting the right rim and wheel combination enhances safety, ride quality, and style in automotive applications.
What is a Wheel? Key Components Explained
A wheel in automotive terms consists of the rim, hub, spokes, and sometimes a disc, serving as the central unit that connects the vehicle to the tires and axle. The rim forms the outer part that holds the tire in place, while the hub is the mounting point that attaches the wheel to the vehicle. Spokes or a solid disc provide structural support, ensuring stability and weight distribution essential for safe driving performance.
Defining a Rim: Purpose and Function
A rim is the outer edge of a wheel that holds the tire securely in place, ensuring proper alignment and stability. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the tire's shape under various driving conditions and supports the vehicle's load. Understanding the distinction between the rim and the wheel is essential, as the wheel includes the rim along with the hub and spokes, forming the complete rotating assembly.
Historical Evolution of Wheels and Rims
The historical evolution of wheels and rims traces back to ancient civilizations where wooden wheels with iron rims improved durability and performance in transport. Over centuries, advancements introduced steel and alloy rims, enhancing strength, weight distribution, and vehicle handling. Modern automotive wheels integrate advanced materials like carbon fiber and aluminum alloys, optimizing fuel efficiency and aesthetic appeal while maintaining structural integrity.
Common Misconceptions: Rim vs Wheel Terminology
Many automotive enthusiasts mistakenly use the terms rim and wheel interchangeably, but a rim specifically refers to the outer edge that holds the tire, while the wheel encompasses the entire assembly including the rim, spokes, hub, and center cap. Understanding this distinction is crucial for selecting compatible components and avoiding confusion during maintenance or upgrades. Proper terminology ensures clearer communication among mechanics, manufacturers, and consumers in the automotive industry.
Materials Used: Comparing Rim and Wheel Construction
Rims are typically constructed from aluminum alloy or steel, offering a balance of strength, weight, and corrosion resistance, while wheels encompass the rim and hub and often incorporate composite materials for enhanced durability and performance. Aluminum alloys provide lightweight advantages that improve fuel efficiency and handling, whereas steel rims are favored for their robustness and cost-effectiveness. Wheels may also integrate carbon fiber or magnesium in high-performance vehicles to achieve superior strength-to-weight ratios and improved thermal management during braking.
Impact on Vehicle Performance: Rim vs Wheel
The rim directly affects tire compatibility, weight, and rotational inertia, playing a crucial role in acceleration, braking, and fuel efficiency. The wheel, encompassing the rim and hub assembly, influences overall structural integrity and load distribution, impacting ride comfort and handling stability. High-performance vehicles benefit from lightweight alloy rims and precision-engineered wheels to optimize traction and reduce unsprung mass.
Maintenance and Care: Rims Compared to Wheels
Rim maintenance often requires frequent cleaning to prevent corrosion, especially in aluminum and alloy materials that are prone to damage from brake dust and road salts. Wheels, incorporating both the rim and tire, demand regular inspection for tire pressure, tread wear, and alignment to ensure safe driving conditions. Proper rim care extends wheel lifespan, enhancing overall vehicle performance and safety.
Customization Options: Wheels and Rims in Aftermarket
Aftermarket customization offers a wide variety of wheels and rims designed to enhance both performance and aesthetics. Rims serve as the structural foundation for tires, while wheels include the rim and other components, influencing vehicle handling and style. Enthusiasts can select from diverse materials, finishes, and sizes to tailor their vehicles to specific driving needs and visual preferences.
Choosing the Right Fit: Rim and Wheel Compatibility
Selecting the right fit for your vehicle involves understanding the difference between rims and wheels, as rims are the outer circular metal parts that hold the tire, while wheels include the rim and the hub assembly. Compatibility depends on factors like bolt pattern, wheel diameter, offset, and center bore to ensure proper installation and optimal performance. Ensuring these specifications match your vehicle's requirements avoids issues such as vibration, poor handling, and premature tire wear.
rim vs wheel Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com