Cross-drilled rotors offer superior heat dissipation by allowing gases and heat to escape through drilled holes, which reduces brake fade during intense driving conditions. Slotted rotors feature grooves that help to remove debris, water, and brake dust from the rotor surface, improving braking performance and pad bite in wet or dirty environments. Choosing between cross-drilled and slotted rotors depends on driving style, with cross-drilled preferred for high-performance vehicles and slotted favored for everyday driving and off-road use.
Table of Comparison
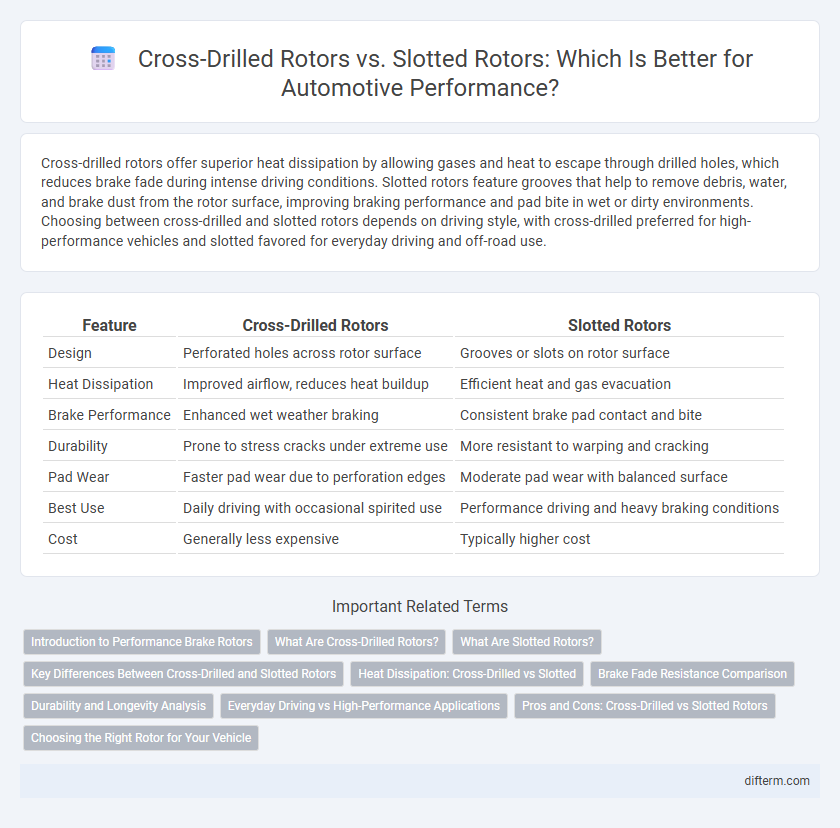
| Feature | Cross-Drilled Rotors | Slotted Rotors |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Perforated holes across rotor surface | Grooves or slots on rotor surface |
| Heat Dissipation | Improved airflow, reduces heat buildup | Efficient heat and gas evacuation |
| Brake Performance | Enhanced wet weather braking | Consistent brake pad contact and bite |
| Durability | Prone to stress cracks under extreme use | More resistant to warping and cracking |
| Pad Wear | Faster pad wear due to perforation edges | Moderate pad wear with balanced surface |
| Best Use | Daily driving with occasional spirited use | Performance driving and heavy braking conditions |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Typically higher cost |
Introduction to Performance Brake Rotors
Cross-drilled rotors enhance cooling and gas dissipation by featuring precisely drilled holes that reduce brake fade during high-performance driving. Slotted rotors improve brake pad bite and help expel debris and water, maintaining consistent friction under aggressive braking conditions. Both designs target improved heat management and braking efficiency, optimizing performance for sports cars and track applications.
What Are Cross-Drilled Rotors?
Cross-drilled rotors feature a pattern of holes drilled through the brake disc to enhance heat dissipation and reduce brake fade during intense driving conditions. These perforations improve water and gas venting, which maintains consistent braking performance in wet or high-temperature environments. Primarily used in high-performance and sports vehicles, cross-drilled rotors offer improved stopping power and cooling compared to standard solid rotors.
What Are Slotted Rotors?
Slotted rotors are high-performance brake discs designed with grooves or slots cut into the surface to improve heat dissipation and gas evacuation during braking. These engineered slots help maintain cleaner contact between the brake pad and rotor, reducing brake fade and enhancing overall stopping power under extreme driving conditions. Commonly used in sports cars and track vehicles, slotted rotors optimize braking efficiency by preventing pad glazing and promoting consistent friction.
Key Differences Between Cross-Drilled and Slotted Rotors
Cross-drilled rotors feature holes drilled through the braking surface to enhance heat dissipation and reduce brake fade, making them ideal for high-performance and track use. Slotted rotors have grooves cut into the surface that improve water, gas, and dust evacuation, ensuring consistent braking performance in wet or dirty conditions. While cross-drilled rotors offer better cooling, slotted rotors provide superior durability and are less prone to cracking under heavy braking stress.
Heat Dissipation: Cross-Drilled vs Slotted
Cross-drilled rotors improve heat dissipation by allowing hot gases and heat to escape through the drilled holes, reducing brake fade during intense braking. Slotted rotors enhance heat management by channeling heat and debris away from the rotor surface, maintaining optimal friction and cooling efficiency. Both designs are engineered to improve thermal performance, but slotted rotors typically offer better heat dissipation under prolonged, high-stress braking conditions.
Brake Fade Resistance Comparison
Cross-drilled rotors feature multiple holes drilled through the braking surface, enhancing heat dissipation and reducing brake fade by allowing gas and heat to escape more efficiently during heavy braking. Slotted rotors use grooves along the surface to channel away water, dust, and brake debris, maintaining better contact between the pad and rotor, which minimizes brake fade in demanding driving conditions. In high-performance and extended braking scenarios, slotted rotors generally offer superior brake fade resistance due to consistent pad contact and improved evacuation of contaminants compared to cross-drilled designs.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Cross-drilled rotors feature holes that help dissipate heat and reduce brake fade but may be prone to cracking under high stress, affecting long-term durability. Slotted rotors provide enhanced debris removal and consistent brake pad contact, leading to improved wear resistance and extended lifespan in demanding driving conditions. Analyzing materials, thermal conductivity, and driving environment is crucial in determining the optimal choice for rotor longevity.
Everyday Driving vs High-Performance Applications
Cross-drilled rotors excel in high-performance applications by improving heat dissipation and reducing brake fade during aggressive driving and track use. Slotted rotors provide enhanced debris removal and consistent braking performance, making them ideal for everyday driving with frequent stop-and-go traffic. Choosing between cross-drilled and slotted rotors depends on driver needs, with cross-drilled favored for extreme performance and slotted preferred for durability and routine use.
Pros and Cons: Cross-Drilled vs Slotted Rotors
Cross-drilled rotors excel in heat dissipation and gas release, reducing brake fade during intense driving, but they are prone to crack development under high stress. Slotted rotors provide superior debris removal and improved surface friction, enhancing wet and aggressive braking performance, yet they tend to wear down brake pads faster compared to drilled variants. Choosing between cross-drilled and slotted rotors depends on specific driving conditions and priorities, such as high-performance racing or daily street driving.
Choosing the Right Rotor for Your Vehicle
Cross-drilled rotors offer enhanced heat dissipation and improved brake cooling, making them ideal for high-performance vehicles subjected to intense braking. Slotted rotors provide better debris removal and consistent braking performance under extreme conditions, reducing brake fade during heavy use. Selecting the right rotor depends on your driving style and vehicle type, with cross-drilled rotors favored for spirited driving and slotted rotors recommended for off-road or track applications.
cross-drilled rotors vs slotted rotors Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com