Carburetors regulate the air-fuel mixture through mechanical means, offering simplicity and ease of repair but often sacrificing fuel efficiency and emissions control. Fuel injection systems deliver precise amounts of fuel directly into the combustion chamber, improving engine performance, fuel economy, and reducing harmful emissions. Modern vehicles favor fuel injection due to its superior accuracy and adaptability to varying engine conditions.
Table of Comparison
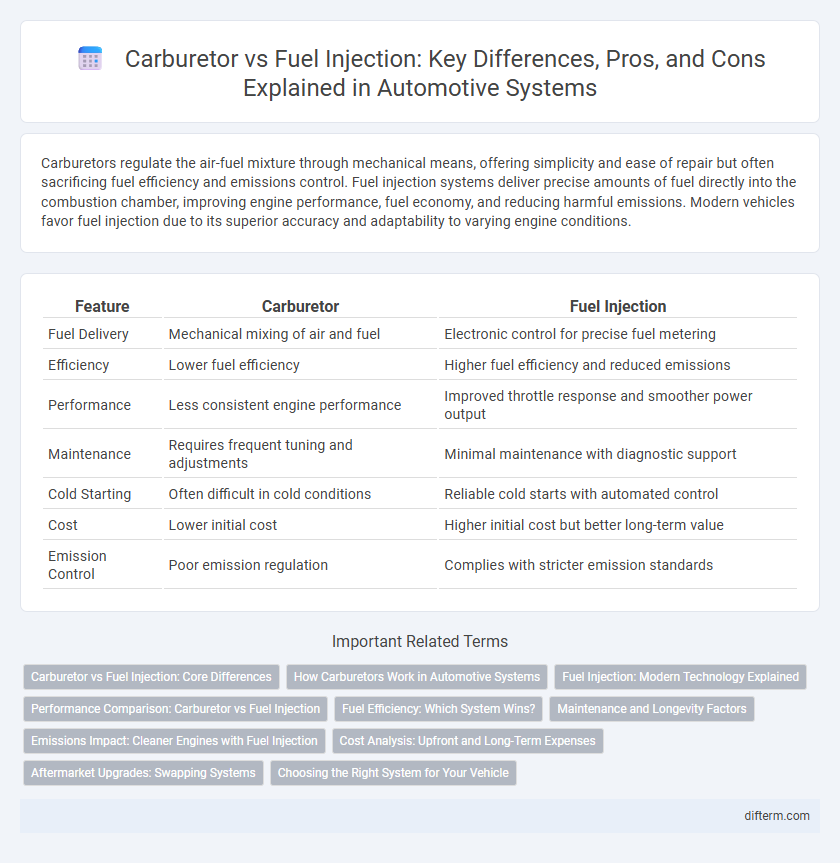
| Feature | Carburetor | Fuel Injection |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Delivery | Mechanical mixing of air and fuel | Electronic control for precise fuel metering |
| Efficiency | Lower fuel efficiency | Higher fuel efficiency and reduced emissions |
| Performance | Less consistent engine performance | Improved throttle response and smoother power output |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent tuning and adjustments | Minimal maintenance with diagnostic support |
| Cold Starting | Often difficult in cold conditions | Reliable cold starts with automated control |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but better long-term value |
| Emission Control | Poor emission regulation | Complies with stricter emission standards |
Carburetor vs Fuel Injection: Core Differences
Carburetors mix air and fuel through mechanical processes, relying on vacuum pressure for fuel delivery, while fuel injection systems use electronic controls for precise fuel atomization directly into the combustion chamber. Fuel injection offers improved fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and better engine responsiveness compared to carburetors, which are generally simpler and less expensive but less accurate in fuel metering. The transition from carburetors to fuel injection reflects advances in automotive technology toward optimized performance and regulatory compliance.
How Carburetors Work in Automotive Systems
Carburetors work by mixing air and fuel in precise proportions to create a combustible mixture for internal combustion engines, utilizing a venturi to generate vacuum pressure that draws fuel into the airflow. The throttle valve controls engine speed by regulating air intake, while the fuel jets meter the amount of gasoline delivered, ensuring efficient combustion. Despite being largely replaced by fuel injection, carburetors remain valued in classic automobiles for their mechanical simplicity and ease of maintenance.
Fuel Injection: Modern Technology Explained
Fuel injection systems precisely deliver fuel into the combustion chamber using electronically controlled injectors, optimizing engine performance and improving fuel efficiency. Unlike carburetors, fuel injection adapts to varying engine conditions by adjusting the air-fuel mixture in real time, reducing emissions and enhancing throttle response. This modern technology integrates sensors and computer controls, enabling better cold starts and overall reliability in automotive engines.
Performance Comparison: Carburetor vs Fuel Injection
Fuel injection systems deliver precise air-fuel mixture control, enhancing engine efficiency, throttle response, and overall performance compared to carburetors. Carburetors rely on mechanical processes and can result in less accurate fuel delivery, leading to lower fuel economy and increased emissions. Modern fuel injection offers superior combustion optimization, enabling higher power output and smoother acceleration under various driving conditions.
Fuel Efficiency: Which System Wins?
Fuel injection systems outperform carburetors in fuel efficiency by delivering precise amounts of fuel directly into the combustion chamber, optimizing air-fuel mixtures for varying engine conditions. Modern electronic fuel injection (EFI) adapts instantly to changes in temperature, altitude, and engine load, significantly reducing fuel consumption and emissions compared to carburetors. Studies show vehicles with fuel injection can improve fuel economy by up to 15%, making EFI the superior choice for maximizing fuel efficiency.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Fuel injection systems require less frequent maintenance compared to carburetors due to their electronic fuel delivery and self-adjusting capabilities, resulting in enhanced longevity and consistent engine performance. Carburetors often demand regular cleaning, adjustments, and tuning to prevent fuel inefficiency and engine wear, which can shorten their operational lifespan. Advances in fuel injection technology contribute to improved durability and reduced long-term costs in automotive maintenance.
Emissions Impact: Cleaner Engines with Fuel Injection
Fuel injection systems precisely control air-fuel mixtures, resulting in more complete combustion and significantly lower emissions compared to carburetors. Modern fuel injection technology reduces harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides, meeting stringent environmental regulations. This cleaner combustion process enhances engine efficiency and contributes to reduced environmental impact in automotive applications.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Carburetors generally have lower upfront costs due to simpler design and easier manufacturing, making them more affordable for initial installation or replacement. Fuel injection systems, while more expensive initially due to advanced electronics and sensors, offer superior fuel efficiency and reduced emissions that lower long-term operational costs. Maintenance expenses for carburetors tend to be higher over time because of frequent adjustments and potential for clogging, whereas fuel injection systems require less frequent servicing but may incur higher repair costs if electronic components fail.
Aftermarket Upgrades: Swapping Systems
Aftermarket upgrades often involve swapping a carburetor for a fuel injection system to enhance engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. Fuel injection offers precise fuel metering and adaptability to modern engine management systems, making it a preferred upgrade for classic car restorations and performance builds. Conversion kits are widely available, providing components like electronic control units (ECUs), sensors, and throttle bodies to seamlessly replace carburetors in various automotive applications.
Choosing the Right System for Your Vehicle
Carburetors are simpler mechanical devices that mix air and fuel for combustion, often preferred in classic cars due to ease of maintenance and lower cost. Fuel injection systems offer precise fuel delivery and improved efficiency, resulting in better performance, lower emissions, and enhanced fuel economy. Choosing the right system depends on your vehicle's model, intended use, and maintenance preferences, with modern vehicles typically benefiting more from fuel injection technology.
Carburetor vs Fuel injection Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com