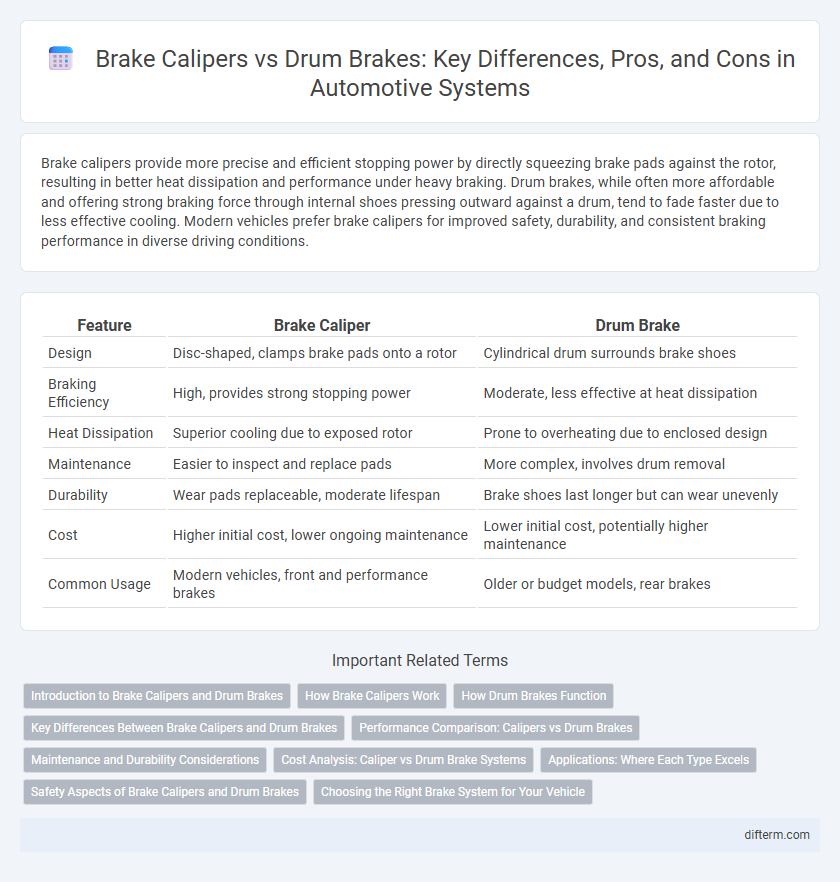
Brake calipers provide more precise and efficient stopping power by directly squeezing brake pads against the rotor, resulting in better heat dissipation and performance under heavy braking. Drum brakes, while often more affordable and offering strong braking force through internal shoes pressing outward against a drum, tend to fade faster due to less effective cooling. Modern vehicles prefer brake calipers for improved safety, durability, and consistent braking performance in diverse driving conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Brake Caliper | Drum Brake |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Disc-shaped, clamps brake pads onto a rotor | Cylindrical drum surrounds brake shoes |
| Braking Efficiency | High, provides strong stopping power | Moderate, less effective at heat dissipation |
| Heat Dissipation | Superior cooling due to exposed rotor | Prone to overheating due to enclosed design |
| Maintenance | Easier to inspect and replace pads | More complex, involves drum removal |
| Durability | Wear pads replaceable, moderate lifespan | Brake shoes last longer but can wear unevenly |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower ongoing maintenance | Lower initial cost, potentially higher maintenance |
| Common Usage | Modern vehicles, front and performance brakes | Older or budget models, rear brakes |
Introduction to Brake Calipers and Drum Brakes
Brake calipers are essential components in disc braking systems, providing precise clamping force by pressing brake pads against a spinning rotor to slow or stop vehicles efficiently. Drum brakes utilize a set of brake shoes that press outward against a rotating drum to create friction and decelerate the vehicle, traditionally favored in rear-wheel applications for cost effectiveness and simplicity. Both systems play critical roles in automotive safety by converting kinetic energy into heat but differ significantly in design, performance, and maintenance requirements.
How Brake Calipers Work
Brake calipers operate by applying hydraulic pressure through brake fluid to squeeze the brake pads against the rotor, creating friction that slows down the vehicle. Unlike drum brakes, which use internal shoes pressing outward against a drum, calipers use a piston mechanism to directly clamp the pads on the rotor surface. This design enhances heat dissipation and provides more consistent braking performance under various driving conditions.
How Drum Brakes Function
Drum brakes function by using brake shoes that press outward against a rotating drum attached to the wheel, creating friction to slow or stop the vehicle. The hydraulic wheel cylinder pushes the shoes apart when the brake pedal is applied, transferring force to the drum's interior surface. This mechanism provides reliable braking performance, especially in parking brake applications and rear wheel assemblies.
Key Differences Between Brake Calipers and Drum Brakes
Brake calipers use a hydraulic system to press brake pads against a rotor, providing precise and consistent stopping power, while drum brakes rely on brake shoes to press outward against a rotating drum. Calipers offer better heat dissipation and performance in high-speed conditions compared to drum brakes, which are typically more cost-effective and easier to maintain. The key differences include calipers' superior stopping efficiency and responsiveness versus drums' simpler design and greater durability in low-performance applications.
Performance Comparison: Calipers vs Drum Brakes
Brake calipers provide superior stopping power and heat dissipation compared to drum brakes, making them more effective for high-performance and heavy-duty vehicles. Calipers offer better resistance to brake fade due to their exposed design, which allows for quicker cooling under repeated braking conditions. Drum brakes, while more cost-efficient and effective in preventing dirt ingress, generally exhibit lower braking performance and slower heat dissipation, resulting in reduced efficiency during intensive use.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Brake calipers, commonly used in disc brake systems, offer easier maintenance due to their exposed design, allowing quick inspection and pad replacement without dismantling the wheel hub. Drum brakes, while generally more durable under harsh conditions because of enclosed components protecting against dirt and moisture, demand more labor-intensive maintenance, often requiring removal of the brake drum to access internal parts. Durability in brake calipers is typically influenced by factors such as seal integrity and corrosion resistance, whereas drum brakes can experience heat-induced expansion affecting longevity and consistent performance.
Cost Analysis: Caliper vs Drum Brake Systems
Brake calipers generally incur higher initial costs compared to drum brakes due to their complex design and materials, but offer better performance and easier maintenance. Drum brakes are more cost-effective upfront, with simpler construction and lower replacement parts expenses, making them suitable for budget-oriented vehicles. Long-term cost efficiency depends on usage patterns, with caliper systems providing improved durability and braking precision that can reduce overall maintenance expenses.
Applications: Where Each Type Excels
Brake calipers excel in high-performance and modern vehicles due to their superior heat dissipation and stopping power, making them ideal for sports cars and heavy-duty trucks. Drum brakes are commonly used in rear-wheel applications of economy cars and light trucks, where cost-efficiency and durability under moderate braking conditions are prioritized. Calipers offer better modulation and fade resistance, while drums provide longer service intervals in less demanding driving environments.
Safety Aspects of Brake Calipers and Drum Brakes
Brake calipers provide superior safety by enabling more consistent and efficient braking through direct hydraulic pressure, resulting in faster stopping times and better heat dissipation compared to drum brakes. Drum brakes, while cost-effective, are prone to overheating and brake fade under heavy use, which can compromise stopping power and safety during prolonged or intense braking. The exposed design of brake calipers allows for better inspection and maintenance, reducing the risk of brake failure and enhancing overall vehicle safety.
Choosing the Right Brake System for Your Vehicle
When choosing the right brake system for your vehicle, brake calipers offer superior stopping power and heat dissipation compared to drum brakes, making them ideal for high-performance and modern vehicles. Drum brakes, while more cost-effective and easier to maintain, are often used on rear wheels of economy cars due to their adequate performance in everyday driving conditions. Evaluating factors like vehicle weight, driving style, and maintenance preferences helps determine whether the precision of disc brakes or the durability of drum brakes best suits your automotive needs.
Brake caliper vs Drum brake Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com