Body roll refers to the vehicle's leaning motion during cornering caused by weight transfer, affecting stability and tire grip. Chassis flex involves the twisting or bending of the vehicle's frame under stress, impacting structural integrity and suspension performance. Minimizing both improves handling precision and driver confidence in automotive pets.
Table of Comparison
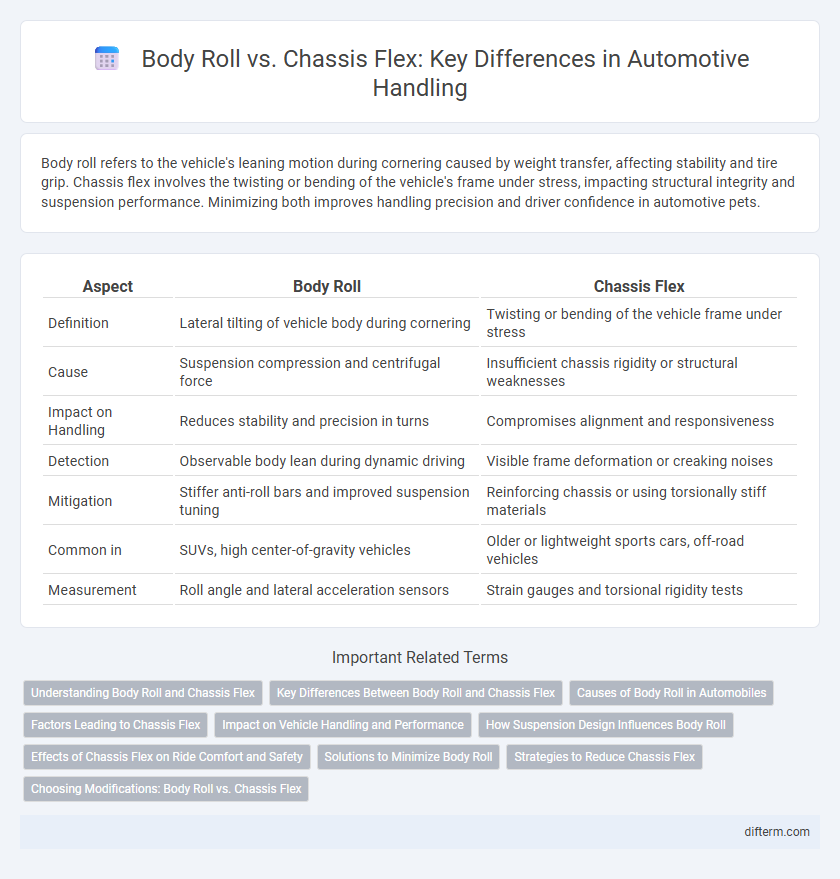
| Aspect | Body Roll | Chassis Flex |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lateral tilting of vehicle body during cornering | Twisting or bending of the vehicle frame under stress |
| Cause | Suspension compression and centrifugal force | Insufficient chassis rigidity or structural weaknesses |
| Impact on Handling | Reduces stability and precision in turns | Compromises alignment and responsiveness |
| Detection | Observable body lean during dynamic driving | Visible frame deformation or creaking noises |
| Mitigation | Stiffer anti-roll bars and improved suspension tuning | Reinforcing chassis or using torsionally stiff materials |
| Common in | SUVs, high center-of-gravity vehicles | Older or lightweight sports cars, off-road vehicles |
| Measurement | Roll angle and lateral acceleration sensors | Strain gauges and torsional rigidity tests |
Understanding Body Roll and Chassis Flex
Body roll refers to the vehicle's leaning motion around its longitudinal axis during cornering, impacting driver control and passenger comfort. Chassis flex is the twisting or bending of the vehicle's frame under stress, potentially compromising structural integrity and handling precision. Understanding the distinction between body roll and chassis flex helps optimize suspension design and improve overall vehicle dynamics.
Key Differences Between Body Roll and Chassis Flex
Body roll refers to the tilting motion of a vehicle's body during cornering, caused by centrifugal forces acting on the suspension system. Chassis flex describes the twisting or bending of the vehicle's frame under stress, affecting structural rigidity and handling precision. Unlike body roll, which primarily impacts ride comfort and weight transfer, chassis flex directly influences the vehicle's overall stability and durability.
Causes of Body Roll in Automobiles
Body roll in automobiles primarily occurs due to the lateral forces generated during cornering, causing the vehicle's body to tilt away from the turn. The suspension system, including the springs, anti-roll bars, and shock absorbers, plays a crucial role in controlling this motion but can be overwhelmed by factors like high center of gravity or soft spring rates. Chassis flex contributes indirectly by affecting suspension geometry, which can exacerbate body roll by reducing the effectiveness of anti-roll mechanisms.
Factors Leading to Chassis Flex
Chassis flex occurs when structural components of a vehicle deform under stress, influenced by factors such as material choice, frame design, and welding quality. Lightweight materials like aluminum or composites can increase flexibility, while complex unibody architectures may introduce stress points contributing to chassis flex. Poor manufacturing processes and lack of proper reinforcement in critical areas also significantly elevate the risk of excessive chassis deformation during dynamic driving conditions.
Impact on Vehicle Handling and Performance
Excessive body roll negatively affects vehicle handling by reducing tire contact with the road, leading to decreased grip and increased understeer or oversteer during cornering. In contrast, controlled chassis flex can enhance traction by allowing better tire compliance on uneven surfaces, improving overall stability and ride comfort. Optimizing the balance between minimizing body roll and enabling beneficial chassis flex is crucial for achieving superior performance and driver confidence.
How Suspension Design Influences Body Roll
Suspension design plays a critical role in controlling body roll by optimizing the balance between stiffness and compliance in the chassis. Components like anti-roll bars, spring rates, and damper settings work collectively to minimize excessive body lean during cornering, enhancing vehicle stability and handling precision. Advanced suspension geometries reduce chassis flex, ensuring consistent tire contact and improving overall driving dynamics in both performance and everyday vehicles.
Effects of Chassis Flex on Ride Comfort and Safety
Chassis flex significantly impacts ride comfort by allowing the vehicle's frame to absorb road irregularities, reducing harshness transmitted to passengers. Excessive chassis flex, however, can compromise safety by causing unpredictable handling and reduced suspension effectiveness, increasing the risk of loss of control. Modern automotive engineering strives to balance stiffness and flexibility to optimize both comfort and vehicle stability.
Solutions to Minimize Body Roll
Upgrading to stiffer anti-roll bars and installing chassis bracing are effective solutions to minimize body roll in vehicles. Performance suspension components, such as upgraded shocks and springs, enhance stability by reducing chassis flex during cornering. Proper tire selection and alignment also play a critical role in maintaining optimal grip and limiting excessive body movement.
Strategies to Reduce Chassis Flex
Reducing chassis flex involves reinforcing key structural components such as the floor pan, rocker panels, and suspension mounting points with high-strength materials like advanced high-strength steel or carbon fiber composites. Implementing strategically placed bracing, such as strut tower braces, roll cages, and subframe connectors, enhances torsional rigidity and minimizes deformation under load. Optimized weld patterns and advanced bonding techniques further improve chassis stiffness, resulting in better handling precision and reduced body roll during dynamic driving conditions.
Choosing Modifications: Body Roll vs. Chassis Flex
Choosing between body roll and chassis flex modifications significantly affects vehicle handling and overall performance. Reducing body roll through upgraded anti-roll bars and stiffer springs improves cornering stability, while addressing chassis flex with reinforcement braces enhances structural rigidity and responsiveness. Prioritizing chassis stiffening is essential for drivers seeking precise control during aggressive driving or track use.
body roll vs chassis flex Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com